Lesson 1 Introduction to networking.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes4 views
Basic concept and terminologies on networking
1 of 16
Download to read offline












Recommended
Internet vs intranet vs extranet



Internet vs intranet vs extranetMohsinHusenManasiya
?
The document defines and compares Internet, intranet, and extranet. The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers accessible to anyone. An intranet is a private internal network, similar to the Internet, contained within an organization. An extranet extends an organization's intranet to allow access to selected external partners and customers while maintaining security. Types of extranets include public, private, and virtual private networks (VPNs) which use encryption tunnels for secure transmission over public networks.Internet vs intranet vs extranet



Internet vs intranet vs extranetMohsinHusenManasiya
?
The document defines and compares Internet, intranet, and extranet. The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers accessible to anyone. An intranet is a private internal network, similar to the Internet, contained within an organization. An extranet extends an organization's intranet to allow access to selected external partners and customers while maintaining security. Types of extranets include public, private, and virtual private networks (VPNs) which use encryption tunnels for secure transmission over public networks.Networks: The Big Picture



Networks: The Big PictureInternational School of Curitiba
?
Networks: The Big Picture (an overview)
ITGS 3.3 Networks
Resources: Stuart Gray www.itgstextbook.com Computer Networks.pptx



Computer Networks.pptxrocky781582
?
computer networks
Applications Of Computer Network
Business Application
Types of Computer Network
PANInternet, intranet and extranet



Internet, intranet and extranetJehra Mae Sevillano ?
?
The document discusses Internet, Intranet, and Extranet. It defines Internet as a global network of computers that exchange information publicly. Intranet is a private network within an organization that uses the same protocols as the Internet but is only accessible to authorized users like employees. Extranet extends an organization's intranet to allow access to selected external users like suppliers or customers. Key benefits of intranets include improved productivity, communication and cost effectiveness for organizations.ICT 101 LECTURE 2 - BASICS OF COMPUTER NETWORKS.pptx



ICT 101 LECTURE 2 - BASICS OF COMPUTER NETWORKS.pptxmbombongafu
?
This document provides an introduction to computer networks. It defines a computer network and lists the basic requirements. It describes types of networks including LAN, MAN, WAN, PAN, intranets and VPNs. It discusses network devices like hubs, bridges, switches and routers. It also covers topics like addressing, messaging types, and network categories.Chapter 6



Chapter 6Jennifer Polack
?
This document discusses computer networks and networking concepts. It defines types of networks like local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and enterprise networks. It also describes network fundamentals such as analog and digital signals, communications media like twisted-pair wire, coaxial cable and fiber optics. Network protocols like Ethernet and TCP/IP are explained. Applications of networks include discovery, communication, collaboration, e-learning/distance learning, and telecommuting. The Internet and how it connects to the World Wide Web is defined.Communications



CommunicationsRana Usman Sattar
?
Computer communications involves the transfer of data between devices using a communications channel. Key components of communication include a sender, receiver, encoding/decoding devices, and transmission medium. Networks connect multiple devices to facilitate communication and sharing of resources. Common network types include local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). Standards define how devices communicate over networks and include protocols, topologies, and technologies like Ethernet, TCP/IP, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.The Basics and Understanding of Computer Networking.pptx



The Basics and Understanding of Computer Networking.pptxBINJAD1
?
Computer networking refers to interconnected computing devices that can exchange data and share resources with each other.Mis jaiswal-chapter-03



Mis jaiswal-chapter-03Amit Fogla
?
This chapter discusses telecommunications and computer networks for business. It covers data transmission units and technologies, types of networks including LANs, WANs and intranets. It describes network devices, switching methods, the OSI model layers and TCP/IP. Intranets and extranets are defined, and applications for internal networks and sharing information with business partners are provided. Internet addressing systems using IP classes are also summarized.Computer networks



Computer networksKeerty Smile
?
Computer networks allow interconnected devices to communicate. They have advantages like resource sharing and cost savings but also disadvantages such as reduced productivity if poorly managed or servers fail. Early networks included ARPANET in 1969 and NSFNET in the 1980s, leading to the modern Internet. Networks transmit data via circuits, packets, or messages using techniques like circuit switching, packet switching, and message switching. Components include nodes, servers, clients, hardware, software and communication channels. Networks can be LANs, MANs, WANs or PANs depending on their area of coverage. Wired networks use media like twisted pair, coaxial or fiber optic cables while wireless uses radio waves.UNIT I DIS.pptx



UNIT I DIS.pptxPremkumar R
?
This document discusses distributed systems and key concepts related to communication in distributed environments. It begins with an introduction to distributed systems and examples. It then covers challenges like APIs for internet protocols, external data representation and marshaling, multicast communication, remote procedure calls, and group communication. Key aspects of distributed systems like features, quality of service parameters, resource sharing, and examples are also summarized.Network models



Network modelsSri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering College
?
This document provides an overview of computer communication networks and their basic components and design. It discusses:
1) The key components of a data communication system including the message, sender, receiver, transmission medium, and protocols.
2) Basic network concepts such as the definition of a network, important network characteristics like performance and reliability, and common network topologies.
3) Categories of networks including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs).
4) Related concepts such as the internet, intranets, and extranets.
5) Protocols and standards that govern data communication and their importance.introduction of network



introduction of networkBishalWosti1
?
This document provides an overview of computer networks and networking concepts. It discusses centralized, distributed, and collaborative network models. It describes common network topologies like star, bus, ring, mesh, and fully connected. The document also covers the OSI reference model and TCP/IP model, detailing the layers and functions of each. Computer network protocols, standards organizations, and interfaces are defined. Uses of networks for organizations and individuals are outlined.Networks-Internet-and-Internet-Protocols.pptx



Networks-Internet-and-Internet-Protocols.pptxHaythanSunday
?
This document provides an overview of computer networks and the internet. It defines key network terms like network, internet protocols, and network architecture models like client-server and peer-to-peer. It also discusses common network devices, internet concepts, and how the world wide web works using protocols like HTTP and URLs. The document concludes with sections on internet etiquette and email operations and etiquette.uniti-websitebasics-230517110223-12e31dbc (1).pptx



uniti-websitebasics-230517110223-12e31dbc (1).pptxbmit1
?
It provides additional features like spell checking, grammar checking,
translation etc.
Networking: It handles all the networking tasks like establishing connection with
server, sending and receiving HTTP requests and responses.
UI Backend: It provides platform specific implementation for user interface.
Data Storage: It stores cookies, cache, bookmarks, history etc.
Plug-ins: It provides support for additional features like Flash, PDF, media players
etc.
JavaScript Interpreter: It interprets and executes the JavaScript code embedded in
web pages.
Browser Security: It provides security features like sandboxing, same-origin policy,
digital signatures etc.
Browser Extensibility: It allows third party extensions to addChapter 11- Emerging Technologies - Sub topic Communications technology



Chapter 11- Emerging Technologies - Sub topic Communications technologynahidibrahimshaikh
?
This presentation was made to explain the chapter 11- communications technology for A Levels CIELecture 2 types of network



Lecture 2 types of networkAlbert Abbosey
?
A computer network connects two or more computers to allow people to share files, peripherals, and communication. It requires at least two devices with network interface cards, a connection medium like cables, and network software. Networks can be local area networks within a building, metropolitan area networks within a city, or wide area networks combining multiple local networks over long distances using services like the internet. The internet itself is a worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that allows for communication services globally.Internet



InternetCoding Man
?
The document discusses various topics related to the Internet and computer networks. It begins with an overview of the Internet as a decentralized network of networks that transmits data packets between computers. It then covers topics like internet service providers, methods for accessing the Internet, internet protocols, internet services, the World Wide Web, intranets and extranets, and issues related to privacy, security and management of the Internet.Computer Networks: Evolution of Computer Networks.pptx



Computer Networks: Evolution of Computer Networks.pptxVishwaTej10
?
The document summarizes the evolution of computer networking from early networks like ARPANET in 1969 to the modern Internet. It discusses key concepts like distributed processing, network criteria of performance, reliability and security. It also covers network transmission technologies including unicast, broadcast and multicast. Different types of networks are defined, from local area networks (LANs) to wide area networks (WANs). Common network devices like hubs, switches and routers are also explained.basic networking and topologies explained.ppt



basic networking and topologies explained.pptLahiruRatnayake2
?
networking fundamentals with architechtures20IT703_PDS_PPT_Unit_I.ppt



20IT703_PDS_PPT_Unit_I.pptsuganthi66742
?
The document outlines the objectives and units of a course on distributed systems. The objectives are to learn about distributed environments, processes and synchronization, peer-to-peer networks, fault tolerance, network filesystems and middleware technologies. Unit 1 introduces distributed systems and covers resource sharing challenges, API protocols, data representation, marshaling, multicast communication and remote procedure calls.interconnected_network_of_internets.pptx



interconnected_network_of_internets.pptxGaganaP13
?
The document discusses the Internet and computer networks. It begins by explaining how the Internet emerged from early experiments connecting computers. It then describes different types of computer networks including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It also discusses wireless networks like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. The document then explains client-server networks and peer-to-peer networks. It provides details on topics like IP addressing, URLs, DNS hierarchy, and accessing the Internet via methods such as dial-up, broadband, and wireless. Finally, it briefly discusses web browsers and cyber ethics.Telecommunication and networks



Telecommunication and networksSergio Bedoya Fernandez
?
This document discusses telecommunications, the internet, wireless technology, and their components. It covers analog and digital signals, wired and wireless transmission methods, network topologies like star, bus, and ring networks. It also discusses local and wide area networks, standards like TCP/IP and OSI models, internet service providers, the world wide web, electronic business technologies, firewalls, extranets, web content management systems, and challenges of new IT infrastructures.A Fundamental elements of a network.pptx



A Fundamental elements of a network.pptxdexdexjoyjoy
?
The document discusses what the internet is, providing definitions and key points. It states that the internet is a global network of interconnected computer networks that uses TCP/IP protocols to connect billions of users. A brief history of the internet is then provided, highlighting milestones like the development of ARPANET, TCP/IP, the World Wide Web, and social media. Key people in the development of the internet like Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn are acknowledged. Finally, common internet services and fundamental elements of a network like hardware, software, clients and connection media are outlined.More Related Content
Similar to Lesson 1 Introduction to networking.pptx (20)
The Basics and Understanding of Computer Networking.pptx



The Basics and Understanding of Computer Networking.pptxBINJAD1
?
Computer networking refers to interconnected computing devices that can exchange data and share resources with each other.Mis jaiswal-chapter-03



Mis jaiswal-chapter-03Amit Fogla
?
This chapter discusses telecommunications and computer networks for business. It covers data transmission units and technologies, types of networks including LANs, WANs and intranets. It describes network devices, switching methods, the OSI model layers and TCP/IP. Intranets and extranets are defined, and applications for internal networks and sharing information with business partners are provided. Internet addressing systems using IP classes are also summarized.Computer networks



Computer networksKeerty Smile
?
Computer networks allow interconnected devices to communicate. They have advantages like resource sharing and cost savings but also disadvantages such as reduced productivity if poorly managed or servers fail. Early networks included ARPANET in 1969 and NSFNET in the 1980s, leading to the modern Internet. Networks transmit data via circuits, packets, or messages using techniques like circuit switching, packet switching, and message switching. Components include nodes, servers, clients, hardware, software and communication channels. Networks can be LANs, MANs, WANs or PANs depending on their area of coverage. Wired networks use media like twisted pair, coaxial or fiber optic cables while wireless uses radio waves.UNIT I DIS.pptx



UNIT I DIS.pptxPremkumar R
?
This document discusses distributed systems and key concepts related to communication in distributed environments. It begins with an introduction to distributed systems and examples. It then covers challenges like APIs for internet protocols, external data representation and marshaling, multicast communication, remote procedure calls, and group communication. Key aspects of distributed systems like features, quality of service parameters, resource sharing, and examples are also summarized.Network models



