Lecture 3 network communication media and devices
- 1. Network Communication Media and Devices
- 2. Introduction • In computer networks, devices/nodes pass data to each other along data connections. The connections or network links between devices/nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media. • Network media: is the physical or wireless channel used for transmission in the network. Wire/cables, and wireless/air are the two main types of media.
- 3. Types of Wired/Cable Media • There are three types of cables used: these are: – Twisted pair – Coaxial cable, – Fiber optic.
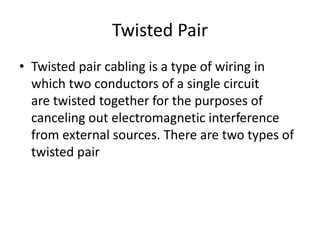
- 4. Twisted Pair • Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference from external sources. There are two types of twisted pair
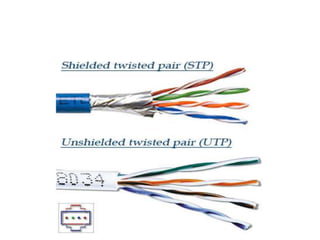
- 5. Twisted Pair Cables • Shielded Twisted Pair – It uses metallic shield wrapping to protect the wire from interference • Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) – This is the most popular form of cables in the network and the cheapest form that you can go with. The UTP has four pairs of wires and all are inside plastic sheathing. The biggest reason that we call it Twisted Pair is to protect the wires from interference from themselves. Each wire is only protected with a thin plastic sheath.
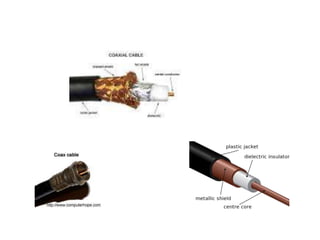
- 7. Coaxial Cable • Coaxial cables are a type of cable that is used by cable TV (e.g. DSTV)and that is also commonly used for data communications. Its made up of a single center solid wire symmetrically surrounded by a braided or foil conductor. Between the center wire and foil is a insulating dielectrics. • Coaxial cable is sometimes used by telephone companies from their central office to the telephone poles near users. It is also widely installed for use in business, Ethernet and other types of local area network.
- 9. Fiber Optic Cable • Its a technology that uses glass (or plastic) threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves.
- 10. Advantages/Disadvantages of Fiber Optics • Advantages – Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth than metal cables. This means that they can carry more data. – Fiber optic cables are less susceptible than metal cables to interference. – Fiber optic cables are much thinner and lighter than metal wires. – Data can be transmitted digitally (the natural form for computer data) rather than analogically. • Disadvantages – Expensive – Difficult to install. In addition, they are more fragile than wire and are difficult to splice (join or merged together).
- 12. Cables Standards and Connectors • Something else to note about cables is that they are defined in numbers also. The bigger the number the better the protection from interference. Most networks should go with no less than a CAT 5 or CAT6 or 6a (Augmented Cat 6) is most recommended. • Now you know about cables we need to know about connectors. This is pretty important and you will most likely need the RJ-45 connector. This is the cousin of the phone jack connector and looks real similar with the exception that the RJ-45 is bigger.
- 13. Connectors
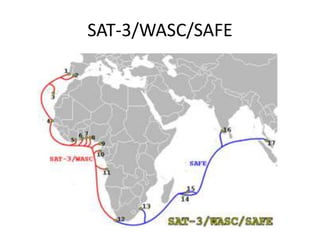
- 15. SAT3 Project • SAT-3/WASC or South Atlantic 3/West Africa Submarine Cable is a submarine communications cable linking Portugal and Spain to South Africa, with connections to several West African countries along the route. • It forms part of the SAT-3/WASC/SAFE cable system, where the South Africa Far East (SAFE) cable links South Africa to Asia. The SAT-3/WASC/SAFE system provides a path between Asia and Europe for telecommunications traffic. • The South Africa Far East cable is an optical fiber submarine communications cable linking South Africa and, Malaysia.
- 16. SAT-3/WASC/SAFE
- 17. Marine Fiber Optic Installation
- 18. Wireless/Air Media • Wireless transmission media send communications signals by using – broadcast radio, – cellular radio, – microwaves, – satellites, – infrared signals.
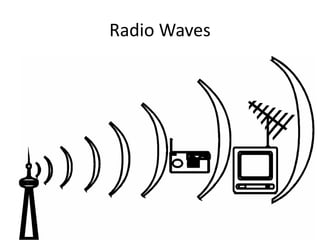
- 19. Radio Waves • Radio waves is a wireless transmission medium that distributes radio signals through the air. Radio waves are widely used as signals on radio communication • A transmitter is needed to send the broadcast signal and a receiver is needed to accept the signal. • Some networks use a transceiver, which both sends and receives signals from wireless devices.
