Lecture8 carbohydrates
- 1. Carbohydrates Classification Monosaccharides Chiral Carbon Atoms Structures of Important Monosaccharides Cyclic Structures 1
- 2. Carbohydrates ? Major source of energy from our diet ? Composed of the elements C, H and O ? Produced by photosynthesis in plants 2
- 3. Types of Carbohydrates ? Monosacchrides ? Disaccharides Contain 2 monosacchride units ? Polysacchrides Contain many monosacchride units 3
- 4. Monosacchrides ? Three Carbons = Triose ? Four Carbons = Tetrose ? Five Carbons = Pentose ? Six Carbons = Hexose 4
- 5. Monosacchrides ? Aldoses are monosacchrides with an aldehyde group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. ? Ketoses are monosacchrides with a ketone group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. 5
- 6. Learning Check C1 Identify each as tetrose, pentose or hexose, and as aldose or ketose H C O CH2OH H C OH C O H C OH HO C H H C OH H C OH H C OH CH2OH CH2OH A B 6
- 7. Solution C1 H C O CH2OH H C OH C O H C OH H C OH HO C H H C OH H C OH CH2OH CH2OH A B aldose, hexose ketose, pentose 7
- 8. Chiral Objects ? Chiral compounds have the same number of atoms arranged differently in space. ? A chiral carbon atom has four different groups attached 8
- 9. Mirror Images ? The three-dimensional structure of a chiral compound has a mirror image. ? Your hands are chiral. Try to superimpose your thumbs, palms, back of hands, and little fingers. Is it possible? Why or why not? 9
- 10. Tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different groups 10
- 11. ARE THERE CHIRAL C-ATOMS IN THESE MOLECULES? CH3CHClCH2CH3 A CH2ClCH3 B 11
- 12. Learning Check C2 Determine if there is a chiral carbon in each compound. Cl Cl H C CH 3 H C CH3 CH 2 CH 3 H A B 12
- 13. Solution C2 Cl Cl H C CH3 H C CH3 CH2CH3 H A Yes, 4 different B No, the groups are attached 2 H atoms to the second C atom are identical 13
- 14. 14
- 15. Glyceraldehyde 15
- 16. D and L Notation ? D,L tells which of the two chiral isomers we are referring to. ? If the ®COH group on the next to the bottom carbon atom points to the right , the isomer is a D-isomer; if it points left, the isomer is L. ? The D form is usually the isomer found in nature. 16
- 17. D notation O H C H C OH H C OH CH2OH Right = D 17
- 18. Glucose H C O H C OH HO C H H C OH H C OH CH2OH D-Glucose 18
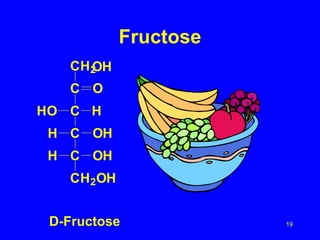
- 19. Fructose CH2 OH C O HO C H H C OH H C OH CH2OH D-Fructose 19
- 20. Galactose H O C H C OH HO C H HO C H H C OH CH2OH D-galactose 20
- 21. Cyclic Structures ? Monosaccharides with 5-6 carbon atoms form cyclic structures ? The hydroxyl group on C-5 reacts with the aldehyde group or ketone group O o 21
- 22. Haworth Structure for D-Isomers The cyclic structure of a D-isomer has the final CH2OH group located above the ring. CH2OH o 22
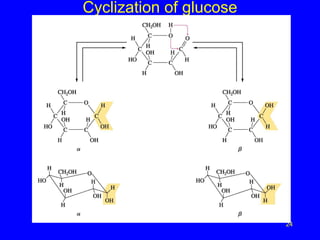
- 23. Haworth Structure for D- Glucose ? Write ®COH groups on the right (C2, C4) up ? Write ®COH groups on the left (C3) down ? The new ®COH on C1 has two possibilites: down for ¶¡ anomer, up for ¶¬ anomer 23
- 24. Cyclization of glucose 24
- 25. Haworth Structure for D- Glucose CH2OH CH2OH o o OH ¶¬ OH OH OH OH OH ¶¡ OH OH ¶¡-D-Glucose ¶¬-D-Glucose 25
- 26. d-fructose 26
- 27. Mutarotation ? Mutarotation: A small amount of open chain is in equilibrium with the cyclic forms. ? The most stable form of glucose is ¶¬-D- glucose . ¶¡-D-glucose D-glucose (open) ¶¬-D-glucose (36%) (trace) (64%) 27
- 28. Learning Check C3 Write the cyclic form of ¶¡-D-galactose H O C H C OH HO C H HO C H H C OH CH2OH 28
- 29. Solution C3 CH2OH OH o OH OH OH ¶¡-D-galactose 29