Lesson 3.1 factorisation
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes533 views
The document discusses different methods for factorizing quadratic expressions. It explains that the traditional method relies on multi-step processes, while the Vedic method makes factorization simpler using two sub-sutras called "Anurupyena" and "Adyamadyenantyamantyena", which mean "proportionately" and "the first by the first and the last by the last". This Vedic method splits the middle term of a quadratic expression into two parts proportionately so that the factors can be determined directly from the coefficients and terms of the expression.
1 of 2
Downloaded 15 times


Recommended
October 18



October 18khyps13
Ã˝
1. Graph E represents the graph where b > 0.5.
2. Graph D represents the graph where x < -7.7.
3. Solving the equation 6(x + 3) + 1 = -11 yields x = -7.Factoring quadratic trinomial



Factoring quadratic trinomialMartinGeraldine
Ã˝
The document discusses factoring quadratic trinomials. It provides three examples of factoring expressions such as x^2 - 5x - 14, x^2 - 10x + 25, and x^2 + 2x - 35. Each example lists the steps to factor the expression which include finding factors of the constant term that sum to the coefficient of the middle term and then factoring the first term.Ma3bfet par 10.7 7 aug 2014



Ma3bfet par 10.7 7 aug 2014Celumusa Godfrey Nkosi
Ã˝
The document contains information about partial fraction decomposition:
1. It discusses four cases for partial fraction decomposition based on the factors of the denominator: distinct linear factors, repeated linear factors, distinct irreducible quadratic factors, and repeated irreducible quadratic factors.
2. It provides examples to illustrate each case, showing how to set up and solve systems of equations to determine the coefficients of the partial fractions.
3. Homework Task 4 on systems of equations and inequalities is due on August 13, and consultation times for Ms. Durandt are on Thursdays and Fridays at 10:30.Solving by factoring remediation notes



Solving by factoring remediation notesMichelle Barnhill
Ã˝
Here are the key steps to factoring when a ≠ 1:
1. Check for GCF. If there is a GCF, factor it out.
2. If no GCF, find two numbers whose product is ac and sum is b. These will be the coefficients of the factors.
3. Split the middle term into two terms using the factors.
4. Factor using the box method, finding the GCF of each row and column.
Some examples:
2x2 + 11x + 5
ac = 10, factors are 2, 5
(2x + 1)(x + 5)
3x2 - 5x - 2
ac = -Dual formulation example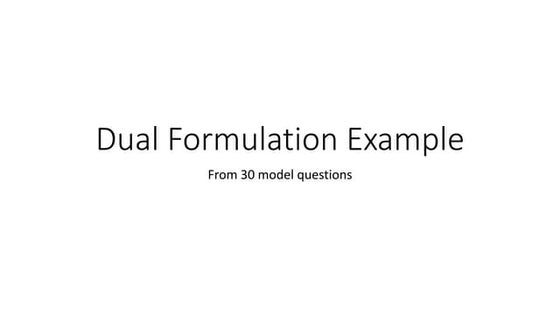



Dual formulation exampleAnurag Srivastava
Ã˝
The document discusses how to formulate the dual of a primal linear programming problem. It provides 10 steps for converting a primal maximization problem into a dual minimization problem. As an example, it formulates the dual of the primal problem: Maximize z = -5x1 + 2x2 subject to x1 - x2 ≥ 2 and 2x1 + 3x2 ≤ 5, with non-negativity constraints. The dual is formulated as: Minimize z = -2y1 + 5y2 subject to -y1 + 2y2 ≥ -5 and y1 + 3y2 ≥ 2, with non-negativity constraints on the dual variables y1 and y2.Rational Expressions



Rational Expressionsking_danickus
Ã˝
Rational expressions are fractions where the numerator and denominator are polynomials. To simplify rational expressions, we first factor the polynomials and then cancel any common factors. Adding and subtracting rational expressions follows the same process as fractions - find the least common denominator, multiply the numerators and denominators to get the same denominator, then add or subtract the numerators. Multiplying rational expressions involves factoring and cancelling common factors between the numerator and denominator. To divide rational expressions, we multiply the first expression by the reciprocal of the second expression and then factor and cancel. Word problems involving rational expressions can be solved by identifying what is known and unknown, setting up equations relating the known and unknown values, and then solving the equations.March 9, 2015



March 9, 2015khyps13
Ã˝
Today's math lesson covers dividing polynomials by monomials and multiplying binomials. Students should bring good notes and their full attention. The warm-up reviews solving binomial equations and discount word problems. Methods for multiplying binomials include the box method and FOIL (First, Outer, Inner, Last). Patterns emerge depending on the signs of terms. Dividing polynomials begins with dividing each term in the numerator by the monomial denominator. Students should take complete, easy to read notes on multiplying and dividing polynomials.Q1 week 1 (common monomial,sum & diffrence of two cubes,difference of tw...



