Lecture on Drought by Harish Singh.pptx
- 1. Drought ’āśIntroduction ’āś Types / Classification & ’āśEffect on water Deficit on Physio ŌĆō Morphological Characteristics of the plant.
- 2. Introduction Drought :- The word ŌĆśdroughtŌĆÖ generally denotes scarcity of water in a region. ’āśAccording to the American Heritage Dictionary (1976) defined drought as a long period with no rain especially during planting season. ’āśThere is no universally accepted definition of drought. ’āśThe two word ŌĆśAridityŌĆÖ & ŌĆśDroughtŌĆÖ both denote the condition of dryness or low moisture present in soil due to insufficient of water/ rainfall. ’āśAccording to Irrigation commission of India ŌĆ£Drought is a situation occurring in any area where the annual rainfall is less than 75% of normal rainfallŌĆØ
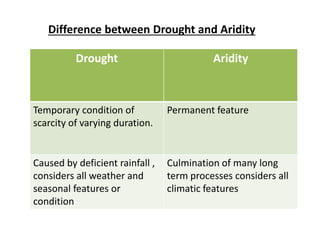
- 3. Difference between Drought and Aridity Drought Aridity Temporary condition of scarcity of varying duration. Permanent feature Caused by deficient rainfall , considers all weather and seasonal features or condition Culmination of many long term processes considers all climatic features
- 4. Classification of Drought 1. Based on duration a). Permanent drought :- This is the characteristic of the desert climate. b). Seasonal drought :- Climate with well defined rainy and dry season. c). Contingent drought :- Abnormal failure of rainfall especially in most part of humid and sub humid climates. d). Invisible drought :- when rainfall is inadequate to meet the ET losses, usually in humid region.
- 5. 2. Based on their relevance to the user (National Commission on Agriculture,1976) a). Meteorological drought :- Condition where the annual precipitation is less than the normal over an area for prolonged period (month, season or year) b). Agricultural drought :- Condition where the requirement of moisture to crop is not sufficient due to high ET. c). Hydrological drought :- meteorological drought, when prolonged results in hydrological drought with depletion of surface water & consequent drying of reservoirs, tanks etc. d). Socio economic drought e). Atmospheric drought.