Lecture_Chapter_8.ppt
- 1. Computer Maintenance and Technical Support Chapter eight I/O Connectors, BIOS 1
- 2. Chapter eight I/O Connectors âĒI/O Connectors The Serial Port The Parallel Port I/O connectors âĒThe Monitor Introduction to Monitor Types of Displays Health and Safety Concerns Monitor Connections Troubleshooting the Video System 2 âĒ BIOS Basic Input/ Output System Error messages and solutions Advanced BIOS Features âĒ Printer Printer Types and Printer Technology Printer Field Replaceable Units Printer Maintenance Techniques
- 3. Serial Connectors âĒ Can use a 9 or 25 pin male sub-D connector âĒ Slowest ports âĒ Used for: â Mice â Keyboards â Modems
- 4. Serial Ports âĒ Also called COM1, COM2, COM3, and COM4 âĒ Can be referred to as a RS-232 port âĒ This is a standard that defines serial communication
- 5. Parallel Ports âĒ Uses a 25 pin female sub-D connector âĒ Data flows over 8 lines âĒ Used for: â Printers â Scanners â Portable drives
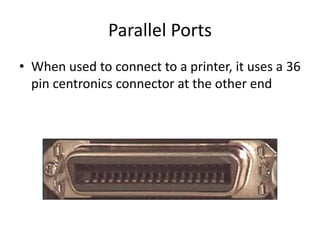
- 6. Parallel Ports âĒ When used to connect to a printer, it uses a 36 pin centronics connector at the other end
- 7. Parallel Ports âĒ Also called LPT1, LPT2, LPT3 âĒ Bi-directional communication â Called Enhanced Printer Port (EPP) âĒ Transmission mode can be set in the BIOS âĒ Maximum cable length is 15 feet
- 8. PS/2 and Keyboard Connectors âĒ PS/2 connectors are used for both mice and keyboard âĒ Also called 6-pin mini DIN âĒ Green for mouse âĒ Purple for keyboard âĒ Not interchangeable âĒ Standard for ATX boards
- 9. DIN-5 Keyboard Connector âĒ Older motherboards use a DIN-5 connector for the keyboard and a 9 pin serial connection for the mouse
- 10. Universal Serial Bus (USB) âĒ Used to connect almost all peripherals âĒ Can connect up to 127 devices âĒ Designed to be hot-swappable âĒ Designed to connect in a daisy chain
- 11. USB Standards âĒ USB 1.1 â 12 Mbps âĒ USB 2.0 â 480 Mbps âĒ USB 3.0 - 5gbps over ten times as fast as the 2.0 âĒ A-Style connector is used on the computer or hub âĒ B-Style connector is used on the device âĒ Must have Windows 98, 2000 or XP and âĒ Not supported in Windows 95 or NT 4.0
- 12. USB Cable Lengths âĒ Hi Powered devices â 5 meters max â Also called hi-speed âĒ Low Powered devices â 3 meters max â Also called low-speed âĒ Can be extended if you use a self-powered hub
- 13. A computer monitor displays images generated by the graphics card. Monitors are almost exclusively 1. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). 2. CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitors Monitors 19 inch Widescreen LCD
- 14. 14
- 15. 15
- 16. Common Monitor Problems 16 âĒ Inverter/power board failure due to bad capacitors. (LCD) âĒ Backlight failure. (LCD) âĒ Not running at native resolution (common for LCDs, results in worse image quality) âĒ Loose solder joint (any) âĒ Burn-out IC, other circuit boards âĒ Power supply burnt-out
- 17. Common Monitor Problems Solution 17 âĒ Backlight failure can solve Replacing the CCFT (Cold- Cathode Fluorescent Tubes. âĒ Find and replacing bad capacitors. âĒ Not running at native resolution problems can fix reinstalling Drivers software. âĒ Soldering the board using hot gun. âĒ Check the brightness control button working properly âĒ Replacing burnt IC with the equivalent code. âĒ Check and maintain the power supply
- 18. BIOS âĒ BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System ,which consists of low- level software that controls the system hardware and act as an interface between the operating system and the hardware. âĒ It is the lowest-level program that runs on your computer. âĒ The BIOS is what runs when you turn on your computer, and what loads your operating. âĒ The BIOS also allows you to set or change many different parameters that control how your computer will function. For example, you tell the BIOS what sort of hard drives you have so it knows how to access them. âĒ Most people know the term BIOS by another nameâdevice drivers, or just drivers âĒ In other words, the BIOS is drivers, meaning all of them. The BIOS is essentially the link between hardware and software in a system. âĒ The BIOS itself is software running in memory that consists of all the various drivers that interface the hardware to the operating system. 18
- 19. BIOS in a PC comes from three possible sources âĒ Mother board âĒ Adapter card(such as that found on video card) âĒ Loaded into RAM from Disk ROM chip also contained a power-on self test (POST) program and a bootstrap loader. âĒ The bootstrap program was designed to initiate the loading of an OS by checking for and loading the boot sector from a floppy disk or, if one was not present, a hard disk âĒ After the OS was loaded, it could call on the low-level routines (device drivers) in the BIOS to interact with the system hardware. 19