Q1 week 1 (common monomial,sum & diffrence of two cubes,difference of tw...Walden Macabuhay
Ã˝
It consists of ten units in which the first unit focuses on the special products and factors. Its deals with the study of rational algebraic expressions. It aims to empower students with life – long learning and helps them to attain functional literacy. The call of the K to 12 curriculum allow the students to have an active involvement in learning through demonstration of skills, manifestations of communication skills, development of analytical and creative thinking and understanding of mathematical applications and connections. Sulalgtrig7e Isg 1 4



Sulalgtrig7e Isg 1 4Joseph Eulo
Ã˝
1. To solve equations with radicals, isolate the radical term by adding or subtracting like terms, then square both sides of the equation.
2. The "u" substitution method can be used to solve quadratic equations in radical form by letting the variable under the radical equal "u" and squaring it.
3. After substitution and factoring, the solutions for "u" are then substituted back in terms of the original variable under the radical.On Application of the Fixed-Point Theorem to the Solution of Ordinary Differe...



On Application of the Fixed-Point Theorem to the Solution of Ordinary Differe...BRNSS Publication Hub
Ã˝
We know that a large number of problems in differential equations can be reduced to finding the solution x to an equation of the form Tx=y. The operator T maps a subset of a Banach space X into another Banach space Y and y is a known element of Y. If y=0 and Tx=Ux−x, for another operator U, the equation Tx=y is equivalent to the equation Ux=x. Naturally, to solve Ux=x, we must assume that the range R (U) and the domain D (U) have points in common. Points x for which Ux=x are called fixed points of the operator U. In this work, we state the main fixed-point theorems that are most widely used in the field of differential equations. These are the Banach contraction principle, the Schauder–Tychonoff theorem, and the Leray–Schauder theorem. We will only prove the first theorem and then proceed.Factoring Polynomials in Modular Approach



Factoring Polynomials in Modular ApproachLorie Jane Letada
Ã˝
The document provides lessons on factoring polynomials with common monomial factors and the difference of two squares. It explains that to factor polynomials with common monomial factors, one must find the greatest common factor (GCF) and divide each term by the GCF. It also explains that to factor the difference of two squares, one must get the square root of each term and use those roots to form the sum and difference as factors. Examples are provided to demonstrate these factoring techniques step-by-step. The document aims to teach learners how to completely factor different types of polynomials.Brians Trinomials



Brians Trinomialsguest912f875
Ã˝
This document provides directions on how to factor the trinomial 3x^2 + 5x + 2 into two binomials. It shows setting up the trinomial with the x terms grouped on the left and the numeric terms on the right, then finding two numbers that multiply to the last term and add to the middle term, resulting in the factored form of (x+1)(3x+2).Section3 stochastic



Section3 stochasticcairo university
Ã˝
1. A bi-variate random variable has a joint probability distribution function (PDF) that defines the probability of two random variables occurring together. The marginal PDF defines the probability of each variable individually, while the conditional PDF defines the probability of one variable given the other.
2. A multi-variate random variable contains multiple random variables defined by a mean vector and covariance matrix. A linear transformation of a Gaussian multi-variate random variable remains Gaussian with a transformed mean vector and covariance matrix.
3. If two random vectors are jointly Gaussian and uncorrelated, they are also independent, as their joint PDF can be written as the product of their individual PDFs.Ec 233 final exam, fall 2020 ozan hatipoğlu answer que



Ec 233 final exam, fall 2020 ozan hatipoğlu answer queronak56
Ã˝
This document outlines the instructions for the EC 233 Final Exam for Fall 2020. It states that students must answer one of two questions and provides details for submitting answers. The questions involve portfolio management, probability density functions, and joint distributions. Students are instructed to show their work and reasoning in a clear manner. The deadline to submit is February 12 at 11:59 PM.Algebra 2 Day 4 Notes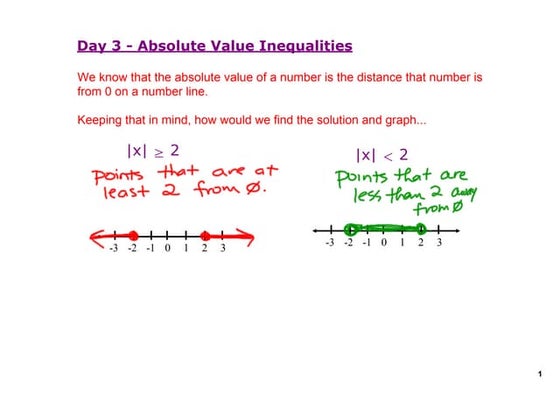



Algebra 2 Day 4 NotesKate Nowak
Ã˝
This document discusses how to solve and graph absolute value inequalities. It explains that the absolute value of a number represents its distance from 0 on a number line. To solve an absolute value inequality, one treats it like an absolute value equation first to find the critical points, then plots those points on a number line to divide it into intervals. Test points from each interval are plugged back into the original inequality to determine if they satisfy it and belong to the solution set. Examples walk through applying this process to solve and graph two absolute value inequalities.factoring



factoringHarish Sahu
Ã˝
The security of the RSA algorithm depends on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. The best known factoring algorithms are trial division, Dixon's algorithm, the quadratic sieve, and the number field sieve. The quadratic sieve and number field sieve are parallelizable algorithms that improve on Dixon's algorithm by using a "sieving" technique to more efficiently find relations between factors. While factoring performance improves incrementally over time, a large key size (over 300 bits) is still considered secure against the best known factoring methods.3



