Lecture 1 precise levelling
- 1. SUG213 : ENGINEERING SURVEYING II PRECISE LEVELLING INTRODUCTION AND INSTRUMENTATION Lecture By: Zuraihan Mohamad Dept. of Surveying Sciences & Geomatics FSPU UiTM Arau
- 2. Aim Of The Topic ’é¦ At the end of this lecture, student should be able to : ’éĀ Understand what is precise levelling and the needs. ’éĀ Understand the methods and instrumentation of precise levelling
- 3. Lecture content ’é¦ Concept of levelling ’é¦ Historical background of Precise Levelling in Malaysia ’é¦ National Geodetic Vertical Datum (NGVD) ’é¦ Malaysia Tidal Network ’é¦ Types of Levelling ’é¦ Precise Levelling ’é¦ Equipment of precise levelling ’ā║ Optical precise levelling ’ā║ Motorized l precise levelling ’ā║ Digital precise levelling
- 4. ▓Ž▒½ĘĪ│¦░š▒§░┐▒ĘŌĆ” Before we begin ’é¦ What is P.L? ’é¦ Why do we need P.L? ’é¦ Are there any differences between P.L n O.L?? ’é¦ Say that that there are indeed differences, they are in terms of what???
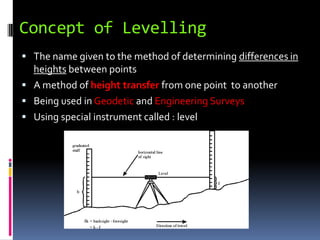
- 5. Concept of Levelling ’é¦ The concept of levelling is based on the horizontal line of the instrument (level) with the level line of the point on the earth. ’é¦ If the heights of A and B can be measured, the height differences can be calculated using the formula : ’üäh = a - b ’é¦ If the RLA is known, RLB can be calculated as: RL B = RLA + ’üäh
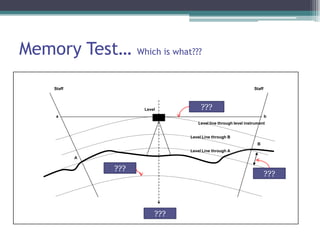
- 6. Memory TestŌĆ” Which is what??? Staff Staff Level ??? a b Level line through level instrument Level Line through B B Level Line through A A ??? ??? ???
- 7. Concept of Levelling ’é¦ The name given to the method of determining differences in heights between points ’é¦ A method of height transfer from one point to another ’é¦ Being used in Geodetic and Engineering Surveys ’é¦ Using special instrument called : level
- 8. Historical Background Several methods of height measurement are being used in surveying and construction works; ’é¦ Trigonometric heighting - Theodolite ’é¦ Barometric heighting - Barometer (pressure) ’é¦ Hydrostatic Levelling - Water tube ’é¦ Tacheometry - Staff ’é¦ GPS - Receiver ’é¦ Direct measurement - Tape ’é¦ Levelling - Level
- 9. ’é¦ 1st vertical datum was established in 1912 based on Mean Sea Level (MSL) produced by British Admiralty. ’é¦ At Port Swettenham (Port Kelang) ’é¦ 1 year tidal observations ’é¦ Also known as Land Survey Datum (LSD) ’é¦ But no records and evidence available
- 10. ’éĪ Mean Sea Level ’é¦ Average level taken up by the sea ’é¦ Coincide with the Geoid ’é¦ Change regularly due to tide ’é¦ Best observation period is 18.6 years ’é¦ Use of Tide Observation Data ’é¦ Determine precise vertical datum ’é¦ Information for research in geodesy, geodynamic and scientific studies ’é¦ Tide & flood prediction ’é¦ Port activities and navigation ’é¦ Marine boundaries, hydrography and aquaculture ’é¦ Delivery of fixed record of sea level ’é¦ To obtain tidal harmonic constant ’é¦ To study tidal characteristics ’é¦ For tidal prediction.
- 11. National Geodetic Vertical Datum (NGVD) ’é¦ JUPEM initiated the establishment of NGVD ’é¦ 12 tidal stations were established in 1981 Objectives: ’é¦ To observe tide levels continuously ’é¦ 18.6 years complete cycle of moon regression ’é¦ To obtain tidal harmonic constants ’é¦ To study tidal characteristics ’é¦ For tidal prediction
- 12. Malaysia Tidal Network ’é¦ 1995 (established n in operation) - 21 tidal stations ’é¦ 12 are installed in Peninsular and 9 in east Malaysia ’é¦ Each station is connected by precise levelling networks
- 13. Tidal Station
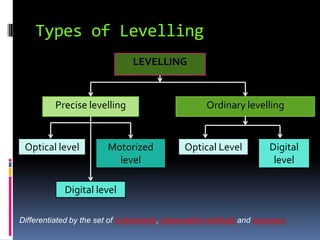
- 14. Types of Levelling LEVELLING Precise levelling Ordinary levelling Optical level Motorized Optical Level Digital level level Digital level Differentiated by the set of instruments, observation methods and accuracy
- 15. Precise Levelling ’é¦ Also known as the highest order of levelling works ’é¦ Readings observed and recorded to decimals of a millimeter ’é¦ Used for : ’ā║ Basic levelling framework of a country ’ā║ Transfer height to bench marks ’ā║ Precision engineering structure ’ā║ Irrigation Scheme, Dam, Tunnels ’ā║ Precision dimensional surveys