- 20. Tasks that the BIOS chip performs include: âĒ Configuration and control of standard devices: âĒ The power-on self test (POST) âĒ The location of an operating system, to which it turns over control of the system by using the Bootstrap loader 20
- 21. The BIOS and Standard Devices: The BIOS is a complex piece of firmware ("software on a chip") that provides support for the following devices and features of your system: âĒ Selection and configuration of storage devices, such as hard drives, floppy drives, and CD-ROM drives âĒ Configuration of main and cache memory: âĒ Configuration of built-in ports, such as IDE hard disk, floppy disk, serial, parallel, PS/2 mouse, and USB âĒ Selection and configuration of special motherboard features, such as memory error correction, antivirus protection, and fast memory access 21
- 22. âĒ Support for different CPU types, speeds, and special features âĒ Support for advanced operating systems, including networks, Windows 9x, and Windows 2000 (Plug and Play) âĒ Power management âĒ Storing System Settings: ïķTo enable the BIOS to perform these tasks, two other components on the mother- board work with the BIOS, these are : 22
- 23. âĒ The CMOS chip, also known as the RTC/NVRAM (Real-Time-Clock/Non-Volatile RAM), âĒ The battery CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide semiconductor) chip stores the settings that you make with the BIOS configuration program. It stores information such as system time,system settings for your PC. It is modified and changed by entering the the CMOS setup. ïķ The CMOS stores the settings that you make with the BIOS configuration program and contains the system's Real-Time- Clock circuit. ïķ Power from a battery attached to the motherboard is used by the CMOS to keep its settings 23
- 24. Fig below shows typical socketed BIOS and battery 24
- 25. POST âĒ The POST (power-on self test) portion of the BIOS allows the BIOS to find and report errors in the computer's hardware. âĒ For the POST to work correctly, the system must be configured correctly 25
- 26. The POST checks the following parts of the computer: âĒ The CPU and the POST ROM portion of the BIOS âĒ The system timer âĒ Video display card âĒ Memory âĒ The keyboard âĒ The disk drives ïķ The system will stop the boot process if it encounters a serious or fatal error 26
- 27. During the POST process, the BIOS uses any one of several methods to report problems: âĒBeep codes âĒOnscreen error messages âĒPOST error codes Beep Codes: âĒare used by most BIOS versions to indicate either a fatal error or a very serious error. âĒare used by most BIOS versions to indicate either a fatal error or a very serious error. 27
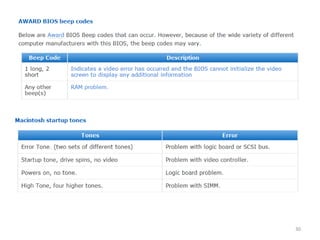
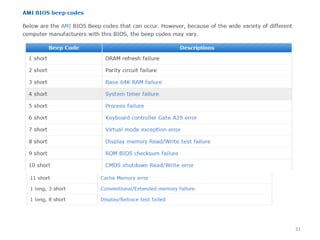
- 28. âĒ A fatal error would include a problem with the CPU, the POST ROM, the system timer, or memory âĒ Beep codes vary by the BIOS maker. âĒ Some companies, such as IBM, Acer, and Compaq, create their own BIOS chips and firmware âĒ most other major brands of computers and virtually all "clones" use BIOS made by one of the "Big Three" BIOS vendors: ïž American Megatrends (AMI), ïž Phoenix Technologies ïž Award Software (now owned by Phoenix Technologies). 28
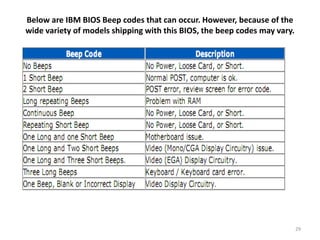
- 29. Below are IBM BIOS Beep codes that can occur. However, because of the wide variety of models shipping with this BIOS, the beep codes may vary. 29
- 30. 30
- 31. 31
- 32. BIOS boot Error Messages: âĒ During the boot process, the bootstrap loader routine in the motherboard ROM BIOS reads the first physical sector of each of the bootable drives or devices. Example : Award BIOS Messages With no valid MBR or bootable device found, systems with an Award BIOS display the following Message: DISK BOOT FAILURE, INSERT SYSTEM DISK AND PRESS ENTER 32
- 33. Phoenix BIOS Messages âĒ With no valid MBR or bootable device found, systems with a Phoenix BIOS display either the message No boot device available - strike F1 to retry boot, F2 for setup utility or this one: No boot sector on fixed disk - strike F1 to retry boot, F2 for setup utility 33
- 34. AMI BIOS Messages âĒ With no valid MBR or bootable device found, systems with an AMI BIOS display the following message: NO ROM BASIC - SYSTEM HALTED 34
- 35. POST error codes âĒ POST checkpoint codes are hexadecimal numeric codes written by POST routines to I/O port address 80h as each major step is begun. âĒ These messages can indicate problem with memory ,keyboard ,hard disk drives, and other components. Example: Error number explanation 1** system board problem 161 CMOS battery failure 2** memory related problem. 3** keyboard problem