3silvia
Ã˝
This document discusses dividing polynomials using long division and synthetic division, as well as the remainder and factor theorems. Long division and synthetic division are methods for dividing polynomials. The remainder theorem states that the remainder of dividing a polynomial function by x-a gives the value of the function at a. The factor theorem states that if a number is a zero of a polynomial function, then x-a is a factor of the polynomial. Examples are provided to demonstrate using these theorems and division methods to find polynomial values and factors.5 3 solving trig eqns



5 3 solving trig eqnsKamarat Kumanukit
Ã˝
To solve trigonometric equations:
1) Use standard algebraic techniques such as collecting like terms and factoring to isolate the trigonometric function.
2) Many equations are of quadratic type (ax^2 + bx + c = 0) and can be solved by factoring or using the Quadratic Formula.
3) Equations involving multiple angles (sin ku, cos ku) are first solved for ku, then divided by k.
4) Inverse trigonometric functions can be used to solve equations, with the domain restrictions of the inverse functions considered.11 applications of factoring



11 applications of factoringelem-alg-sample
Ã˝
The document discusses applications of factoring polynomials. It provides examples of how factoring can be used to evaluate polynomials by substituting values into the factored form. Factoring is also useful for determining the sign of outputs and for solving polynomial equations, which is described as the most important application of factoring. Examples are given to demonstrate evaluating polynomials both with and without factoring, and checking the answers obtained from factoring using the expanded form.Synthetic Division



Synthetic Divisionscnbmitchell
Ã˝
The document provides an explanation and examples of using synthetic division to divide polynomials. Synthetic division allows dividing a polynomial by a divisor of the form (x - k). The process involves writing the coefficients of the dividend in descending order and placing k below. Then, successive multiplication and addition steps provide the coefficients of the quotient polynomial and remainder. Two examples are worked through to demonstrate synthetic division for (2x^3 - 7x^2 - 8x + 16) / (x - 4) and (5x^3 + x^2 - 7) / (x + 1).11.2



11.2nglaze10
Ã˝
The document defines rational expressions as expressions that can be written as a ratio of two polynomials where the denominator is not 0. It provides examples of finding excluded values, which make the expression undefined, by setting the denominator equal to 0. It also discusses simplifying rational expressions by dividing out common factors in the numerator and denominator and putting them in simplest form. Examples are provided of factoring, dividing out monomials, recognizing opposites, and simplifying a rational model.Rational expressions



Rational expressionsMark Ryder
Ã˝
This document discusses working with rational expressions, including:
1) Finding the numbers that must be excluded from the domain to avoid undefined expressions.
2) Simplifying rational expressions by factoring numerators and denominators and cancelling common factors.
3) Multiplying, dividing, adding, and subtracting rational expressions by finding common denominators.Rational expressions ppt



Rational expressions pptDoreen Mhizha
Ã˝
This document discusses simplifying rational expressions by dividing out common factors, factoring numerators and denominators, and dividing common factors. It provides examples of simplifying various rational expressions step-by-step and explains how to identify excluded values that would make denominators equal to zero.Chandrayan quadratic equation



Chandrayan quadratic equationAnjani
Ã˝
The guru asked his disciples to solve a problem involving building an animal shelter with limited fencing for goats and cows. Most disciples tried to solve it as a quadratic equation by setting up equations for the area and fencing. However, they could not find the solutions. One disciple realized the original numbers were for the reward animals, so he set up the equations with one less goat and cow. His solution was a length of 7 units and breadth of 6 units. The document then explained quadratic equations and how the discriminant determines the number of real solutions.5.4 long division



5.4 long divisionleblance
Ã˝
Long division can be used to divide polynomials in a similar way to dividing numbers. The key steps are to set up the division problem, divide the term of the dividend by the term of the divisor, multiply the divisor by the quotient term and subtract, then bring down the next term of the dividend and repeat. This polynomial long division allows polynomials to be factored by finding all divisor polynomials that give a remainder of zero. The factor theorem can also be used to check if a linear polynomial is a factor by setting it equal to zero and checking if it makes the other polynomial equal to zero.Polynomial division



Polynomial divisionmason5
Ã˝
This document provides instructions for dividing polynomials. It explains that to divide polynomials, you first divide the divisor by the dividend by dividing one variable at a time. Synthetic division is also covered, which divides polynomials by only the root of the divisor.Module 1 polynomial functions



Module 1 polynomial functionsdionesioable
Ã˝
This module introduces polynomial functions of degree greater than 2. It covers identifying polynomial functions from relations, determining the degree of a polynomial, finding quotients of polynomials using division algorithm and synthetic division, and applying the remainder and factor theorems. The document provides examples and practice problems for each topic. It aims to teach students how to work with higher degree polynomial functions.multiplication properties



multiplication propertiesAlex Blank
Ã˝
This document discusses several multiplication properties:
1) The commutative property, which states that multiplying two numbers results in the same product regardless of order.
2) The zero property of multiplication, where any number multiplied by zero equals zero.
3) The identity property of multiplication, where any number multiplied by one equals that original number.
It instructs students to practice these properties by completing independent practice questions and a re-teach page in their workbook.Synthetic and Remainder Theorem of Polynomials.ppt



Synthetic and Remainder Theorem of Polynomials.pptMarkVincentDoria1
Ã˝
This document discusses synthetic division, a shortcut method for long division of polynomials when dividing by divisors of the form x - k. Synthetic division works by setting up an array and adding terms in columns, multiplying the results by -k. The remainder obtained has an important interpretation related to the Remainder Theorem - evaluating the polynomial function at x = k. The Factor Theorem also relates dividing a polynomial by (x - k) to determining if (x - k) is a factor. Examples demonstrate using synthetic division and these theorems to factor polynomials and find zeros.Chapter 9 differentiation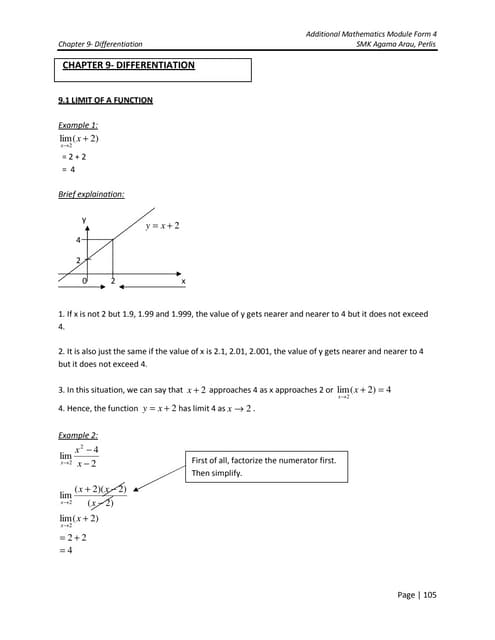



Chapter 9 differentiationatiqah ayie
Ã˝
This document provides an explanation of differentiation and examples of calculating limits and derivatives using the first principle definition of the derivative. It begins by defining the limit of a function and providing examples of evaluating limits. It then introduces the concept of the derivative as the slope of the tangent line to a curve and explains how to calculate derivatives using small changes in x and y. The document provides examples of finding derivatives using this first principle definition. It also discusses rules for deriving composite functions and products of polynomials. Exercises are provided throughout for students to practice differentiation.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Sulalgtrig7e Isg 1 4



Sulalgtrig7e Isg 1 4Joseph Eulo
Ã˝
1. To solve equations with radicals, isolate the radical term by adding or subtracting like terms, then square both sides of the equation.
2. The "u" substitution method can be used to solve quadratic equations in radical form by letting the variable under the radical equal "u" and squaring it.
3. After substitution and factoring, the solutions for "u" are then substituted back in terms of the original variable under the radical.On Application of the Fixed-Point Theorem to the Solution of Ordinary Differe...



On Application of the Fixed-Point Theorem to the Solution of Ordinary Differe...BRNSS Publication Hub
Ã˝
We know that a large number of problems in differential equations can be reduced to finding the solution x to an equation of the form Tx=y. The operator T maps a subset of a Banach space X into another Banach space Y and y is a known element of Y. If y=0 and Tx=Ux−x, for another operator U, the equation Tx=y is equivalent to the equation Ux=x. Naturally, to solve Ux=x, we must assume that the range R (U) and the domain D (U) have points in common. Points x for which Ux=x are called fixed points of the operator U. In this work, we state the main fixed-point theorems that are most widely used in the field of differential equations. These are the Banach contraction principle, the Schauder–Tychonoff theorem, and the Leray–Schauder theorem. We will only prove the first theorem and then proceed.Factoring Polynomials in Modular Approach



Factoring Polynomials in Modular ApproachLorie Jane Letada
Ã˝
The document provides lessons on factoring polynomials with common monomial factors and the difference of two squares. It explains that to factor polynomials with common monomial factors, one must find the greatest common factor (GCF) and divide each term by the GCF. It also explains that to factor the difference of two squares, one must get the square root of each term and use those roots to form the sum and difference as factors. Examples are provided to demonstrate these factoring techniques step-by-step. The document aims to teach learners how to completely factor different types of polynomials.Brians Trinomials



Brians Trinomialsguest912f875
Ã˝
This document provides directions on how to factor the trinomial 3x^2 + 5x + 2 into two binomials. It shows setting up the trinomial with the x terms grouped on the left and the numeric terms on the right, then finding two numbers that multiply to the last term and add to the middle term, resulting in the factored form of (x+1)(3x+2).Section3 stochastic



Section3 stochasticcairo university
Ã˝
1. A bi-variate random variable has a joint probability distribution function (PDF) that defines the probability of two random variables occurring together. The marginal PDF defines the probability of each variable individually, while the conditional PDF defines the probability of one variable given the other.
2. A multi-variate random variable contains multiple random variables defined by a mean vector and covariance matrix. A linear transformation of a Gaussian multi-variate random variable remains Gaussian with a transformed mean vector and covariance matrix.
3. If two random vectors are jointly Gaussian and uncorrelated, they are also independent, as their joint PDF can be written as the product of their individual PDFs.Ec 233 final exam, fall 2020 ozan hatipoğlu answer que



Ec 233 final exam, fall 2020 ozan hatipoğlu answer queronak56
Ã˝
This document outlines the instructions for the EC 233 Final Exam for Fall 2020. It states that students must answer one of two questions and provides details for submitting answers. The questions involve portfolio management, probability density functions, and joint distributions. Students are instructed to show their work and reasoning in a clear manner. The deadline to submit is February 12 at 11:59 PM.Algebra 2 Day 4 Notes



