lever
Download as PPTX, PDF5 likes618 views
This document discusses the design of a bell crank lever. It begins with introductions to levers, including their classification into three types based on the position of the fulcrum, effort, and load. It then describes various lever types like angular, bell crank, and compound levers. The document outlines the design procedure for a bell crank lever, including calculating the required effort, designing the fulcrum pin, pins at points A and B, and determining the lever thickness and width to withstand bending stresses.
1 of 14
Downloaded 28 times
![Shri Sâad Vidya Mandal Institute of Technology
Topic : LEVER , CLASSIFICATION OF LEVER,TYPES OF
LEVER AND DESIGN PROCIDRE OF BELL CRANK LEVER
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
MACHINE DESIGN AND INDSTRIAL DRAFTING
PREPARED BY :
1] Rana manthan - 170450119044
2] Shah jay - 170450119046
3] