Lesson template
- 1. LESSON TEMPLATE CURRICULAR STATEMENT Constructing different dimensions of knowledge among pupils about the structure of human heart through observation, identification, group discussion and lecturing and evaluation through participation in group activities and questioning. CONTENT ANALYSIS Terms Heart, sternum, thoracic cavity, pericardium, pericardial fluid, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, superior venacava, inferior venacava, aorta, tricuspid value, bicuspid valve, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein. Facts ï· Circulatory system in higher forms of life consists of the heart, blood and the blood vessels. PRELIMINARY DETAILS Name of the teacher : Priya V P Standard : IX Name of the school : M.T.G.H.S., Kottarakkara Strength : 57/59 Subject : Biology Date :17/8/15 Unit : Circularory Pathways Duration : 45 minutes Topic : Heart - Structure
- 2. ï· Heart is completely a muscular. ï· Heart acts as a pumping organ. ï· Heart plays a major role in transporting the food particles absorbed by the blood to different parts of the body. ï· In human, the heart is situated behind the sternum in the thoracic cavity. ï· A personâs heart is generally as large as his or her fist. ï· Adult human heart is approximately 12 cm long, 9 cm broad and weighs about 300 grams. ï· Pericardium is the double membrane which covers heart. Concepts Major concept ï· Heart is the central pumping stations in our body, which has complex structure. Minor concepts ï· Heart is situated in the thoracic cavity. ï· Human heart has his four chambers â two atria and two ventricles. ï· Pulmonary artery carries blood from heart to lungs and pulmonary vein carries blood from lungs to heart. ï· Superior and inferior venacavae collect impure blood from different body parts and give it to heart. ï· Valves are seen between atrium and ventricle. ï· Blood enter and leaves the heart by the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the cardiac muscles. LEARNING OUTCOMES Enable the pupils o develop; ï· Factual knowledge about the structure of heart through
- 3. - Recalling the terms, facts and concepts mentioned in the content analysis - Remembering the position and size of heart ï· Conceptual knowledge about the structure of heart through - Recognising the four chambers of heart - Understanding the functions of each chamber ï· Procedural knowledge about the structure of heart through - Identifying the weight, position and protective structures of heart - Listing the chambers, valves and blood vessels of heart ï· Metacognitive knowledge about the structure of heart through - Realizing the complex structure of heart - Executing the activities as per the instruction ï· Scientific attitude about the structure of heart through developing knowledge about the structural complexity. ï· Different process skills, - Observation skill through viewing the chart - Communication skill through participating in group work PREREQUISITES ï· Heart is the central pumping organ of our body ï· Heart is a muscular organ TEACHING LEARNING RESOURCES ï· Chart showing the structure of heart ï· Activity cards for group activity
- 4. TEACHING LEARNING INTERACTION Classroom interaction procedure Pupils response Preparation Teacher stats the class with friendly talks and asks some questions How the water in well reaches to tank? Through pipes Which machine helps for this pumping of water from well? Motor Likewise is there any motor in our body? Pupils say their own answers Which is the water in our body? Blood Which are the pipes in our body? Blood vessels Then who pumps blood to blood vessels? Heart Yes. Its heart. Today we are going to discuss about heart âHeartâ [BB] Presentation Activity 1 Teacher divides the students into groups and provides them activity card which contains questions Students try to find out the related to the position , shape and protective membranes of heart. The answers are given as jumbled answers words .Teacher instructs the students to find out the correct answers. Finally teacher explains detail Pupils listen carefully about the answers. ï· Heart is situated in âĶâĶ.. cavity C I C A R O H T ï· Heart is roughly âĶâĶ. in shape L A C I N O C ï· The double membrane that protects heart is âĶ. M U I D R A C I R E P ï· âĶâĶ. fluid protects heart from external shocks L A D I R A R I C E P ï· Boney protection of heart is âĶâĶ and âĶâĶ S B I R , M U N T E R S
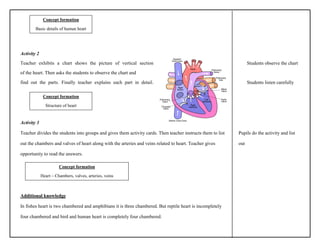
- 5. Activity 2 Teacher exhibits a chart shows the picture of vertical section Students observe the chart of the heart. Then asks the students to observe the chart and find out the parts. Finally teacher explains each part in detail. Students listen carefully Activity 3 Teacher divides the students into groups and gives them activity cards. Then teacher instructs them to list Pupils do the activity and list out the chambers and valves of heart along with the arteries and veins related to heart. Teacher gives out opportunity to read the answers. Additional knowledge In fishes heart is two chambered and amphibians it is three chambered. But reptile heart is incompletely four chambered and bird and human heart is completely four chambered. Concept formation Basic details of human heart Concept formation Structure of heart Concept formation Heart â Chambers, valves, arteries, veins
- 6. Closure Heart is the central pumping station of human body. In man heart is situated behind the sternum in the Students listen carefully thoracic cavity, between the lungs and tilted slightly towards left. A double membrane called pericardium covers and protects the heart. Human heart has four chambers- two atria and two ventricles, separated by muscular walls. Valves are present between the atrium and ventricles to obstruct the backward flow of blood. Superior and inferior venavae collect impure blood from different body parts and gives to heart. Pulmonary artery carries impure blood to lungs for purification. Purified blood is transported to heart through pulmonary vein. Aorta carries pure blood all over the body FORMATIVE EVALUATION PROCEDURES Review questions 1. Where heart is situated? 2. Name the double membrane which protects heart 3. Which are the four chambers of heart? 4. What is the function of valves? 5. Which blood vessel carries impure blood from heart? 6. Which is the largest blood vessel in our body? Follow up activities 1. Draw a neatly labeled diagram of the structure of heart in your science diary 2. âHeart is a complex organâ. Justify and prepare a short note.


![TEACHING LEARNING INTERACTION
Classroom interaction procedure Pupils response
Preparation
Teacher stats the class with friendly talks and asks some questions
How the water in well reaches to tank? Through pipes
Which machine helps for this pumping of water from well? Motor
Likewise is there any motor in our body? Pupils say their own answers
Which is the water in our body? Blood
Which are the pipes in our body? Blood vessels
Then who pumps blood to blood vessels? Heart
Yes. Its heart. Today we are going to discuss about heart âHeartâ [BB]
Presentation
Activity 1
Teacher divides the students into groups and provides them activity card which contains questions Students try to find out the
related to the position , shape and protective membranes of heart. The answers are given as jumbled answers
words .Teacher instructs the students to find out the correct answers. Finally teacher explains detail Pupils listen carefully
about the answers.
ï· Heart is situated in âĶâĶ.. cavity C I C A R O H T
ï· Heart is roughly âĶâĶ. in shape L A C I N O C
ï· The double membrane that protects heart is âĶ. M U I D R A C I R E P
ï· âĶâĶ. fluid protects heart from external shocks L A D I R A R I C E P
ï· Boney protection of heart is âĶâĶ and âĶâĶ S B I R , M U N T E R S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessontemplate-151030181509-lva1-app6892/85/Lesson-template-4-320.jpg)