Network modelsSri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering College
?
This document provides an overview of computer communication networks and their basic components and design. It discusses:
1) The key components of a data communication system including the message, sender, receiver, transmission medium, and protocols.
2) Basic network concepts such as the definition of a network, important network characteristics like performance and reliability, and common network topologies.
3) Categories of networks including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs).
4) Related concepts such as the internet, intranets, and extranets.
5) Protocols and standards that govern data communication and their importance.introduction of network



introduction of networkBishalWosti1
?
This document provides an overview of computer networks and networking concepts. It discusses centralized, distributed, and collaborative network models. It describes common network topologies like star, bus, ring, mesh, and fully connected. The document also covers the OSI reference model and TCP/IP model, detailing the layers and functions of each. Computer network protocols, standards organizations, and interfaces are defined. Uses of networks for organizations and individuals are outlined.Networks-Internet-and-Internet-Protocols.pptx



Networks-Internet-and-Internet-Protocols.pptxHaythanSunday
?
This document provides an overview of computer networks and the internet. It defines key network terms like network, internet protocols, and network architecture models like client-server and peer-to-peer. It also discusses common network devices, internet concepts, and how the world wide web works using protocols like HTTP and URLs. The document concludes with sections on internet etiquette and email operations and etiquette.uniti-websitebasics-230517110223-12e31dbc (1).pptx



uniti-websitebasics-230517110223-12e31dbc (1).pptxbmit1
?
It provides additional features like spell checking, grammar checking,
translation etc.
Networking: It handles all the networking tasks like establishing connection with
server, sending and receiving HTTP requests and responses.
UI Backend: It provides platform specific implementation for user interface.
Data Storage: It stores cookies, cache, bookmarks, history etc.
Plug-ins: It provides support for additional features like Flash, PDF, media players
etc.
JavaScript Interpreter: It interprets and executes the JavaScript code embedded in
web pages.
Browser Security: It provides security features like sandboxing, same-origin policy,
digital signatures etc.
Browser Extensibility: It allows third party extensions to addChapter 11- Emerging Technologies - Sub topic Communications technology



Chapter 11- Emerging Technologies - Sub topic Communications technologynahidibrahimshaikh
?
This presentation was made to explain the chapter 11- communications technology for A Levels CIELecture 2 types of network



Lecture 2 types of networkAlbert Abbosey
?
A computer network connects two or more computers to allow people to share files, peripherals, and communication. It requires at least two devices with network interface cards, a connection medium like cables, and network software. Networks can be local area networks within a building, metropolitan area networks within a city, or wide area networks combining multiple local networks over long distances using services like the internet. The internet itself is a worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that allows for communication services globally.Internet



InternetCoding Man
?
The document discusses various topics related to the Internet and computer networks. It begins with an overview of the Internet as a decentralized network of networks that transmits data packets between computers. It then covers topics like internet service providers, methods for accessing the Internet, internet protocols, internet services, the World Wide Web, intranets and extranets, and issues related to privacy, security and management of the Internet.Computer Networks: Evolution of Computer Networks.pptx



Computer Networks: Evolution of Computer Networks.pptxVishwaTej10
?
The document summarizes the evolution of computer networking from early networks like ARPANET in 1969 to the modern Internet. It discusses key concepts like distributed processing, network criteria of performance, reliability and security. It also covers network transmission technologies including unicast, broadcast and multicast. Different types of networks are defined, from local area networks (LANs) to wide area networks (WANs). Common network devices like hubs, switches and routers are also explained.basic networking and topologies explained.ppt



basic networking and topologies explained.pptLahiruRatnayake2
?
networking fundamentals with architechtures20IT703_PDS_PPT_Unit_I.ppt



20IT703_PDS_PPT_Unit_I.pptsuganthi66742
?
The document outlines the objectives and units of a course on distributed systems. The objectives are to learn about distributed environments, processes and synchronization, peer-to-peer networks, fault tolerance, network filesystems and middleware technologies. Unit 1 introduces distributed systems and covers resource sharing challenges, API protocols, data representation, marshaling, multicast communication and remote procedure calls.interconnected_network_of_internets.pptx



interconnected_network_of_internets.pptxGaganaP13
?
The document discusses the Internet and computer networks. It begins by explaining how the Internet emerged from early experiments connecting computers. It then describes different types of computer networks including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It also discusses wireless networks like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. The document then explains client-server networks and peer-to-peer networks. It provides details on topics like IP addressing, URLs, DNS hierarchy, and accessing the Internet via methods such as dial-up, broadband, and wireless. Finally, it briefly discusses web browsers and cyber ethics.Telecommunication and networks



Telecommunication and networksSergio Bedoya Fernandez
?
This document discusses telecommunications, the internet, wireless technology, and their components. It covers analog and digital signals, wired and wireless transmission methods, network topologies like star, bus, and ring networks. It also discusses local and wide area networks, standards like TCP/IP and OSI models, internet service providers, the world wide web, electronic business technologies, firewalls, extranets, web content management systems, and challenges of new IT infrastructures.A Fundamental elements of a network.pptx



A Fundamental elements of a network.pptxdexdexjoyjoy
?
The document discusses what the internet is, providing definitions and key points. It states that the internet is a global network of interconnected computer networks that uses TCP/IP protocols to connect billions of users. A brief history of the internet is then provided, highlighting milestones like the development of ARPANET, TCP/IP, the World Wide Web, and social media. Key people in the development of the internet like Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn are acknowledged. Finally, common internet services and fundamental elements of a network like hardware, software, clients and connection media are outlined.More from Omar Fernandez (9)
Lesson 2 - Intro to Remote access methods.pptx



Lesson 2 - Intro to Remote access methods.pptxOmar Fernandez
?
Describes the basic lesson in remote access methodsLesson 1 ICT-in-the-Context-of-Global-Communication.pptx



Lesson 1 ICT-in-the-Context-of-Global-Communication.pptxOmar Fernandez
?
ICT-in-the-Context-of-Global-CommunicationLesson 3 - Cybersecurity and its impact to e-commerce (32).pptx



Lesson 3 - Cybersecurity and its impact to e-commerce (32).pptxOmar Fernandez
?
intro to Cybersecurity and its impact to e-commerceRecently uploaded (20)
Unlocking DevOps Secuirty :Vault & Keylock



Unlocking DevOps Secuirty :Vault & KeylockHusseinMalikMammadli
?
DevOps i? t?hl¨¹k?sizliyi sizi maraqland?r?r? ?st?r developer, ist?r t?hl¨¹k?sizlik m¨¹h?ndisi, ist?rs? d? DevOps h?v?skar? olun, bu t?dbir ??b?k?l??m?k, bilikl?rinizi b?l¨¹?m?k v? DevSecOps sah?sind? ?n son t?cr¨¹b?l?ri ?yr?nm?k ¨¹?¨¹n m¨¹k?mm?l f¨¹rs?tdir!
Bu workshopda DevOps infrastrukturlar?n?n t?hl¨¹k?sizliyini nec? art?rmaq bar?d? dan??acay?q. DevOps sisteml?ri qurulark?n avtomatla?d?r?lm??, y¨¹ks?k ?l?atan v? etibarl? olmas? il? yana??, h?m d? t?hl¨¹k?sizlik m?s?l?l?ri n?z?r? al?nmal?d?r. Bu s?b?bd?n, DevOps komandolar?n?n t?hl¨¹k?sizliy? y?n?lmi? praktikalara riay?t etm?si vacibdir.Wondershare Filmora Crack 14.3.2.11147 Latest



Wondershare Filmora Crack 14.3.2.11147 Latestudkg888
?
https://ncracked.com/7961-2/
Note: >> Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link
Free Download Wondershare Filmora 14.3.2.11147 Full Version - All-in-one home video editor to make a great video.Free Download Wondershare Filmora for Windows PC is an all-in-one home video editor with powerful functionality and a fully stacked feature set. Filmora has a simple drag-and-drop top interface, allowing you to be artistic with the story you want to create.Video Editing Simplified - Ignite Your Story. A powerful and intuitive video editing experience. Filmora 10 hash two new ways to edit: Action Cam Tool (Correct lens distortion, Clean up your audio, New speed controls) and Instant Cutter (Trim or merge clips quickly, Instant export).Filmora allows you to create projects in 4:3 or 16:9, so you can crop the videos or resize them to fit the size you want. This way, quickly converting a widescreen material to SD format is possible.What Makes "Deep Research"? A Dive into AI Agents



What Makes "Deep Research"? A Dive into AI AgentsZilliz
?
About this webinar:
Unless you live under a rock, you will have heard about OpenAI¡¯s release of Deep Research on Feb 2, 2025. This new product promises to revolutionize how we answer questions requiring the synthesis of large amounts of diverse information. But how does this technology work, and why is Deep Research a noticeable improvement over previous attempts? In this webinar, we will examine the concepts underpinning modern agents using our basic clone, Deep Searcher, as an example.
Topics covered:
Tool use
Structured output
Reflection
Reasoning models
Planning
Types of agentic memoryFuture-Proof Your Career with AI Options



Future-Proof Your Career with AI OptionsDianaGray10
?
Learn about the difference between automation, AI and agentic and ways you can harness these to further your career. In this session you will learn:
Introduction to automation, AI, agentic
Trends in the marketplace
Take advantage of UiPath training and certification
In demand skills needed to strategically position yourself to stay ahead
? If you have any questions or feedback, please refer to the "Women in Automation 2025" dedicated Forum thread. You can find there extra details and updates.A Framework for Model-Driven Digital Twin Engineering



A Framework for Model-Driven Digital Twin EngineeringDaniel Lehner
?
ºÝºÝߣs from my PhD Defense at Johannes Kepler University, held on Janurary 10, 2025.
The full thesis is available here: https://epub.jku.at/urn/urn:nbn:at:at-ubl:1-83896DevNexus - Building 10x Development Organizations.pdf



DevNexus - Building 10x Development Organizations.pdfJustin Reock
?
Developer Experience is Dead! Long Live Developer Experience!
In this keynote-style session, we¡¯ll take a detailed, granular look at the barriers to productivity developers face today and modern approaches for removing them. 10x developers may be a myth, but 10x organizations are very real, as proven by the influential study performed in the 1980s, ¡®The Coding War Games.¡¯
Right now, here in early 2025, we seem to be experiencing YAPP (Yet Another Productivity Philosophy), and that philosophy is converging on developer experience. It seems that with every new method, we invent to deliver products, whether physical or virtual, we reinvent productivity philosophies to go alongside them.
But which of these approaches works? DORA? SPACE? DevEx? What should we invest in and create urgency behind today so we don¡¯t have the same discussion again in a decade?The Future of Repair: Transparent and Incremental by Botond De?nes



The Future of Repair: Transparent and Incremental by Botond De?nesScyllaDB
?
Regularly run repairs are essential to keep clusters healthy, yet having a good repair schedule is more challenging than it should be. Repairs often take a long time, preventing running them often. This has an impact on data consistency and also limits the usefulness of the new repair based tombstone garbage collection. We want to address these challenges by making repairs incremental and allowing for automatic repair scheduling, without relying on external tools.Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)



Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)nick896721
?
Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation preview by User Interviews.EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Key



EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Keykherorpacca127
?
https://ncracked.com/7961-2/
Note: >> Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link
EASEUS Partition Master Crack is a professional hard disk partition management tool and system partition optimization software. It is an all-in-one PC and server disk management toolkit for IT professionals, system administrators, technicians, and consultants to provide technical services to customers with unlimited use.
EASEUS Partition Master 18.0 Technician Edition Crack interface is clean and tidy, so all options are at your fingertips. Whether you want to resize, move, copy, merge, browse, check, convert partitions, or change their labels, you can do everything with a few clicks. The defragmentation tool is also designed to merge fragmented files and folders and store them in contiguous locations on the hard drive.
[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web AppsSafe Software
?
Ready to simplify workflow sharing across your organization without diving into complex coding? With FME Flow Apps, you can build no-code web apps that make your data work harder for you ¡ª fast.
In this webinar, we¡¯ll show you how to:
Build and deploy Workspace Apps to create an intuitive user interface for self-serve data processing and validation.
Automate processes using Automation Apps. Learn to create a no-code web app to kick off workflows tailored to your needs, trigger multiple workspaces and external actions, and use conditional filtering within automations to control your workflows.
Create a centralized portal with Gallery Apps to share a collection of no-code web apps across your organization.
Through real-world examples and practical demos, you¡¯ll learn how to transform your workflows into intuitive, self-serve solutions that empower your team and save you time. We can¡¯t wait to show you what¡¯s possible!FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptx



FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptxTracxn
?
US FinTech 2024, offering a comprehensive analysis of key trends, funding activities, and top-performing sectors that shaped the FinTech ecosystem in the US 2024. The report delivers detailed data and insights into the region's funding landscape and other developments. We believe this report will provide you with valuable insights to understand the evolving market dynamics.DAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)



DAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)Tsuyoshi Hirayama
?
DAO UTokyo 2025
–|¾©´óѧÇéˆóѧh ¥Ö¥í¥Ã¥¯¥Á¥§©`¥óÑо¿¥¤¥Ë¥·¥¢¥Æ¥£¥Ö
https://utbciii.com/2024/12/12/announcing-dao-utokyo-2025-conference/
Session 1 :DLT mass adoption
IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (ƽɽÒã)How Discord Indexes Trillions of Messages: Scaling Search Infrastructure by V...



How Discord Indexes Trillions of Messages: Scaling Search Infrastructure by V...ScyllaDB
?
This talk shares how Discord scaled their message search infrastructure using Rust, Kubernetes, and a multi-cluster Elasticsearch architecture to achieve better performance, operability, and reliability, while also enabling new search features for Discord users.World Information Architecture Day 2025 - UX at a Crossroads



World Information Architecture Day 2025 - UX at a CrossroadsJoshua Randall
?
User Experience stands at a crossroads: will we live up to our potential to design a better world? or will we be co-opted by ¡°product management¡± or another business buzzword?
Looking backwards, this talk will show how UX has repeatedly failed to create a better world, drawing on industry data from Nielsen Norman Group, Baymard, MeasuringU, WebAIM, and others.
Looking forwards, this talk will argue that UX must resist hype, say no more often and collaborate less often (you read that right), and become a true profession ¡ª in order to be able to design a better world.Cloud of everything Tech of the 21 century in Aviation



Cloud of everything Tech of the 21 century in AviationAssem mousa
?
AI, Block chain, Digital Currency, Cloud, Cloud of Things, Tactile Internet, Digital Twins, IOT, AR, VR, MR, U commerce, data and robotics."
Unlock AI Creativity: Image Generation with DALL¡¤E



Unlock AI Creativity: Image Generation with DALL¡¤EExpeed Software
?
Discover the power of AI image generation with DALL¡¤E, an advanced AI model that transforms text prompts into stunning, high-quality visuals. This presentation explores how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing digital creativity, from graphic design to content creation and marketing. Learn about the technology behind DALL¡¤E, its real-world applications, and how businesses can leverage AI-generated art for innovation. Whether you're a designer, developer, or marketer, this guide will help you unlock new creative possibilities with AI-driven image synthesis.UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 2



UiPath Automation Developer Associate Training Series 2025 - Session 2DianaGray10
?
In session 2, we will introduce you to Data manipulation in UiPath Studio.
Topics covered:
Data Manipulation
What is Data Manipulation
Strings
Lists
Dictionaries
RegEx Builder
Date and Time
Required Self-Paced Learning for this session:
Data Manipulation with Strings in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h 30m - https://academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-strings-in-studio
Data Manipulation with Lists and Dictionaries in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-lists-and-dictionaries-in-studio
Data Manipulation with Data Tables in UiPath Studio (v2022.10) 2 modules - 1h 30m - https:/academy.uipath.com/courses/data-manipulation-with-data-tables-in-studio
?? For any questions you may have, please use the dedicated Forum thread. You can tag the hosts and mentors directly and they will reply as soon as possible. Lesson 1 Introduction to networking.pptx
- 2. Network concepts ? Internet ? intranet ? extranet ? client-server ? peer-to-peer ? transmission types o (unicast, multicast, broadcast), ? network devices including IoT
- 3. Network concepts ? Internet - a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities, consisting of interconnected networks using standardized communication protocols.
- 4. Network concepts ? Intranet - An intranet is a private network that allows employees within an organization to communicate, share information, and collaborate on tasks. ? Intranets are similar to the internet, but only authorized users within an organization can access them.
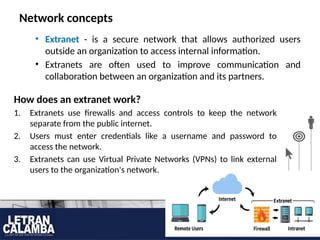
- 5. Network concepts ? Extranet - is a secure network that allows authorized users outside an organization to access internal information. ? Extranets are often used to improve communication and collaboration between an organization and its partners. How does an extranet work? 1. Extranets use firewalls and access controls to keep the network separate from the public internet. 2. Users must enter credentials like a username and password to access the network. 3. Extranets can use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to link external users to the organization's network.
- 6. Network concepts ? Client-server - model is a computing system that allows clients to access data and services from a server. The server acts as a central hub that manages the data and provides services to the clients. How it works 1. A client, such as a web browser, sends a request to a server for data or services 2. The server responds to the request with a message, such as a file or the result of an authentication 3. The client receives the response from the server
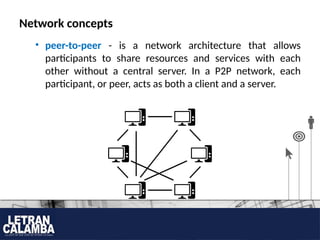
- 8. Network concepts ? peer-to-peer - is a network architecture that allows participants to share resources and services with each other without a central server. In a P2P network, each participant, or peer, acts as both a client and a server.
- 9. Network concepts ? transmission types o (unicast, multicast, broadcast) ? Unicast is a type of network communication that sends data from one sender to one receiver. It's similar to a one-on-one conversation.
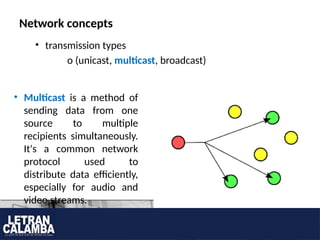
- 10. Network concepts ? transmission types o (unicast, multicast, broadcast) ? Multicast is a method of sending data from one source to multiple recipients simultaneously. It's a common network protocol used to distribute data efficiently, especially for audio and video streams.
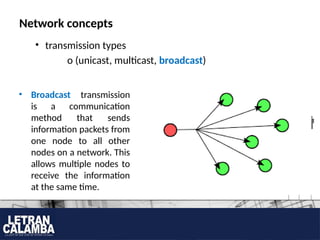
- 11. Network concepts ? transmission types o (unicast, multicast, broadcast) ? Broadcast transmission is a communication method that sends information packets from one node to all other nodes on a network. This allows multiple nodes to receive the information at the same time.
- 13. Network concepts ? network devices including IoT - encompass a wide range of devices that connect to the internet and can collect, send, and receive data, including smart home appliances like smart thermostats, security cameras, smart lights, wearables like fitness trackers, industrial sensors, medical devices, and more, all communicating through various network protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and specialized IoT protocols like LoRaWAN and Zigbee.
- 14. network devices including IoT
- 15. Questions????











