lect22.ppt
- 1. 1 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Lecture 22: Object-Oriented Programming COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Spring 2002 Felix Hernandez-Campos March 11 The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- 2. 2 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Fundamental Concepts in OOP • Encapsulation – Data Abstraction – Information hiding – The notion of class and object • Inheritance – Code reusability – Is-a vs. has-a relationships • Polymorphism – Dynamic method binding
- 3. 3 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Encapsulation • Data abstraction allow programmers to hide data representation details behind a (comparatively) simple set of operations (an interface) • What the benefits of data abstraction? – Reduces conceptual load » Programmers need to knows less about the rest of the program – Provides fault containment » Bugs are located in independent components – Provides a significant degree of independence of program components » Separate the roles of different programmer Software Engineering Goals
- 4. 4 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Encapsulation Classes, Objects and Methods • The unit of encapsulation in an O-O PL is a class – An abstract data type » The set of values is the set of objects (or instances) • Objects can have a – Set of instance attributes (has-a relationship) – Set of instance methods • Classes can have a – Set of class attributes – Set of class methods Method calls are known as messages • The entire set of methods of an object is known as the message protocol or the message interface of the object
- 5. 5 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Inheritance • Encapsulation improves code reusability – Abstract Data Types – Modules – Classes • However, it is generally the case that the code a programmer wants to reuse is close but not exactly what the programmer needs • Inheritance provides a mechanism to extend or refine units of encapsulation – By adding or overriding methods – By adding attributes
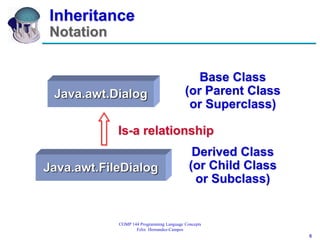
- 6. 6 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Inheritance Notation Java.awt.Dialog Java.awt.FileDialog Base Class (or Parent Class or Superclass) Derived Class (or Child Class or Subclass) Is-a relationship
- 7. 7 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Polymorphism • The is-a relationship supports the development of generic operations that can be applied to objects of a class and all its subclasses – This feature is known as polymorphism – E.g. paint() method • The binding of messages to method definition is instance-dependent, and it is known as dynamic binding – It has to be resolved at run-time – Dynamic binding requires the virtual keyword in C++ – Static binding requires the final keyword in Java
- 8. 8 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Encapsulation Modules and Classes • The basic unit of OO, the class, is a unit of scope – This idea originated in module-based languages in the mid-70s » E.g. Clu, Modula, Euclid • Rules of scope enforce data hiding – Names have to be exported in order to be accessible by other modules – What kind of data hiding mechanisms we have in Java? » http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/java/javaOO/accesscontrol .html – And in Python? » http://www.python.org/doc/current/tut/node11.html#SECTION00 11600000000000000000
- 9. 9 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Classes and Encapsulation Two Views • Module-as-type – A module is an abstract data type – Standardized constructor and destructor syntax – Object-oriented design is applied everywhere – E.g. Java, Smalltalk, Eiffel, C++, Python • Module-as-manager – A module exports an abstract data type – Create and destroy operations – Object-oriented design is optional (OO as an extension) – E.g. Ada 95, Modula-3, Oberon, CLOS, Perl
- 10. 10 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Ada 95
- 11. 11 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Ada 95
- 12. 12 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Ada 95
- 13. 13 COMP 144 Programming Language Concepts Felix Hernandez-Campos Reading Assignment • Scott – Read Ch. 10 intro – Read Sect. 10.1 » Study the list and queue examples – Read Sect. 10.2 » Go through the documents linked in slide 8