Lec 7 elements_of_the_state
- 1. State and Government Lecture 7 AY 2011 -2012 Second Semester
- 2. Concepts of State and Government Objectives: a) Familiarity with basic concepts related to state and government b) Familiarity with the profile of the Philippines as a state
- 3. CONCEPTS OF STATE State A community of persons more or less numerous, permanently occupying a definite portion of territory, having a government of their own to which the great body of inhabitants render obedience and enjoying freedom from external control. Elements of the State a) People b) Territory c) Government d) Sovereignty
- 4. Elements of the State a) People: the mass of population living within the state ’ü« Population 97,976,603 (July 2009 est.) ’ü« Age structure 0-14 years: 35.2% (male 17,606,352/female 16,911,376) 15-64 years: 60.6% (male 29,679,327/female 29,737,919) 65 years and over: 4.1% (male 1,744,248/female 2,297,381) ’ü« Median age total: 22.5 years male: 22 years Female: 23 years ’ü« Population growth rate 1.957% ’ü« Ethnic groups Tagalog 28.1%, Cebuano 13.1%, Ilocano 9%, Bisaya/Binisaya 7.6%, Hiligaynon Ilonggo 7.5%, Bikol 6%, Waray 3.4%, Kapampangan 3%, other 25.3% (2000 census)
- 7. Elements of the State b) Territory: it includes not only the land over which the jurisdiction of the state extends but also the rivers and lakes therein, a certain area of the sea which abuts upon its coasts and the air space above it.
- 8. Elements of the State: Territory ’ü« Area: total: 300,000╠²km2 land: 298,170╠²km2 water: 1,830╠²km2 ’ü« Coastline: 36,289╠²km ’ü« Maritime claims: measured from claimed archipelagic baselines continental shelf: to depth of exploitation exclusive economic zone: 200╠²nautical miles (370╠²km) territorial sea: irregular polygon extending up to 100 nautical miles (185╠²km) from coastline as defined by 1898 treaty; since late 1970s has also claimed polygonal-shaped area in South China Sea up to 285 nautical miles (528╠²km) in breadth. ’ü« Natural resources: timber, petroleum, nickel, cobalt, silver, gold, salt, copper ’ü« Land use: arable land: 19% permanent crops: 12% permanent pastures: 4% forests and woodland: 46% other: 19% (1993 est.) ’ü« Irrigated land: 15,800╠²km2 (1993 est.) ’ü« Distances from Manila: 10,000╠²km ŌĆō San Francisco 8,000╠²km ŌĆō Honolulu, Hawaii 3,400╠²km ŌĆō Micronesia 2,900╠²km ŌĆō Tokyo 2,400╠²km ŌĆō Singapore 1,000╠²km ŌĆō Taiwan and Hong Kong
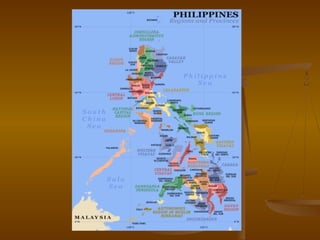
- 11. Elements of the State: Territory The Philippines is divided into three island groups: Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao. These are divided into 17 regions, 80 provinces, 120 cities, 1,511 municipalities and 42,008 barangays. The Philippines is an archipelago comprising 7,107 islands with a total land area of 300,000╠²km2. The 11 largest islands contain 94% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000╠²kms. The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000╠²km. The archipelago is around 800 kms from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.
- 12. Elements of the State: Territory The islands are divided into three groups: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The Luzon islands include Luzon itself, Palawan, Mindoro, Marinduque, Masbate and Batanes Islands . The Visayas is the group of islands in the central Philippines, the largest of which are: Panay, Negros, Cebu, Bohol, Leyte and Samar. The Mindanao islands include Mindanao itself, plus the Sulu Archipelago, composed primarily of Basilan, Sulu and Tawi-Tawi. The island of Romblon lies exactly at the center of the Philippine archipelago.
- 13. Region Designation Regional center Ilocos Region Region I San Fernando, La Union Cagayan Valley Region II Tuguegarao, Cagayan Central Luzon Region III San Fernando, Pampanga CALABARZON Region IV-A Calamba City, Laguna MIMAROPA Region IV-B Calapan, Mindoro Bicol Region Region V Legazpi, Albay Western Visayas Region VI Iloilo City Central Visayas Region VII Cebu City Eastern Visayas Region VIII Tacloban Zamboanga Peninsula Region IX Pagadian, Zamboanga del Sur Northern Mindanao Region X Cagayan de Oro City Davao Region Region XI Davao City SOCCSKSARGEN Region XII Koronadal, South Cotabato Caraga Region XIII Butuan Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao ARMM Cotabato City Cordillera Administrative Region CAR Baguio National Capital Region NCR Manila
- 15. Elements of the State: Territory List of Landlocked provinces in the Philippines ’ü« A landlocked province is one that has no coastline, meaning no access to sea or ocean. There are 16 landlocked provinces in the Philippines: ’ü« All provinces of Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR): Apayao, Abra, Kalinga, Mt. Province, Ifugao and Benguet. ’ü« Two provinces of Cagayan Valley (Region II): Nueva Vizcaya and Quirino ’ü« Two provinces of Central Luzon (Region III): Nueva Ecija and Tarlac ’ü« Four provinces of Mindanao: ’ü« Bukidnon of Northern Mindanao (Region X) ’ü« Cotabato Province of Soccsksargen (Region XII) ’ü« Agusan del Sur of Caraga (Region XIII), and ’ü« Maguindanao of Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM). ’ü« Similarly, Laguna and Rizal Province and of Calabarzon (Region IV-A) have coastlines on Laguna de Bay. Since lakes do not allow access to seaborne trade, these provinces are still considered to be landlocked.