Algebra 2 Day 4 NotesKate Nowak
Ã˝
This document discusses how to solve and graph absolute value inequalities. It explains that the absolute value of a number represents its distance from 0 on a number line. To solve an absolute value inequality, one treats it like an absolute value equation first to find the critical points, then plots those points on a number line to divide it into intervals. Test points from each interval are plugged back into the original inequality to determine if they satisfy it and belong to the solution set. Examples walk through applying this process to solve and graph two absolute value inequalities.factoring



factoringHarish Sahu
Ã˝
The security of the RSA algorithm depends on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. The best known factoring algorithms are trial division, Dixon's algorithm, the quadratic sieve, and the number field sieve. The quadratic sieve and number field sieve are parallelizable algorithms that improve on Dixon's algorithm by using a "sieving" technique to more efficiently find relations between factors. While factoring performance improves incrementally over time, a large key size (over 300 bits) is still considered secure against the best known factoring methods.3



3silvia
Ã˝
This document discusses dividing polynomials using long division and synthetic division, as well as the remainder and factor theorems. Long division and synthetic division are methods for dividing polynomials. The remainder theorem states that the remainder of dividing a polynomial function by x-a gives the value of the function at a. The factor theorem states that if a number is a zero of a polynomial function, then x-a is a factor of the polynomial. Examples are provided to demonstrate using these theorems and division methods to find polynomial values and factors.5 3 solving trig eqns



5 3 solving trig eqnsKamarat Kumanukit
Ã˝
To solve trigonometric equations:
1) Use standard algebraic techniques such as collecting like terms and factoring to isolate the trigonometric function.
2) Many equations are of quadratic type (ax^2 + bx + c = 0) and can be solved by factoring or using the Quadratic Formula.
3) Equations involving multiple angles (sin ku, cos ku) are first solved for ku, then divided by k.
4) Inverse trigonometric functions can be used to solve equations, with the domain restrictions of the inverse functions considered.11 applications of factoring



11 applications of factoringelem-alg-sample
Ã˝
The document discusses applications of factoring polynomials. It provides examples of how factoring can be used to evaluate polynomials by substituting values into the factored form. Factoring is also useful for determining the sign of outputs and for solving polynomial equations, which is described as the most important application of factoring. Examples are given to demonstrate evaluating polynomials both with and without factoring, and checking the answers obtained from factoring using the expanded form.Synthetic Division



Synthetic Divisionscnbmitchell
Ã˝
The document provides an explanation and examples of using synthetic division to divide polynomials. Synthetic division allows dividing a polynomial by a divisor of the form (x - k). The process involves writing the coefficients of the dividend in descending order and placing k below. Then, successive multiplication and addition steps provide the coefficients of the quotient polynomial and remainder. Two examples are worked through to demonstrate synthetic division for (2x^3 - 7x^2 - 8x + 16) / (x - 4) and (5x^3 + x^2 - 7) / (x + 1).11.2



11.2nglaze10
Ã˝
The document defines rational expressions as expressions that can be written as a ratio of two polynomials where the denominator is not 0. It provides examples of finding excluded values, which make the expression undefined, by setting the denominator equal to 0. It also discusses simplifying rational expressions by dividing out common factors in the numerator and denominator and putting them in simplest form. Examples are provided of factoring, dividing out monomials, recognizing opposites, and simplifying a rational model.Rational expressions



Rational expressionsMark Ryder
Ã˝
This document discusses working with rational expressions, including:
1) Finding the numbers that must be excluded from the domain to avoid undefined expressions.
2) Simplifying rational expressions by factoring numerators and denominators and cancelling common factors.
3) Multiplying, dividing, adding, and subtracting rational expressions by finding common denominators.Rational expressions ppt



Rational expressions pptDoreen Mhizha
Ã˝
This document discusses simplifying rational expressions by dividing out common factors, factoring numerators and denominators, and dividing common factors. It provides examples of simplifying various rational expressions step-by-step and explains how to identify excluded values that would make denominators equal to zero.Chandrayan quadratic equation



Chandrayan quadratic equationAnjani
Ã˝
The guru asked his disciples to solve a problem involving building an animal shelter with limited fencing for goats and cows. Most disciples tried to solve it as a quadratic equation by setting up equations for the area and fencing. However, they could not find the solutions. One disciple realized the original numbers were for the reward animals, so he set up the equations with one less goat and cow. His solution was a length of 7 units and breadth of 6 units. The document then explained quadratic equations and how the discriminant determines the number of real solutions.5.4 long division



5.4 long divisionleblance
Ã˝
Long division can be used to divide polynomials in a similar way to dividing numbers. The key steps are to set up the division problem, divide the term of the dividend by the term of the divisor, multiply the divisor by the quotient term and subtract, then bring down the next term of the dividend and repeat. This polynomial long division allows polynomials to be factored by finding all divisor polynomials that give a remainder of zero. The factor theorem can also be used to check if a linear polynomial is a factor by setting it equal to zero and checking if it makes the other polynomial equal to zero.Polynomial division



