Lecture 4 organizational_design_part-ii
- 2. DifferentiationDifferentiation ïAll organizations must split their workAll organizations must split their work into tasksinto tasks ïThe division of labor into tasks isThe division of labor into tasks is called differentiationcalled differentiation
- 3. Three Types of DifferentiationThree Types of Differentiation ï§ Horizontal differentiation:Horizontal differentiation: division ofdivision of work to be done into tasks and sub-work to be done into tasks and sub- tasks at the same organizational leveltasks at the same organizational level ï§ Vertical differentiation:Vertical differentiation: division of workdivision of work by level of authority, hierarchy, orby level of authority, hierarchy, or chain of commandchain of command ï§ Spatial differentiationSpatial differentiation involves theinvolves the geographical location of differentgeographical location of different organizational activitiesorganizational activities
- 4. Vertical DifferentiationVertical Differentiation ï§Span of control (division of authority)Span of control (division of authority) ï§ The number of subordinates that a singleThe number of subordinates that a single manager directly manages.manager directly manages. ï§Organizational hierarchy choicesOrganizational hierarchy choices ï§ Flat structuresFlat structures ï§ Few organizational levelsFew organizational levels ï§ Wide spans of controlWide spans of control ï§ Tall structuresTall structures ï§ Many organizational levelsMany organizational levels ï§ Narrow spans of controlNarrow spans of control
- 5. Differentiation (cont.)Differentiation (cont.) ï§In aIn a simplesimple organization, differentiation isorganization, differentiation is low because the division of labor is low.low because the division of labor is low. That is, individuals typically perform all theThat is, individuals typically perform all the organizational tasks.organizational tasks. ï§In aIn a complexcomplex organization, differentiation isorganization, differentiation is high because the division of labor is high.high because the division of labor is high. In other words, the total process is âdividedIn other words, the total process is âdivided upâ so that individuals perform separateupâ so that individuals perform separate tasks.tasks.
- 6. Differentiation (cont.)Differentiation (cont.) ï§ As the division of labor increases,As the division of labor increases, managers specialize in some roles andmanagers specialize in some roles and hire people to specialize in others.hire people to specialize in others. ï§ SpecializationSpecialization allows people to developallows people to develop their individual abilities and knowledgetheir individual abilities and knowledge within their specific role.within their specific role.
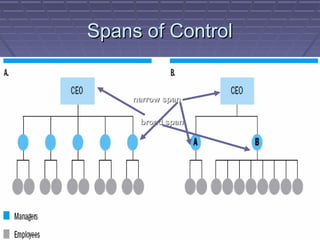
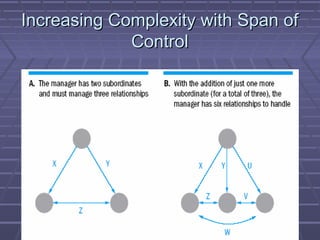
- 7. Span of ControlSpan of Control ï§ Span of controlSpan of control is the number of peopleis the number of people who report to one manager.who report to one manager. ï§ If there are very few people:If there are very few people: narrownarrow spanspan of control.of control. If there are many people:If there are many people: broadbroad span ofspan of control.control.
- 8. Spans of ControlSpans of Control narrow spannarrow span broad spanbroad span
- 9. Increasing Complexity with Span ofIncreasing Complexity with Span of ControlControl
- 10. Span of Control (cont.)Span of Control (cont.) ï§ A broad span might be appropriate where:A broad span might be appropriate where: ï§ Work is straightforwardWork is straightforward ï§ There are standard rules and procedures toThere are standard rules and procedures to guide workersguide workers ï§ Workers are highly capable and experiencedWorkers are highly capable and experienced ï§ Relatively autonomous work groups are usedRelatively autonomous work groups are used
- 11. Span of Control (cont.)Span of Control (cont.) ï§ With a narrow span of control:With a narrow span of control: ï§ More managers/workersMore managers/workers ï ï Cost ofCost of management is greater.management is greater. ï§ Few workers/managersFew workers/managers ï ï ManagersManagers have more time for managerial duties.have more time for managerial duties. ï§ Closer supervisionCloser supervision ï ï Workers getWorkers get more individual attention but have lessmore individual attention but have less autonomy.autonomy. ï§ Likely to be more levels of hierarchy.Likely to be more levels of hierarchy.
