Lec15 graph laplacian embedding
- 1. Image Analysis & Retrieval CS/EE 5590 Special Topics (Class Ids: 44873, 44874) Fall 2016, M/W 4-5:15pm@Bloch 0012 Lec 15 Graph Laplacian Embedding Zhu Li Dept of CSEE, UMKC Office: FH560E, Email: lizhu@umkc.edu, Ph: x 2346. http://l.web.umkc.edu/lizhu p.1Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 2. Outline ? Recap: ? Eigenface ? Fisherface ? Graph Embedding ? Laplacianface ? Graph Fourier Transform ?Summary p.2Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 3. Subspace Learning for Face Recognition ? Project face images to a subspace with basis A ? Matlab: x=faces*A(:,1:kd) eigf1 eigf2 eigf3 = 10.9* + 0.4* + 4.7* p.3Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 4. PCA & FisherĪ»s Linear Discriminant ? Between-class scatter ? Within-class scatter ? Where ©C c is the number of classes ©C ?i is the mean of class ?i ©C | ?i | is number of samples of ?i.. T ii c i iBS ))(( 1 ????? ??? ?? ? ?? ? ??? c i x T ikikW ik xS 1 ))(( ? ??? ?1 ?2 ? ?1 ?2 p.4Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
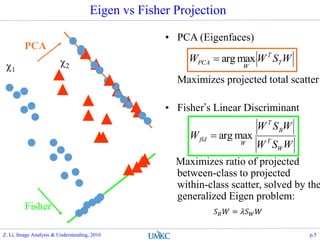
- 5. Eigen vs Fisher Projection p.5 ? PCA (Eigenfaces) Maximizes projected total scatter ? FisherĪ»s Linear Discriminant Maximizes ratio of projected between-class to projected within-class scatter, solved by the generalized Eigen problem: WSWW T T W PCA maxarg? WSW WSW W W T B T W fld maxarg? ?1 ?2 PCA Fisher ? ? ? = ?? ? ? Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 6. LDA implementation ? myLDA.m p.6 % compute class mean mx = mean(x); ids = unique(y); m = length(ids); Sb = zeros(kd, kd); for k=1:m indx = find(y==ids(k)); nk(k) = length(indx); % class mean m_cx(k,:) = mean(x(indx, :)); % between class scatter Sb = Sb + nk(k)*(m_cx(k,:) - mx)'*(m_cx(k,:) - mx); end % compute intra-class scatter Sw = zeros(kd, kd); for k=1:m indx = find(y==ids(k)); nk(k) = length(indx); % remove mean xk = x(indx, :) - repmat(m_cx(k,:), [nk(k), 1]); % adding up Sw = Sw + (xk'*xk); end Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 7. LDA Implementation ? Find projection by generalized Eigen problem solution p.7 % generalized eigen problem [A, v]=eigs(Sb, Sw); if dbg figure(31); subplot(2,2,1); imagesc(Sb); colormap('gray'); title('S_b'); subplot(2,2,2); imagesc(Sw); colormap('gray'); title('S_w'); z = x*A; dist = pdist2(z, z); subplot(2,2,3); imagesc(dist); title('dist(j,k)'); subplot(2,2,4); stem(diag(v), '.'); grid on; hold on; title('eig v'); end ? ? ? = ?? ? ? Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
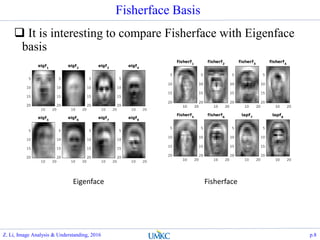