Polynomial divisionmason5
Ã˝
This document provides instructions for dividing polynomials. It explains that to divide polynomials, you first divide the divisor by the dividend by dividing one variable at a time. Synthetic division is also covered, which divides polynomials by only the root of the divisor.Module 1 polynomial functions



Module 1 polynomial functionsdionesioable
Ã˝
This module introduces polynomial functions of degree greater than 2. It covers identifying polynomial functions from relations, determining the degree of a polynomial, finding quotients of polynomials using division algorithm and synthetic division, and applying the remainder and factor theorems. The document provides examples and practice problems for each topic. It aims to teach students how to work with higher degree polynomial functions.multiplication properties



multiplication propertiesAlex Blank
Ã˝
This document discusses several multiplication properties:
1) The commutative property, which states that multiplying two numbers results in the same product regardless of order.
2) The zero property of multiplication, where any number multiplied by zero equals zero.
3) The identity property of multiplication, where any number multiplied by one equals that original number.
It instructs students to practice these properties by completing independent practice questions and a re-teach page in their workbook.On Application of the Fixed-Point Theorem to the Solution of Ordinary Differe...



On Application of the Fixed-Point Theorem to the Solution of Ordinary Differe...BRNSS Publication Hub
Ã˝
Similar to Lesson 3.1 factorisation (20)
Synthetic and Remainder Theorem of Polynomials.ppt



Synthetic and Remainder Theorem of Polynomials.pptMarkVincentDoria1
Ã˝
This document discusses synthetic division, a shortcut method for long division of polynomials when dividing by divisors of the form x - k. Synthetic division works by setting up an array and adding terms in columns, multiplying the results by -k. The remainder obtained has an important interpretation related to the Remainder Theorem - evaluating the polynomial function at x = k. The Factor Theorem also relates dividing a polynomial by (x - k) to determining if (x - k) is a factor. Examples demonstrate using synthetic division and these theorems to factor polynomials and find zeros.Chapter 9 differentiation



Chapter 9 differentiationatiqah ayie
Ã˝
This document provides an explanation of differentiation and examples of calculating limits and derivatives using the first principle definition of the derivative. It begins by defining the limit of a function and providing examples of evaluating limits. It then introduces the concept of the derivative as the slope of the tangent line to a curve and explains how to calculate derivatives using small changes in x and y. The document provides examples of finding derivatives using this first principle definition. It also discusses rules for deriving composite functions and products of polynomials. Exercises are provided throughout for students to practice differentiation.Chapter 9- Differentiation Add Maths Form 4 SPM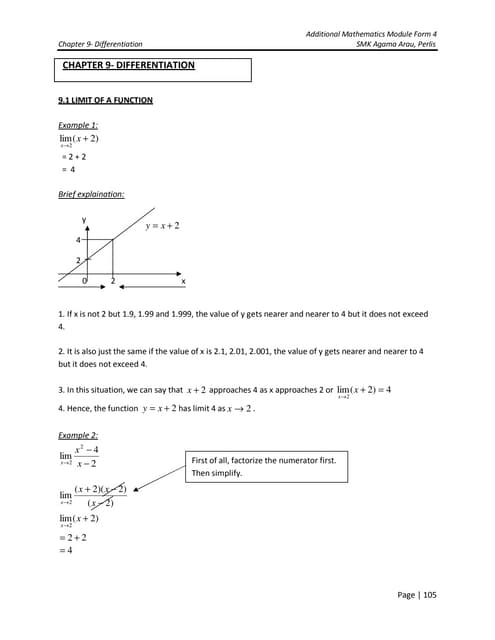



Chapter 9- Differentiation Add Maths Form 4 SPMyw t
Ã˝
This document provides an explanation of differentiation and examples of calculating limits and derivatives using the first principle definition of the derivative. It begins by defining the limit of a function and providing examples of evaluating limits. It then introduces the concept of the derivative as the slope of the tangent line to a curve and explains how to calculate derivatives using small changes in x and y. The document provides examples of finding derivatives using this first principle definition. It also discusses rules for deriving composite functions and products of polynomials. Exercises are provided throughout for students to practice differentiation.Algebra part 2



Algebra part 2Nadrah Afiati
Ã˝
This document summarizes the history of algebra, beginning with the contributions of Al-Khwarizmi. It discusses how Al-Khwarizmi synthesized Greek and Hindu knowledge and introduced the concepts of algebra, including the use of zero. It then explains the six standard forms Al-Khwarizmi used to reduce equations. Next, it provides examples and explanations of how to perform basic algebraic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and exponents on algebraic expressions. Finally, it discusses operations on fractions including simplifying, adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing fractions with algebraic expressions.Algebra



AlgebraNadrah Afiati
Ã˝
This document summarizes the history of algebra, beginning with the contributions of Al-Khwarizmi. It discusses how Al-Khwarizmi synthesized Greek and Hindu knowledge and introduced the concepts of algebra, including the use of zero. It then explains the six standard forms Al-Khwarizmi used to reduce equations. Next, it provides examples and explanations of how to perform operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and exponents on algebraic expressions. Finally, it discusses operations on fractions including simplifying, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of algebraic fractions.Implicit Differentiation, Part 1