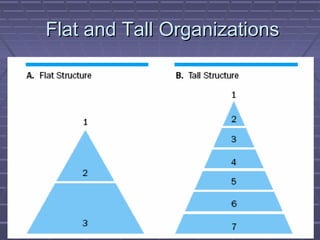
- 12. Flat and Tall OrganizationsFlat and Tall Organizations
- 13. Flat and Tall HierarchiesFlat and Tall Hierarchies ï§ In a flat organization:In a flat organization: ï§ Communication is generally faster and lessCommunication is generally faster and less distorted.distorted. ï§ Decisions can be made faster.Decisions can be made faster. ï§ Employees at lower levels are more in touchEmployees at lower levels are more in touch with top management.with top management. ï§ Support provided by more levels ofSupport provided by more levels of management obtained by having more self-management obtained by having more self- sufficient employees at lower levels.sufficient employees at lower levels. ï§ Fewer opportunities for promotion.Fewer opportunities for promotion.
- 14. Flat and Tall Hierarchies (cont.)Flat and Tall Hierarchies (cont.) ï§ In a tall organization:In a tall organization: ï§ Supervisory load is less for each manager.Supervisory load is less for each manager. Tighter supervision may be more productive.Tighter supervision may be more productive. ï§ More opportunities for promotion.More opportunities for promotion. ï§ Decisions take longer to take.Decisions take longer to take. ï§ Communication is slower and likely to be lessCommunication is slower and likely to be less accurate.accurate.
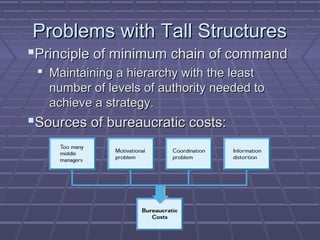
- 15. Problems with Tall StructuresProblems with Tall Structures ï§Principle of minimum chain of commandPrinciple of minimum chain of command ï§ Maintaining a hierarchy with the leastMaintaining a hierarchy with the least number of levels of authority needed tonumber of levels of authority needed to achieve a strategy.achieve a strategy. ï§Sources of bureaucratic costs:Sources of bureaucratic costs:
- 16. Centralization and DecentralizationCentralization and Decentralization ï§ When managers at the top of theWhen managers at the top of the hierarchy retain the authority to makehierarchy retain the authority to make important decisions, the organization isimportant decisions, the organization is viewed as highlyviewed as highly centralizedcentralized.. ï§ When managers at all levels are allowedWhen managers at all levels are allowed to make decisions regarding resourcesto make decisions regarding resources and new projects, the organization isand new projects, the organization is viewed as highlyviewed as highly decentralizeddecentralized..
- 17. Centralization orCentralization or DecentralizationDecentralization ï§Authority patterns in organizations:Authority patterns in organizations: ï§ CentralizedCentralized ï§ Decision making retained in theDecision making retained in the hands of upper-level managers.hands of upper-level managers. ï§ DecentralizedDecentralized ï§ Decisions delegated to lowerDecisions delegated to lower levels in the organization.levels in the organization.
- 18. Centralization (Structural)Centralization (Structural) Choice?Choice? ï§Advantages ofAdvantages of decentralizationdecentralization ï§ Reduced informationReduced information overload on upperoverload on upper managers.managers. ï§ Increased motivationIncreased motivation and accountabilityand accountability throughout organization.throughout organization. ï§ Fewer managers; lowerFewer managers; lower bureaucratic costs.bureaucratic costs. ï§ Faster decision makingFaster decision making and response.and response. ï§Advantages ofAdvantages of centralizationcentralization ï§ Easier coordination ofEasier coordination of organizational activities.organizational activities. ï§ Decisions fitted to broadDecisions fitted to broad organizational objectives.organizational objectives. ï§ Exercise of strongExercise of strong leadership in crisis.leadership in crisis.
- 19. Reasons to CentralizeReasons to Centralize ï§ Control:Control: ï§ Company has to meet legal requirementsCompany has to meet legal requirements ï§ Decisions made at the local level will affectDecisions made at the local level will affect the whole companythe whole company ï§ Cost: Economies of scale.Cost: Economies of scale.
- 20. Reasons to DecentralizeReasons to Decentralize ï§ Responsiveness to local conditionsResponsiveness to local conditions ï§ Independence at lower levels helpsIndependence at lower levels helps build a pool of candidates for higherbuild a pool of candidates for higher level positionslevel positions ï§ Sophisticated information systemsSophisticated information systems enable authority to be delegated toenable authority to be delegated to lower levels while still keeping toplower levels while still keeping top management well informed.management well informed.
