Lecture 3 spread spectrum
- 1. Lecture 3 Communication basics. (2 hours) 01/01/04 1
- 2. Contents ? Spread spectrum ¨C FHSS ¨C DSSS ¨C CDMA ¨C OFDM ? Multiple Access techniques ¨C FDMA ¨C TDMA ¨C CDMA 01/01/04 2
- 3. Spread Spectrum ? Transmit analog or digital data as analog signals. ? Spread the signal over a wider bandwidth to avoid jamming and frequency interception. ? This technique is used for military and intelligence applications. Also used in wireless and cordless networks. ? Three techniques are commonly used FHSS, DSSS and CDMA. 01/01/04 3
- 4. Spread Spectrum - Frequency Hopping FHSS ? Broadcast the signal over a random series of radio frequencies, hopping at fixed interval. ? The receiver should hop at those frequencies to demodulate the signal. ? s(t) = A cos (2? (f0 + fi +(bi+1)?f/2) t ) ¨C ?f is the frequency separation, bi is equal to 1 for binary 1 and -1 for binary 0. The frequencies fi are random, at a hop equals to the bit duration. ¨C The ith bit interval has a frequency f0+fi , if it is 0 and f0+fi+?f if it is 1. ? Using MFSK, implementation ˇ next 01/01/04 4
- 5. Example with M=4 and K=2, two bits random sequence (PN) 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 01 11 00 11 11 01 10 00 00 01 Tc T | Ts 11 10 01 00 11 10 01 00 11 10 01 00 11 10 01 00 11 10 01 00 PN Input data Slow FHSS 01/01/04 5
- 6. 00 11 01 10 00 10 00 11 10 00 10 11 11 01 00 01 10 11 01 10 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 11 10 01 00 11 10 01 00 11 10 01 00 11 10 01 00 T Ts Tc 01/01/04 6 11 10 01 00 PN Input data Fast FHSS
- 7. Spread Spectrum - Direct Sequence DSSS ? A digital random signal is generated (1, 0) as PN (pseudonoise) or a chip code. ? This signal is XORed with the data signal - at a rate of 4 times, higher rate exist, to generate a wider spectrum, and modulated using BPSK. ? Any jamming signal will be filtered out by the receiver without affecting the data. ? (Data ? Random) ? Random = Data 01/01/04 7
- 8. Example 4 Ran Data Data?Ran DSSS 01/01/04 8
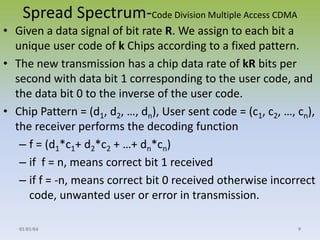
- 9. Spread Spectrum-Code Division Multiple Access CDMA ? Given a data signal of bit rate R. We assign to each bit a unique user code of k Chips according to a fixed pattern. ? The new transmission has a chip data rate of kR bits per second with data bit 1 corresponding to the user code, and the data bit 0 to the inverse of the user code. ? Chip Pattern = (d1, d2, ˇ, dn), User sent code = (c1, c2, ˇ, cn), the receiver performs the decoding function ¨C f = (d1*c1+ d2*c2 + ˇ+ dn*cn) ¨C if f = n, means correct bit 1 received ¨C if f = -n, means correct bit 0 received otherwise incorrect code, unwanted user or error in transmission. 01/01/04 9
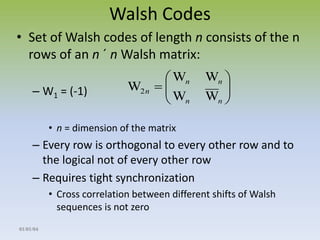
- 10. Walsh Codes ? Set of Walsh codes of length n consists of the n rows of an n ? n Walsh matrix: ¨C W1 = (-1) ? ? W W n W W ? n = dimension of the matrix ? n n ¨C Every row is orthogonal to every other row and to the logical not of every other row ¨C Requires tight synchronization ? Cross correlation between different shifts of Walsh sequences is not zero 01/01/04 ? ? ? ?? ? n n W2
- 11. Example ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1 1 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1 1 ? ? ? ? ? 1 1 1 1 ? ? ? ? 1 1 1 1 ? ? ? ? 1 1 1 1 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1 ( 1) ? ? W 1 n 2 2 2 n W W ? ? ? ? 1 1 1 1 W W 1 1 1 1 W W 2 2 W W 2 2 2 4 01/01/04 11 n W W W W n
- 12. User A chip code (-1, -1, -1, -1) User B chip code (-1, +1, -1, +1) Case 1: A transmits bit 1 and B transmits bit 1, we have A + B = (-1, -1, -1, -1) + (-1, +1, -1, +1) = (-2, 0, -2, 0). The receiver filters A by multiplying, inner product operation, the received signals by the chip code of A. f = (-2, 0, -2, 0)*(-1, -1, -1, -1) = -2*-1 ¨C1*0 ¨C2*-1 +0*-1 = 2+2 = 4. Thus confirming that A is sending a bit 1. Case 2: A transmits bit 0 and B transmits bit 1, we have AˇŻ + B = (1, 1, 1, 1)+(-1, +1, -1, +1) = (0, 2, 0, 2, ) f = (0, 2, 0, 2, )*(-1, -1, -1, -1) = 0*-1 + 2*-1 + 0*-1 + 2*-1 = -2 ¨C2 = -4. Thus conforming that A transmits bit 0. 01/01/04 12
- 13. +2 01/01/04 13 A B CDMA 1 0 1 0 0 -2
- 14. OFDM ? Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing. ? Inter Symbol Interferences (ISI) occur if the symbol time is smaller than the channel delay spread, this is always the case for higher transmission rates. ? The idea is to divide the wideband incoming data stream into L narrow band streams (LTs >> ?) ? 1 symbol is send during a time Ts, or L symbols are sent during a time LTs produces the same rate of transmission. ? Implementation of OFDM uses Circular convolution and the DFT. ? IFFT/FFT algorithms with circular convolution create ISI-free channel. 01/01/04 14
- 15. + R/L bps R/L bps . . . Rbps R/L bps Cos(2?fc) Cos(2?fc + ?f) Cos(2?fc + (L-1)?f) S(t) . . . fc fc+ ?f fc+ (L-1)?f B B/L L RF Radios 01/01/04 15
- 16. Quiz 1. How does FSSS work? 2. What is the most popular technique used for 3rd generation mobile phones? 3. What is the technique used for 4th generation mobile phones? 01/01/04 16