Implicit Differentiation, Part 1Pablo Antuna
Ã˝
The document discusses implicit differentiation, which allows one to find the derivative of functions defined by a relation rather than explicitly. It gives an example of implicitly differentiating the relation x^2 + y^2 = 25 using the chain rule. Applying implicit differentiation and the chain rule derives the solution y = -x/y, which verifies the original implicit definition of the function.Solutions of a linear equation



Solutions of a linear equationjulienorman80065
Ã˝
1) The document discusses using the distributive property to solve linear equations and discusses how not all linear equations have solutions. It provides examples of using the distributive property to both simplify and expand expressions.
2) The distributive property is applied only to terms within a group and not to terms outside of the group. An equation has no solution if it can be transformed into an untrue statement when solving.
3) The document concludes by reminding students how to use the distributive property to transform equations and that some equations have no solutions. It provides recommendations for additional practice on IXL.Polynomials Grade 10



Polynomials Grade 10ingroy
Ã˝
This document provides instructions on how to multiply, divide, and factor polynomials. It discusses:
1) Multiplying polynomials by distributing terms and using FOIL for binomials.
2) Dividing polynomials using long division.
3) Factoring polynomials using grouping, finding two numbers whose product is the constant and sum is the coefficient, and recognizing difference of squares.Long division, synthetic division, remainder theorem and factor theorem



Long division, synthetic division, remainder theorem and factor theoremJohn Rome Aranas
Ã˝
This document summarizes four methods for working with polynomials: long division, synthetic division, the remainder theorem, and the factor theorem. It provides examples of using each method to divide the polynomial 4x^4 + 2x^3 + x + 5 by the divisor x + 2. Both long division and synthetic division yield a quotient of 4x^3 - 6x^2 + 12x - 23 and remainder of 51. The remainder theorem and factor theorem also verify this solution.solving a trig problem and sketching a graph example problems



solving a trig problem and sketching a graph example problemsTyler Murphy
Ã˝
We go through (in great detail) a problem involving solving a trig problem and a problem involving sketching a graphMathematics 9 Quadratic Functions (Module 1)



Mathematics 9 Quadratic Functions (Module 1)Juan Miguel Palero
Ã˝
This learner's module discusses or talks about the topic of Quadratic Functions. It also discusses what is Quadratic Functions. It also shows how to transform or rewrite the equation f(x)=ax2 + bx + c to f(x)= a(x-h)2 + k. It will also show the different characteristics of Quadratic Functions.Lesson 1: Functions and their representations (slides)



Lesson 1: Functions and their representations (slides)Mel Anthony Pepito
Ã˝
The function is the fundamental unit in calculus. There are many ways to describe functions: with words, pictures, symbols, or numbers.Lesson 1: Functions and their representations (slides)



Lesson 1: Functions and their representations (slides)Matthew Leingang
Ã˝
The function is the fundamental unit in calculus. There are many ways to describe functions: with words, pictures, symbols, or numbers.
Module 1 quadratic functions



Module 1 quadratic functionsdionesioable
Ã˝
This module introduces quadratic functions. It discusses identifying quadratic functions as those with the highest exponent of 2, rewriting quadratic functions in general form f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c and standard form f(x) = a(x-h)^2 + k, and the key properties of quadratic graphs including the vertex and axis of symmetry. The module provides examples of identifying quadratic functions from equations and ordered pairs/tables and rewriting quadratic functions between general and standard form using completing the square.Calculus 08 techniques_of_integration



Calculus 08 techniques_of_integrationtutulk
Ã˝
Trigonometric substitutions can help evaluate integrals involving trigonometric functions. The document provides examples of using trigonometric substitutions to evaluate integrals of powers of sine and cosine functions. Specifically:
1) Integrals of powers of sine and cosine can be evaluated by rewriting the functions using trigonometric identities and then substituting variables. For example, sin5x can be rewritten as sinx(sin2x)2 and evaluated using the substitution u=cosx.
2) More complex integrals may require multiple steps and identities. For example, evaluating sin6x requires rewriting sin2x using an identity and then integrating four resulting terms.
3) Trigonometric substitutions allow rewriting integrals involvingMaths Notes - Differential Equations



Maths Notes - Differential EquationsJames McMurray
Ã˝
This document summarizes methods for solving ordinary differential equations (ODEs). It discusses:
1) Types of ODEs including order, degree, linear/nonlinear.
2) Four methods for solving 1st order ODEs: separable variables, homogeneous equations, exact equations, and integrating factors.
3) Solutions to higher order linear ODEs using complementary functions and particular integrals.
4) Finding complementary functions and particular integrals for ODEs with constant coefficients.Em05 pe



Em05 penahomyitbarek
Ã˝
The document provides examples and explanations for solving various types of polynomial equations, beginning with linear equations and then simultaneous linear equations. It then introduces quadratic equations.
Key steps for solving linear equations include isolating the variable, usually by subtracting or dividing both sides by a constant. For simultaneous linear equations, common techniques are elimination (subtracting equations to remove a variable) and substitution.
Several examples demonstrate solving systems of two and three linear equations graphically or algebraically. The document emphasizes setting up equivalent equations to efficiently eliminate variables. Finally, quadratic equations are introduced but no examples are provided.More from A V Prakasam (6)
Basics of Vedic Mathematics - Multiplication (1 of 2)



