Lecture_Chapter_7.ppt
- 1. Computer Maintenance and Technical Support Chapter Seven Bus and Cards 1
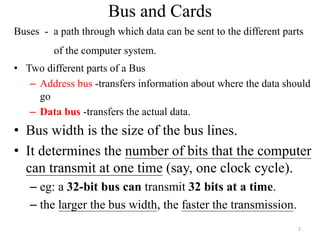
- 2. Bus and Cards Buses - a path through which data can be sent to the different parts of the computer system. âĒ Two different parts of a Bus â Address bus -transfers information about where the data should go â Data bus -transfers the actual data. âĒ Bus width is the size of the bus lines. âĒ It determines the number of bits that the computer can transmit at one time (say, one clock cycle). â eg: a 32-bit bus can transmit 32 bits at a time. â the larger the bus width, the faster the transmission. 2
- 3. Examples âĒ Expansion buses or âslotsâ âĒ Disk interfaces/Buses âĒ External buses âĒ Communications buses 3
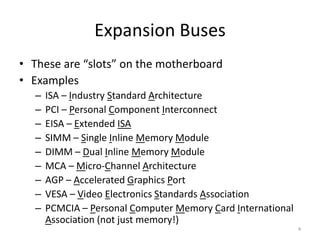
- 4. Expansion Buses âĒ These are âslotsâ on the motherboard âĒ Examples â ISA â Industry Standard Architecture â PCI â Personal Component Interconnect â EISA â Extended ISA â SIMM â Single Inline Memory Module â DIMM â Dual Inline Memory Module â MCA â Micro-Channel Architecture â AGP â Accelerated Graphics Port â VESA â Video Electronics Standards Association â PCMCIA â Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (not just memory!) 4
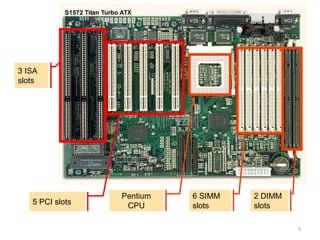
- 5. 3 ISA slots 5 PCI slots Pentium CPU 6 SIMM slots 2 DIMM slots 5
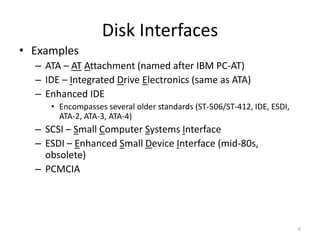
- 6. Disk Interfaces âĒ Examples â ATA â AT Attachment (named after IBM PC-AT) â IDE â Integrated Drive Electronics (same as ATA) â Enhanced IDE âĒ Encompasses several older standards (ST-506/ST-412, IDE, ESDI, ATA-2, ATA-3, ATA-4) â SCSI â Small Computer Systems Interface â ESDI â Enhanced Small Device Interface (mid-80s, obsolete) â PCMCIA 6
- 7. External Buses âĒ Examples â Parallel â sometimes called LPT (âline printerâ) â Serial â typically RS232C (sometimes RS422) â PS/2 â for keyboards and mice â USB â Universal Serial Bus â IrDA â Infrared Device Attachment â FireWire â new, very high speed, developed by IEEE 7
- 8. Communications Buses âĒ For connecting systems to systems âĒ Parallel/LPT â special purpose, e.g., using special software (Laplink) to transfer data between systems âĒ Serial/RS232C â To connect a system to a voice-grade modem âĒ Ethernet â To connect a system to a high-speed network 8
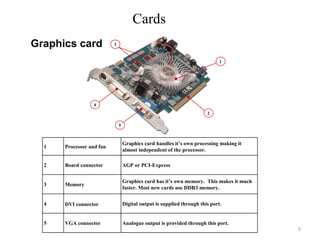
- 9. Cards 3 1 2 4 5 1 Processor and fan Graphics card handles itâs own processing making it almost independent of the processor. 2 Board connector AGP or PCI-Express 3 Memory Graphics card has itâs own memory. This makes it much faster. Most new cards use DDR3 memory. 4 DVI connector Digital output is supplied through this port. 5 VGA connector Analogue output is provided through this port. Graphics card 9
- 10. Cards Graphic card - screen images are made up of dots called pixels (picture elements). The graphics card must process each of these pixels to create the image. The resolution of a screen is the number of pixels being displayed. Typical resolutions include: âĒ 800 x 600 - 480,000 pixels âĒ 1024 x 768 - 786,432 pixels âĒ 1280 x 1024: - 1,310,720 pixels âĒ 1600 x 1200: - 1,920,000 pixels 10
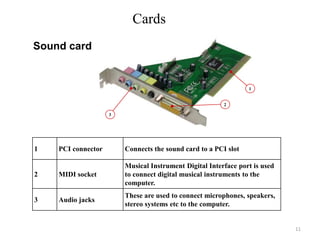
- 11. Cards 1 2 3 Sound card 1 PCI connector Connects the sound card to a PCI slot 2 MIDI socket Musical Instrument Digital Interface port is used to connect digital musical instruments to the computer. 3 Audio jacks These are used to connect microphones, speakers, stereo systems etc to the computer. 11
- 12. Cards âĒ allows computers join a network. Can be wired or wireless. The standard used is called Ethernet - covers wired and wireless networks. The wired standards include: âĒ Fast Ethernet - transmission speed of 100Mbps. âĒ Gigabyte Ethernet - transmission speed of 1000Mbps. PCI PC card USB Network card 12
- 13. Cards The wireless standards include: âĒ The B standard - introduced in 1999, it has a transmission rate of 11Mbps and a range of 30 Metres. âĒ The G standard - introduced in 2003, it has a transmission rate of 54Mbps and a range of 30 Metres. âĒ The N standard - introduced in 2006, it has a transmission speed of 540Mbps and a range of 50 metres. PCI PC Card USB 13
- 14. Cards Replaces floppy drives in new computers. They can read media cards from most digital cameras: âĒ Microdrive: âĒ Smartmedia: âĒ SD memory card: âĒ Memory stick/Duo/Pro: âĒ xD picture card: Card readers Card reader drive 14
- 15. Quiz Name ______________ID ______ 1. Write one example of Expansion Buses/slot? Ans =SIMM,DIMM,PCMCIA,ISA,PCI,EISAâĶ.. 2. Write one example Disk interfaces ? Ans =ATA,IDE,SCSI,ESDI,PCMCIAâĶ.. 3. Write one example External buses ? Ans=PARALLEL,SERIAL PS/2,VGA,USBâĶ. 4. Write one example Communications buses? Ans =âĶ.. ., using special software (Laplink) 5. Write two examples of Cards? Ans=GRAPHIC CARD AND SOUND CARD 15