Lecture 5--Research Questions II
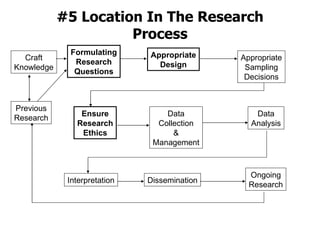
- 1. #5 Location In The Research Process Formulating Research Questions Previous Research Craft Knowledge Appropriate Design Appropriate Sampling Decisions Ensure Research Ethics Data Collection & Management Data Analysis Interpretation Dissemination Ongoing Research
- 2. Concept to variable In order for a concept (a mental image that symbolizes an idea) to be a variable it must meet three conditions. It is comprised of more than one value (attribute), so it is capable of varying It is chosen for investigation in a research study It must be translated into observable terms
- 3. Operational Definitions Describe your variables Must be sufficiently clear to allow other researchers to replicate your study Clearly describe the procedures that you used **Clear operational definitions are essential to building a useful body of knowledge
- 4. Independent Variables Believed to influence the outcome of a study Controlled by the researcher through random assignment Compared by the researcher through contrasted existing groups An important predictor of an outcome in a correlational study
- 5. Dependent Variables Influenced by changes in the independent variable Outcome variables Changes in Affect Changes in Behavior Changes in Cognition Changes in the dependent variable depend on changes in the independent variable
- 6. Hypothesis and Variable Relationships A hypothesis predicts the relationship between variables . Positive Relationship- both independent and dependent variables move in the same direction as the independent variable is changed. Negative Relationship (inverse)- The independent and dependent variables move in opposite directions. As the independent variable increases, the dependent variable decreases (and vice-versa). Curvilinear Relationship-The nature of the relationship changes at certain levels of the variables (goes from positive to negative or negative to positive.)
- 7. Spurious Relationships A relationship between variables that disappears when a third variable is controlled for, is said to be a Spurious Relationship. We must be careful in our reporting of relationships we find in research. eg. Ice Cream Sales Incidents of Sexual Assault Relationship goes away when weather is controlled for.
- 8. Question 1 The local substance abuse agency wants to know if alcoholic clients are more likely to be clinically depressed than people in the general population. What are the independent variables that might be used in this study? What are the dependent variables that might be used in this study?
- 9. Ethical Questions Are the benefits from the research to participants and society greater than the risks that the participants are exposed to? Are the intended participants members of a vulnerable population? What will I do to ensure that the participants rights are protected?