Basics of Vedic Mathematics - Multiplication (1 of 2)A V Prakasam
Ã˝
An e-learning module based on ‘Vedic Mathematics’ by Jagadguru Swami Sri Bharati Krishna Tirthaji Maharaja.
Note: The PowerPoint version of this presentation has animation and transitions. So some slides may appear cluttered or odd since these features may not be supported in ∫›∫›fl£Share.Lesson 2.2 division



Lesson 2.2 divisionA V Prakasam
Ã˝
The document describes the Paravartya method for division of algebraic expressions. It begins by explaining the method using an example of dividing 12x^2 - 8x - 32 by x - 2. It shows setting up the problem in two columns, with the divisor in column 1 and decreasing powers of x in column 2. The dividend coefficients are placed below, and the quotient terms are calculated by multiplying the prior term by the divisor coefficient and adding. Several more examples are provided to illustrate dividing polynomials. The method is then explained for divisors with more than one term, and examples are given. Finally, applications to dividing numbers are demonstrated.Lesson 2.1 division



Lesson 2.1 divisionA V Prakasam
Ã˝
The document discusses the Nikhilam method for division. It provides examples and explanations for dividing numbers with divisors of 9, 8, 7 and 6. There are four cases covered: 1) divisor of 9 with 2-digit or more dividends, 2) divisor of 9 with 3+ digit dividends, 3) divisor of 9 with remainders greater than 9, and 4) divisors of 8, 7, 6. The method involves placing digits below a line, adding adjacent digits, and using remainders to get the quotient and remainder. Worked examples with step-by-step explanations are provided for each case.Lesson 1.2 multiplication



Lesson 1.2 multiplicationA V Prakasam
Ã˝
The Urdhva-Tirayk Sutra describes a method for multiplying multi-digit numbers by representing each number as the sum of its digits multiplied by powers of ten, then distributing and combining terms. It provides rules for determining each digit of the product by multiplying corresponding digits of the factors and adding carry values. Examples show applying the method to multiply numbers, calculate areas, volumes, and solve word problems involving currency conversions. The use of vinculums to represent negative digits is also introduced.Lesson 1.1 multiplication



Lesson 1.1 multiplicationA V Prakasam
Ã˝
This document introduces the Nikhilam Sutra, a method of Vedic mathematics for multiplication. It explains the principles and provides examples of multiplying numbers near and away from multiples of 10 using appropriate bases. The key steps are to make the numbers equal in digits, choose a base, find the differences from the base, add the numbers and differences, and multiply the differences. It also covers cases where the numbers are slightly above or below multiples and proportional methods for numbers with rational relationships. Practice problems are provided to demonstrate applying the sutra.Lesson 2.3 division



Lesson 2.3 divisionA V Prakasam
Ã˝
The document describes the Urdhva Tiryak method of division from Vedic mathematics. It provides examples to illustrate the method. For algebraic divisions, the divisor terms are divided in descending order to obtain the quotient terms. The examples show finding the quotient and remainder when dividing polynomials using this method. In the recap, it notes this method is well-suited for algebraic expressions but more difficult for arithmetic calculations, and each of the Vedic division methods only apply to certain cases rather than providing a single general division algorithm.Lesson 3.1 factorisation
- 1. Factorisation of Simple Quadratics Factorisation of Simple Quadratcis Example 1: Factorise x2+7x+10 When the coefficient of x2 is 1, factorisation is easy even according to the current system. Split the middle coefficient into two parts so that their sum is the middle coefficient and their product is the absolute term. In this example split 7 into 5 and 2 sothat 5+2=7 and 5X2=10. Then the facotrs can be written as (x+2)(X+5) But in the case of quadratics whose coefficent of x2 is not unit, the students depend upon a multi-step method. For example: Example 2: Factorise 2x2 +5x+2 2x2 +5x+2 = 2x2+4x+x+2 = 2x(x+2)+1(x+2) = (2x+1)(x+2) The vedic system, however, makes the factorisation symple through two small sub-sutras – Anurupyena and Adyamadyenantyamantyena, which mean ‘proportionately’ and ‘the first by the first and the last by the last’. This will be explained in the next slide.
- 2. Factorisation of Simple Quadratics Consider the previous example – 2x2+5x+2 (i) Split the middle quotient, 5x, into two parts so that the coefficient of the first part is the same as the ratio of the second part to the last quotient. In other words split 5 into 4 and 1 so that the ration2:4 is the same as the ratio1:2. now this ratio 1:2 is one factor which is x+s (ii) The second factor is obtained by dividing the first quotient of the quadratic, i.e. 2x 2, by the first quotient of the factor already found i.e. x, giving 2x and the last quotient of the quadratic i.e. 2 by the last quotient of the factor already found i.e. by 2 giving 1. The second factory is then 2x+1 The following additional examples would be found useful; Examples: 1. 2x2-5x-3 = (x+3)(2x-1) 2. 2x2+7x+5 = (x+1)(2x+5) 3. 2x2+9x+10 = (x+2)(2x+5) 4. 2x2-5x-3 = (x-3)(2x+1) 5. 9x2-15x+4 = (3x-1)(3x-4)