- 36. Post cards âĒ Inoperative device can sometimes disrupt the POST ,forcing the machine to an endless loop. âĒ This cause the PC to dead- no beeps and nothing on the screen. âĒ In this case ,you need a device, called Post card. âĒ These cards are available in versions that plug into either ISA or PCI expansion slots. âĒ The simplest ones have a two-digit LED area that displays the hex codes, whereas more complicated (and expensive) models also have additional built-in tests. âĒ The same hex code has different meanings to different BIOSes. 36
- 37. Warm and Cold Booting: âĒ A cold boot or hard boot refers to starting the computer with the power or reset switch, which runs the entire POST and bootstrap process. âĒ A warm boot or soft boot skips the POST and refers to restarting the computer with the MS- DOS Ctrl+Alt+Del key sequence or the Windows 9x/2000 Start, Shutdown, Restart menu 37
- 38. Starting the Setup Program: âĒ ROM-based setup programs are normally started by pressing one or more keys in combination within the first few seconds after turning on the computer. âĒ Although these keystrokes vary from system to system, the most popular keys on current systems include: ïthe escape (Esc) key ï the Delete key ïthe F1 key ïvarious combinations of Ctrl+Alt+ another specified key
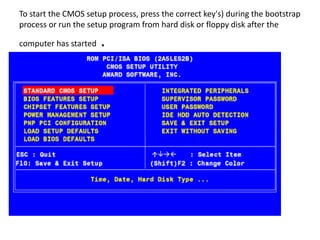
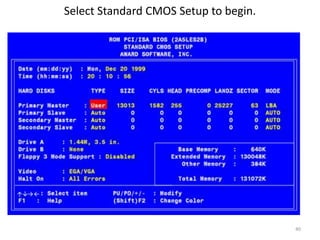
- 39. To start the CMOS setup process, press the correct key's) during the bootstrap process or run the setup program from hard disk or floppy disk after the computer has started .
- 40. Select Standard CMOS Setup to begin. 40
- 41. To clear an unknown BIOS password âĒ On the motherboard locate the BIOS clear /password jumper or DIP switch and change its position . Once cleared ,turn the computer off and return the jumper or DIP switch to its original position. âĒ Remove the CMOS Battery for at least 10 minutes. âĒ If none of these works ,contact the computer /motherboard manufacturer for steps on clearing the computer password. âĒ Precaution: When inside the computer please be sure of the potential of ESD. 41
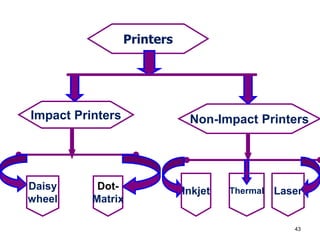
- 42. 42 Printer âĒ An external hardware device responsible for taking computer data and generating a hard copy of that data. Printers are one of the most commonly used peripherals and they print text and still images on the paper. Thermal Inkjet Dot-Matrix Laser
- 43. 43 Printers Impact Printers Non-Impact Printers Daisy wheel Dot- Matrix Inkjet Thermal Laser
- 44. Common printer problems 44 âĒ paper jams âĒ Windows is sending print jobs to the wrong printer. âĒ your printer may run out of memory. âĒ Printer is too slow âĒ Toner does not stick to the page or smears âĒ Printer is displaying a 50.4 error message
- 45. Printer Problems Solution 45 âĒ Periodically wipe the feeder tires clean and from time to time, vacuum away dust build up inside the printer âĒ Load quality paper in the try. âĒ Select the working printer as a default. âĒ Expand/insert additional printer memory size. âĒ Reinstalling the driver.
- 46. 46 a. The fuser assembly may be defective or it is at the end of life. The solution is to replace the fuser . The fuser is considered a consumable and can be replaced b. You may have a defective toner cartridge. Simply replace the cartridge and see if this fixes the problem, or c. Toner may have spilled into the printer. Clean out the printer. Toner does not stick to the page or smears a. Periodically clean the printer b. Replacing rollers/gears c. Use the correct paper type paper jams
- 47. 47 a. If the printer is plugged into a UPS, or a power strip, unplug it and plug the printer directly into the wall. b. A laser printer should never be plugged into a UPS because of the power surges required by the printer. These surges are required by the printer to keep the fuser assembly warm. Printer is displaying a 50.4 error message a. The printer is low on toner, so Remove the toner cartridge, and shake. b. The print density is set too low, or change the setting c. The printer may have the Economode turned on. So you need Turn Economode off Part of or all of the printed page is faded
- 48. 48 As new operating systems are released/installed , new drivers need to be loaded for your exiting printers in the computer . Canât find a driver for a particular operating system a. correct it with the application by clicking on Printer Properties and find the tray selection source. b. check the printer. Make sure that the paper size on the control panel matches what is actually in the paper tray. Printer is not printing from the expected tray
- 49. End of Class 49 Thank You