- 20. Radio Waves
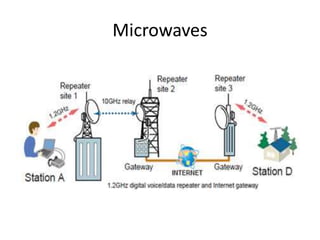
- 21. Microwaves • Microwaves are radio waves that provide a high-speed signal transmission. Microwaves transmission involves sending signals from one microwave station to another. • Microwaves transmission is fast but is limited to line-of-sight transmission, which means that the microwaves must transmit in a straight line with no obstructions between microwave antennas.
- 22. Microwaves • Microwaves stations are often located on the tops of buildings, towers, or mountains to avoid possible obstructions. Microwaves transmission is used where installing physical transmission media is difficult or impossible (e.g., deserts, lakes), but where line-of-sight transmission is available. • Radio waves in general have long distance communication capabilities, than microwaves..
- 23. Microwaves
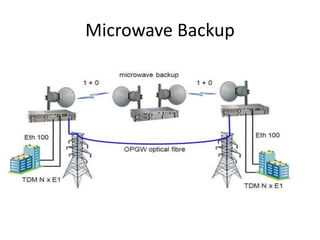
- 24. Microwave Backup
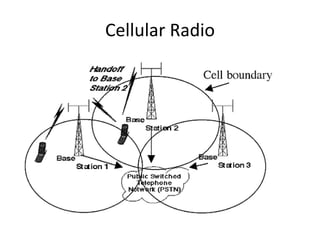
- 25. Cellular Radio • Cellular radio is a form of broadcast radio that is used widely for mobile communications, specifically cellular telephones. • Its used over land areas called cells, with each served by at least one fixed location transceiver, known as a Cell Site or Base Station. • When joined together these cells provide radio coverage over a wide geographic area. This enables a large number of portable transceivers (e.g., mobile phones, pagers, etc.) to communicate with each other and with fixed transceivers and telephones anywhere in the network, via base stations
- 26. Cellular Radio
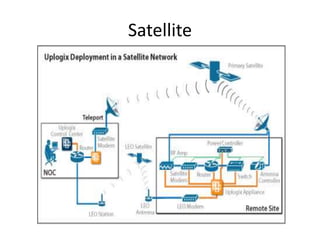
- 27. Satellite Communication • A communications satellite is a station in space that receives microwaves signals from an earth-based station, amplifies the signals, and broadcasts the signals back over a wide area to many earth-based stations. • Communications satellites are usually placed about 22,300 miles above the Earth's equator and moves at the same rate as the Earth. • Applications of communications satellite include television and radio broadcasts, videoconferencing, paging, and global positioning systems(GPS).
- 28. Satellite
- 29. Infrared • Infrared (IR) is a wireless transmission media that sends signals using infrared light waves. • IR transmission also requires a line-of-sight transmission as that required by microwaves. • Computer devices such as a mouse, printer, and digital camera, which have an IrDA port may transfer data from one device to another using infrared light waves. • IR is an alternative to short-range broadcast radio communications such as Bluetooth.
- 30. Bluetooth • Bluetooth is a kind of short-range (about 10 meters) broadcast radio communications, which can transmit data at a rate of 1 Mbps among Bluetooth-enabled devices. • Examples of Bluetooth devices include desktop computers, notebook computers, handheld computers, Internet appliances, cellular telephones, and printers.
- 31. Network Devices • Repeaters – A hardware device that amplifies a signal that has traveled a long distance. • Switches – It’s a small hardware device that joins multiple computers together within one local area network. Switches have the ability to selectively forward data packets to a specific destination. • Bridges – A hardware device that connect two networks and breaks the segments of one network into smaller groups. Bridges filter incoming traffic and decide whether to forward or discard it.
- 32. Network Devices • Routers – A network device that determines where information packets should go and sends them to their destination by the shortest, most efficient route. • Network Interface Cards – A computer circuit board or card that is installed in a computer so that it can be connected to a network. Network interface cards provide a dedicated, full-time connection to the network. • Patch Panel – A patch panel is a mounted hardware unit containing an assembly of port locations in a communications or other electronic or electrical system. It serves as a sort of static switchboard, using cables to interconnect computers within the area of a local area network
- 33. END OF LECTURE