- 8. Fisherface Basis ? It is interesting to compare Fisherface with Eigenface basis p.8 FisherfaceEigenface Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 9. Fisherface Performance ? Fisher vs Eigenface performance: (fisherface.m) ? 1200 face images, 144 subjects ? Eigen kd=32 p.9 144 subjects ROC Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 10. Outline ? Recap: ? Eigenface ? Fisherface ? Graph Embedding ? Locality Preserving Projection ? Laplacian Face ? Graph Fourier Transform ?Summary p.10Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
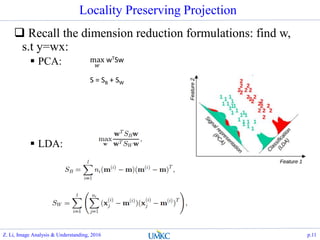
- 11. Locality Preserving Projection ? Recall the dimension reduction formulations: find w, s.t y=wx: ? PCA: ? LDA: p.11 max ? wTSw S = SB + SW Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 12. LPP Formulation ©C Affinity ? To preserve local affinity relationship ? Affinity map ? Selection of heat kernel size and threshold are important ? Hint: affinity matrix should be sparse p.12 affinity histogram Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 13. LPP Formulation ©C Affinity Supervised ? How to utilize the label info ? ? Heat map mapping is good for intra-class affinity modelling, but how about intra-class affinity ? ? One direct solution is to set affinity to zero for intra class pairs p.13 % LPP - compute affinity f_dist1 = pdist2(x1, x1); % heat kernel size mdist = mean(f_dist1(:)); h = - log(0.15)/mdist; S1 = exp(-h*f_dist1); id_dist = pdist2(ids, ids); subplot(2,2,3); imagesc(id_dist); title('label distance'); S2=S1; S2(find(id_dist~=0)) = 0; subplot(2,2,4); imagesc(S1); colormap('gray'); title('affinity- supervised'); Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 14. LPP- Affinity Preserving Projection ? Find a projection that best preserves the affinity matrix p.14 min ? ? ? ??,? ?? ? ?? 2 , ?. ?. ? = ?? min ? ? ? ??,? ??? ? ??? 2 ?. ?, ??,? = ?exp ?? ? ?? 2 ? , ?? ?? ? ?? Ī▄ ? 0, ???? Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 15. LPP Formulation ?L = D-S: ? nxn matrix, called graph Laplacian ?Normalizing factor: nxn D ? Diagonal matrix, entry Dii = sum of col/row affinity ? The larger the value, the more important data point is ? Constraint on D: ? p.15Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
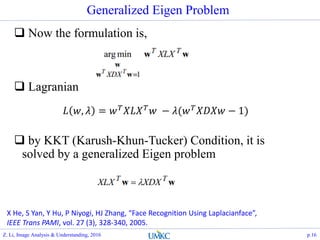
- 16. Generalized Eigen Problem ? Now the formulation is, ? Lagranian ? by KKT (Karush-Khun-Tucker) Condition, it is solved by a generalized Eigen problem p.16 ? ?, ? = ? ? ??? ? ? ? ?(? ? ???? ? 1) Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016 X He, S Yan, Y Hu, P Niyogi, HJ Zhang, Ī░Face Recognition Using LaplacianfaceĪ▒, IEEE Trans PAMI, vol. 27 (3), 328-340, 2005.