- 21. Factors to ConsiderFactors to Consider ï§ Make sure decisions are made by peopleMake sure decisions are made by people who are as close as possible to the sourcewho are as close as possible to the source of information and the field of action.of information and the field of action. ï§ Duration: How far into the future does theDuration: How far into the future does the decision commit the organization? Howdecision commit the organization? How fast can it be reversed?fast can it be reversed?
- 22. Factors to Consider (cont.)Factors to Consider (cont.) ï§ What is the effect of the decision on otherWhat is the effect of the decision on other departments and the organization as adepartments and the organization as a whole?whole? ï§ What is the cost (including loss ofWhat is the cost (including loss of customer confidence or employee morale)customer confidence or employee morale) of implementing the decision?of implementing the decision?
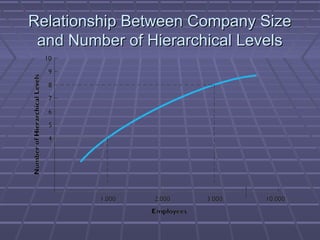
- 23. Relationship Between Company SizeRelationship Between Company Size and Number of Hierarchical Levelsand Number of Hierarchical Levels
- 24. Subunit OrientationsSubunit Orientations ï§ While horizontal differentiation enablesWhile horizontal differentiation enables specialization and increase productivity,specialization and increase productivity, it also leads to subunit orientation.it also leads to subunit orientation. ï§ Subunit orientationSubunit orientation refers to therefers to the tendency to view oneâs role in thetendency to view oneâs role in the organization strictly from theorganization strictly from the orientations of oneâs subunit.orientations of oneâs subunit.
- 25. IntegrationIntegration Integration, or coordination, isIntegration, or coordination, is the prime responsibility ofthe prime responsibility of managers. The functions ofmanagers. The functions of managementâdecision-makingmanagementâdecision-making and influenceâimplyand influenceâimply coordinating and integrating.coordinating and integrating.
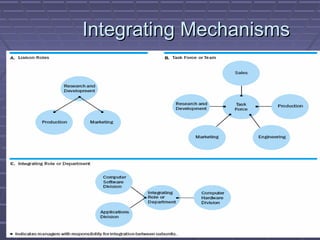
- 26. Integration MechanismsIntegration Mechanisms ï§ Hierarchy of AuthorityHierarchy of Authorityââwho reports toââwho reports to who.âwho.â ï§ Direct ContactDirect Contactâmanagers meet face toâmanagers meet face to face to coordinate activities.face to coordinate activities. ï§ Liaison RoleLiaison RoleâA specific manager is givenâA specific manager is given responsibility for coordinating withresponsibility for coordinating with managers from other subunits on behalf ofmanagers from other subunits on behalf of their subunit.their subunit.
- 27. Integration Mechanisms (cont.)Integration Mechanisms (cont.) ï§ Task ForceTask ForceâManagers meet in temporaryâManagers meet in temporary committees to coordinate cross-functionalcommittees to coordinate cross-functional activities.activities. ï§ TeamTeamâManagers meet regularly inâManagers meet regularly in permanent committees to coordinatepermanent committees to coordinate activities.activities.
- 28. Integration Mechanisms (cont.)Integration Mechanisms (cont.) ï§ Integrating RoleIntegrating RoleâA new role isâA new role is established to coordinate the activities ofestablished to coordinate the activities of two or more functions or divisions.two or more functions or divisions. ï§ Integrating DepartmentIntegrating DepartmentâA newâA new department is created to coordinate thedepartment is created to coordinate the activities of functions or divisions.activities of functions or divisions.
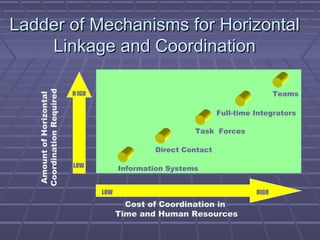
- 30. Ladder of Mechanisms for HorizontalLadder of Mechanisms for Horizontal Linkage and CoordinationLinkage and Coordination HIGHLOW LOW Information Systems Direct Contact Task Forces Full-time Integrators Teams AmountofHorizontal CoordinationRequired Cost of Coordination in Time and Human Resources H IGH
- 31. Standardization and Mutual AdjustmentStandardization and Mutual Adjustment ï§ StandardizationStandardization is conformity to specificis conformity to specific models or examples (rules and norms).models or examples (rules and norms). ï§ Many rules are written in aMany rules are written in a formalizedformalized organization.organization. ï§ Mutual adjustmentMutual adjustment is the process ofis the process of allowing people to use their judgementallowing people to use their judgement rather than standardized rules to addressrather than standardized rules to address a problem.a problem.