- 16. Elements of the State: Territory List of island provinces in the Philippines An island province completely surrounded by water, is the opposite of a landlocked one. There are 15 island provinces in the Philippines: ’ü« One province of Cagayan Valley (Region II): Batanes ’ü« Three provinces of MIMAROPA (Region IV-B): Marinduque, Romblon and Palawan ’ü« Two provinces of Bicol (Region V): Catanduanes and Masbate ’ü« One province of Western Visayas (Region VI): Guimaras ’ü« Three provinces of Central Visayas (Region VII): Cebu, Bohol and Siquijor ’ü« One province of Eastern Visayas (Region VIII): Biliran ’ü« One province of Northern Mindanao (Region X): Camiguin ’ü« Three provinces of Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM): Basilan, Sulu and Tawi-Tawi ’ü« One province of Caraga Region: Dinagat Islands
- 17. Elements of the State: Territory Ten largest cities The following is a list of the ten largest cities in the country in terms of population, with their population according to the 2007 census. Component cities and municipalities of Metro Manila and Metro Cebu are taken as one to show the extent of urbanization. Rank City╠²Population in 2007╠² 1. Metro Manila 11,553,427 2. Metro Cebu 2,314,897 3. Davao City 1,363,337 4. Zamboanga City 774,407 5. Antipolo City 633,971 6. Cagayan de Oro City 553,966 7. General Santos City 529,542 8. Bacolod City 499,497 9. Iloilo City 418,710 10. Iligan City 308,046
- 18. Elements of the State: Government It refers to the agency through which the will of the state is formulated, expressed and carried out. Forms of government may be classified according to the number of persons exercising authority (monarchy, aristocracy and democracy); extent of powers exercised by central or national government (unitary or federal); relationship between executive and legislative branches (parliamentary and presidential)
- 19. Elements of the State: Government ACCORDING TO THE NUMBER OF PERSONS EXERCISING SOVEREIGN POWER Monarchy: one in which the supreme and final authority is in the hands of a single person Kinds of monarchy: a) Absolute monarchy ŌĆō one in which the ruler rules by divine right b) Limited monarchy ŌĆō one in which the ruler rules in accordance with the constitution
- 20. Elements of the State: Government Aristocracy: one in which political power is exercised by a few privileged class Democracy: one in which political power is exercised by a majority of the people a) Direct or pure democracy: one in which the will of the State is formulated or expressed directly and immediately through the people in a mass meeting or primary assembly a) Indirect, representative or republican democracy or one in which the will of the state is formulated and expressed through the agency of a relatively small and select body of persons chosen by the people to act as their representatives
- 21. Elements of the State: Government ACCORDING TO THE EXTENT OF POWERS EXERCISED BY THE CENTRAL GOVERNMENT Unitary government: one in which the control of national and local affairs is exercised by the central or national government Federal government: one in which the powers of government are divided between two sets of organs, one for national affairs and the other for local affairs.
- 22. Elements of the State: Government ACCORDING TO THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE EXECUTIVE AND THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Parliamentary: one in which the state confers upon the legislature the power to terminate the tenure of office of the real executive Presidential government: one in which the state makes the executive constitutionally independent of the legislature as regards his policies and acts
- 23. Elements of the State: Government The politics of the Philippines takes place in an organized framework of a presidential, representative and democratic republic whereby the president is both the head of state and the head of government within a pluriform multi-party system. This system revolves around three separate and sovereign yet interdependent branches: the legislative branch (the law-making body), the executive branch (the law-enforcing body), and the judicial branch (the law-interpreting body). Executive power is exercised by the government under the leadership of the president. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two-chamber congress -- the Senate (the upper chamber) and the House of Representatives (the lower chamber). Judicial power is vested in the courts with the Supreme Court of the Philippines as the highest judicial body.
- 24. Theories on Origin of the State ’ü« Divine Right Theory: the state is a divine creation and the ruler is ordained by God to rule the people. ’ü« Necessity or force theory: state was created through force ’ü« Paternalistic theory: state developed from a single nuclear family under the authority of a single parent ’ü« Social contract theory: state must have been formed by deliberate and voluntary contract among the people to form a society and organize government for their own good
- 25. Important Distinctions ’ü« State: a political concept (see the previous definition) ’ü« Nation: an ethnic concept; a group of people bound by common social and cultural origin ’ü« Government: an agency through which the state expresses its will; its main purpose is the promotion of common good or public welfare
- 26. the endŌĆ”.