- 17. Matlab Implementation ? laplacianface.m p.17 %LPP n_face = 1200; n_subj = length(unique(ids(1:n_face))); % eigenface kd=32; x1 = faces(1:n_face,:)*A1(:,1:kd); ids=ids(1:n_face); % LPP - compute affinity f_dist1 = pdist2(x1, x1); % heat kernel size mdist = mean(f_dist1(:)); h = -log(0.15)/mdist; S1 = exp(-h*f_dist1); figure(32); subplot(2,2,1); imagesc(f_dist1); colormap('gray'); title('d(x_i, d_j)'); subplot(2,2,2); imagesc(S1); colormap('gray'); title('affinity'); %subplot(2,2,3); grid on; hold on; [h_aff, v_aff]=hist(S(:), 40); plot(v_aff, h_aff, '.-'); % utilize supervised info id_dist = pdist2(ids, ids); subplot(2,2,3); imagesc(id_dist); title('label distance'); S2=S1; S2(find(id_dist~=0)) = 0; subplot(2,2,4); imagesc(S1); colormap('gray'); title('affinity-supervised'); % laplacian face lpp_opt.PCARatio = 1; [A2, eigv2]=LPP(S2, lpp_opt, x1); Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 18. Laplacian Face ? Now, we can model face as a LPP projection: p.18 Eigenface Laplacian Face Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 19. Laplacian vs Eigenface ? 1200 faces, 144 subjects p.19Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 20. LPP and PCA ? Graph Embedding is an unifying theory on dimension reduction ? PCA becomes special case of LPP, if we do not enforce local affinity p.20Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 21. LPP and LDA ?How about LDA ? ? Recall within class scatter: p.21 This is i-th class Data covariance Li has diagonal entry of 1/ni, Equal affinity among data points Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 22. LPP and LDA ? Now consider the between class scatter ? C is the data covariance, regardless of label ? L is graph Laplacian computed from the affinity rule that, p.22 ? ?, ? = 1 ? ? , ?? ??, ?? ??? ???? ????? ? 0, ???? Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 23. LDA as a special case of LPP ? The same generalized Eigen problem p.23Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 24. Graph Embedding Interpretation of PCA/LDA/LPP ? Affinity graph S, determines the embedding subspace W, via ?PCA and LDA are special cases of Graph Embedding ? PCA: ? LDA ? LPP p.24 ??,? = ?exp ?? ? ?? 2 ? , ?? ?? ? ?? Ī▄ ? 0, ???? ??,? = 1 ? ? , ?? ??, ?? Ī╩ ? ? 0, ???? ??,? = 1/? Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 25. Applications: facial expression embedding ? Facial expressions embedded in a 2-d space via LPP p.25 frown sad happy neutral Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016
- 26. Application: Compression of SIFT ? Compression of SIFT, preserve matching relationship, rather than reconstruction: Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016 p.26 ? = arg min ? ? ? ??,? ??? ? ?? ? 2
- 27. Homework-3: Subspace Methods ? Objective: ? Understand the graph embedding connections among popular subspace methods like PCA, LDA and LPP ? Practical experiences with serious size data set ? Data Set: ? https://umkc.app.box.com/s/0qu7tc3jb88at2h53l1dpcuqkt9pn 7ww ? 417 subjects, 6650 image face data set, pre-processed to 20x20 pel images, intensity normalized to [0, 1] ? Add your own face images, 10~15, frontal ? Tasks: ? Compute Eigenface, Fisherface and Laplacianface models ? ROC plot on verification performance ? mAP for retrieval/identification performance Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016 p.27
- 28. HW-3 test run ? Laplacian face is powerful. ? Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016 p.28
- 29. Graph Fourier Transform ? David I. Shuman, Sunil K. Narang, Pascal Frossard, Antonio Ortega, Pierre Vandergheynst: The Emerging Field of Signal Processing on Graphs: Extending High-Dimensional Data Analysis to Networks and Other Irregular Domains. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 30(3): 83-98 (2013) Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016 p.29