- 16. Equipments of Precise Levelling ’é¦ Level (Precise type) ’é¦ Invar or bar-coded staff ’é¦ Survey Tripods ’é¦ Change plate (staff support) ’é¦ Staff bubble ’é¦ Handles and steadying rods (bipod) ’é¦ Thermometer ’é¦ Umbrella
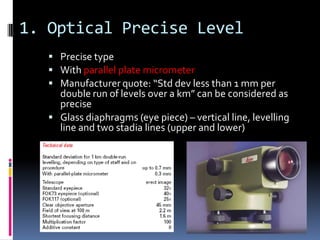
- 18. 1. Optical Precise Level ’é¦ Precise type ’é¦ With parallel plate micrometer ’é¦ Manufacturer quote: ŌĆ£Std dev less than 1 mm per double run of levels over a kmŌĆØ can be considered as precise ’é¦ Glass diaphragms (eye piece) ŌĆō vertical line, levelling line and two stadia lines (upper and lower)
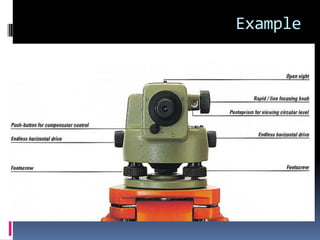
- 19. Example
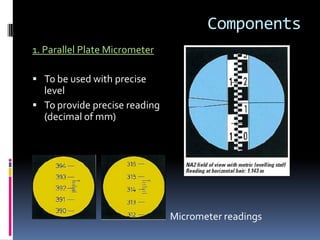
- 20. Components 1. Parallel Plate Micrometer ’é¦ To be used with precise level ’é¦ To provide precise reading (decimal of mm) Micrometer readings
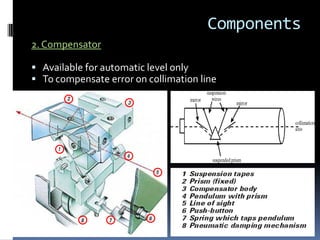
- 21. Components 2. Compensator ’é¦ Available for automatic level only ’é¦ To compensate error on collimation line
- 22. Components 3. Precise Staff ’é¦ Two precise/Invar staffs ’é¦ Invar Strip ŌĆō stable material (low sensitivity to heat) ’é¦ Small expansion coefficient ’é¦ Graduations 0.02ft / 0.01 m on invar strip ’é¦ With handle / staff holder ’é¦ To be calibrated every 3 months
- 24. 2. Motorized Precise Level ’é¦ Were used in the DSMM (Late 80s) - No longer used ’é¦ Modification of conventional method ’é¦ Three vehicles ŌĆō 1 for the level and observer, 2 for the staffs ’é¦ Invar staffs are fitted to the vehicles ’é¦ Advantage: ’ā║ Faster and convenient ’é¦ Disadvantage: ’ā║ High cost ’ā║ Not suitable in busy roads
- 26. 3. Digital Precise Level ’é¦ Use digital level (automatic level) and bar-coded staffs ’é¦ Use infrared detector to scan the bar-coded staff ’é¦ Scanned staff image is compared to actual staff pattern stored in the instrument ’é¦ Provide staff reading and horizontal distance ’é¦ Advantages: ’ā║ Levels are recorded automatically ’ā║ Reduce human error (reading and booking) ’ā║ Reduce observation time ’ā║ Include processing software
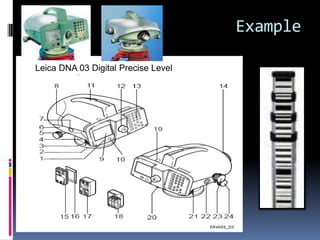
- 27. Example Leica DNA 03 Digital Precise Level
- 28. Leica DNA 03 Digital Precise Level ’é¦ Elements: 1 On/ off button 16 PCMCIA or CF-card with 2 Base plate adapter (optional) 3 Foot screws 17 Battery GEB121 (optional) 4 Horizontal circle 18 Battery adapter GAD39; 6 5 Lever to unlatch battery single cells (optional) 6 Battery compartment 19 Light duct for circular level 7 Button to unlatch card compartment 20 Plug stopper for crosshair cover adjustment knob 8 Card compartment cover 21 RS232 serial interface 9 Display with external power supply 10 Circular level 22 Measuring button 11 Hand grip with aiming sight 23 Focusing drive 12 Ocular 24 Endless horizontal drive 13 Keyboard (bi-directional) 14 Objective 15 Battery GEB111 (optional)
- 29. Leica DNA 03 Digital Precise Level ’é¦ Characteristics: ’é¦ Limited target distance <30m ’é¦ Minimum ground clearance of >0.5m required to minimized refractionary influences of ground proximity. ’é¦ Double observance (BFFB, aBFFB) to increase the reliability of measurement and to reduce possible errors caused by staff sinking. ’é¦ Applying alternating observations procedures (aBFFB = BFFB FBBF) to eliminate horizontal tilt ( residual error of the automatic compensator) ’é¦ Use an umbrella in strong sunlight.
- 31. 1. Base/Change Plate ’é¦ Staffs are to be supported on turning points ’é¦ Made from mild steel ’é¦ Round head and collars ’é¦ To reduce error during turning (for soft ground)
- 32. 2. Handles/Bipods ’é¦ To support precise staff ’é¦ For long observation period ’é¦ Stable (verticality)
![[ Nor Khalila Na'ima ]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/profile-photo-AmianRon-48x48.jpg?cb=1550151814)






























































![Electrical measurement & measuring instruments [emmi (nee-302) -unit-5]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/electricalmeasurementmeasuringinstrumentsemmi-nee-302-unit-5-170607091755-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)







