Lecture 10 focusing and colimating
- 1. FOCUSING AND COLLIMATING Prof. Sekartedjo Iwan Cony Setiadi
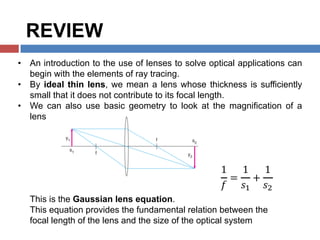
- 2. ŌĆó An introduction to the use of lenses to solve optical applications can begin with the elements of ray tracing. ŌĆó By ideal thin lens, we mean a lens whose thickness is sufficiently small that it does not contribute to its focal length. ŌĆó We can also use basic geometry to look at the magnification of a lens This is the Gaussian lens equation. This equation provides the fundamental relation between the focal length of the lens and the size of the optical system 1 Øæō = 1 ØæĀ% + 1 ØæĀ' REVIEW
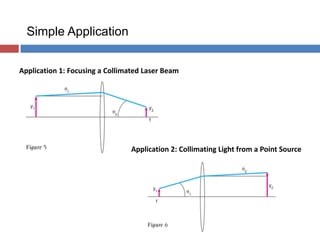
- 3. Application 1: Focusing a Collimated Laser Beam Application 2: Collimating Light from a Point Source Simple Application
- 4. Application 3: Expanding a Laser Beam Simple Application Application 4: Focusing an Extended Source to a Small Spot
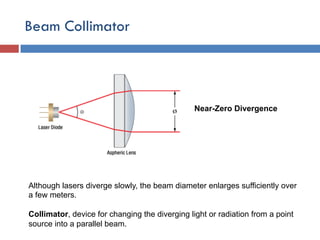
- 6. Beam Collimator Near-Zero Divergence Although lasers diverge slowly, the beam diameter enlarges sufficiently over a few meters. Collimator, device for changing the diverging light or radiation from a point source into a parallel beam.
- 7. ŌĆó A collimated beam of light is a beam (typically a laser beam) which has a low beam divergence, so that the beam radius does not undergo significant changes within moderate propagation distances. ŌĆó A divergent beam can be collimated with a beam collimator device, which in simple case is essentially a lens or a curved mirror BEAM EXPANDER What is divergence? Divergence describes the expansion of a laser beam over a long distance
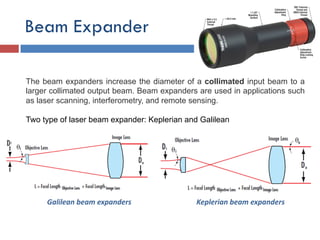
- 8. Beam Expander The beam expanders increase the diameter of a collimated input beam to a larger collimated output beam. Beam expanders are used in applications such as laser scanning, interferometry, and remote sensing. Two type of laser beam expander: Keplerian and Galilean Keplerian beam expandersGalilean beam expanders
- 9. ŌĆó When using the Keplerian or Galilean designs in laser beam expander applications, it is important to be able to calculate the output beam divergence. ŌĆó This determines the deviation from a perfectly collimated source. The beam divergence is dependent on the diameters of the input and output laser beam ŌĆó In addition, it is important to be able to calculate the output beam diameter at a specific working distance (L). The output beam diameter is a function of the input beam diameter and the beam divergence after a specific working distance (L)
- 10. A laser's input beam diameter and divergence can be used to calculate the output beam diameter at a specific working distance.
- 11. Application 1. Reducing Power Density 2. Minimizing Beam Diameter at a Distance 3. Minimizing Focused Spot Size 4. Laser Beam Size Compensation
- 12. Beam Shaper ŌĆó In general, a beam shaper (or beam converter) is an optical device which somehow reshapes a light beam, i.e., it modifies its spatial profile. ŌĆó In various industries there is a need to focus a laser beam to a well-defined size and shape with uniform intensity (flat top). ŌĆó A flat top spot enables uniform laser treatment of the working surface, and maintains the same active area regardless of pulse energy.
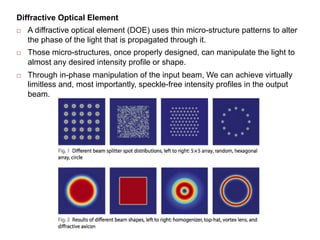
- 13. Diffractive Optical Element ┬© A diffractive optical element (DOE) uses thin micro-structure patterns to alter the phase of the light that is propagated through it. ┬© Those micro-structures, once properly designed, can manipulate the light to almost any desired intensity profile or shape. ┬© Through in-phase manipulation of the input beam, We can achieve virtually limitless and, most importantly, speckle-free intensity profiles in the output beam.
- 14. The beam shaping element is a diffractive optical element (DOE) used to transform a near-gaussian incident laser beam into a uniform- intensity spot of either round, rectangular, square, line or other shape with sharp edges in a specific work plane. Each beam shaper is designed for use with a specific set of optical system parameters: ŌĆó Wavelength ŌĆó Input Beam Size (D) ŌĆó Output Spot Size (d)
- 16. Why do we need beam shaper?
- 19. Discussion Question: Do you need to get intense light delivered at a distance? There are two choices: 1) Collimate the light or 2) Focus the light. ┬© Collimation expands the beam and sends it forward in relatively parallel beams. ┬© A focuser mounts on a collimator and either shrinks or magnifies the spot at a specific working distance. Which option is best for you?