- 30. Signal on Graph ? non-uniformly sampled p.30 Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 31. Graph Fourier Transform ? GFT is different from Laplacian Embedding: p.31 Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 32. GFT Example ?Graph Laplacian p.32 Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 33. Normalized Graph Laplacian ?Normalize by edge pair degree p.33 Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 34. Graph Frourier Transform ? Analogous to FT p.34 Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 35. Graph Spectrum p.35 Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 36. Graph Signal Smoothness ? Quadratic form on L: p.36 Z. Li, Adv. Multimedia Communciation, 2016 Fall
- 37. Summary ? Graph Laplacian Embedding is an unifying theory for feature space dimension reduction ? PCA is a special case of graph embedding o Fully connected affinity map, equal importance ? LDA is a special case of graph embedding o Fully connected intra class o Zero affinity inter class ? LPP: preserves pair wise affinity. ? GFT: eigen vectors of graph Laplacian, has Fourier Transform like characteristics. ? Many applications in ? Face recognition ? Pose estimation ? Facial expression modeling ? Compression of Graph signals. p.37Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016





![LDA implementation
? myLDA.m
p.6
% compute class mean
mx = mean(x);
ids = unique(y); m = length(ids);
Sb = zeros(kd, kd);
for k=1:m
indx = find(y==ids(k)); nk(k) = length(indx);
% class mean
m_cx(k,:) = mean(x(indx, :));
% between class scatter
Sb = Sb + nk(k)*(m_cx(k,:) - mx)'*(m_cx(k,:) - mx);
end
% compute intra-class scatter
Sw = zeros(kd, kd);
for k=1:m
indx = find(y==ids(k)); nk(k) = length(indx);
% remove mean
xk = x(indx, :) - repmat(m_cx(k,:), [nk(k), 1]);
% adding up
Sw = Sw + (xk'*xk);
end
Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec15-graphlaplacianembedding-161108174529/85/Lec15-graph-laplacian-embedding-6-320.jpg)
![LDA Implementation
? Find projection by generalized Eigen problem solution
p.7
% generalized eigen problem
[A, v]=eigs(Sb, Sw);
if dbg
figure(31);
subplot(2,2,1); imagesc(Sb);
colormap('gray'); title('S_b');
subplot(2,2,2); imagesc(Sw);
colormap('gray'); title('S_w');
z = x*A; dist = pdist2(z, z);
subplot(2,2,3); imagesc(dist);
title('dist(j,k)');
subplot(2,2,4); stem(diag(v), '.'); grid on;
hold on; title('eig v');
end
? ? ? = ?? ? ?
Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec15-graphlaplacianembedding-161108174529/85/Lec15-graph-laplacian-embedding-7-320.jpg)





![Matlab Implementation
? laplacianface.m
p.17
%LPP
n_face = 1200; n_subj = length(unique(ids(1:n_face)));
% eigenface
kd=32; x1 = faces(1:n_face,:)*A1(:,1:kd); ids=ids(1:n_face);
% LPP - compute affinity
f_dist1 = pdist2(x1, x1);
% heat kernel size
mdist = mean(f_dist1(:)); h = -log(0.15)/mdist;
S1 = exp(-h*f_dist1);
figure(32); subplot(2,2,1); imagesc(f_dist1); colormap('gray'); title('d(x_i, d_j)');
subplot(2,2,2); imagesc(S1); colormap('gray'); title('affinity');
%subplot(2,2,3); grid on; hold on; [h_aff, v_aff]=hist(S(:), 40); plot(v_aff, h_aff,
'.-');
% utilize supervised info
id_dist = pdist2(ids, ids);
subplot(2,2,3); imagesc(id_dist); title('label distance');
S2=S1; S2(find(id_dist~=0)) = 0;
subplot(2,2,4); imagesc(S1); colormap('gray'); title('affinity-supervised');
% laplacian face
lpp_opt.PCARatio = 1;
[A2, eigv2]=LPP(S2, lpp_opt, x1);
Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec15-graphlaplacianembedding-161108174529/85/Lec15-graph-laplacian-embedding-17-320.jpg)









![Homework-3: Subspace Methods
? Objective:
? Understand the graph embedding connections among popular
subspace methods like PCA, LDA and LPP
? Practical experiences with serious size data set
? Data Set:
? https://umkc.app.box.com/s/0qu7tc3jb88at2h53l1dpcuqkt9pn
7ww
? 417 subjects, 6650 image face data set, pre-processed to
20x20 pel images, intensity normalized to [0, 1]
? Add your own face images, 10~15, frontal
? Tasks:
? Compute Eigenface, Fisherface and Laplacianface models
? ROC plot on verification performance
? mAP for retrieval/identification performance
Z. Li, Image Analysis & Understanding, 2016 p.27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec15-graphlaplacianembedding-161108174529/85/Lec15-graph-laplacian-embedding-27-320.jpg)









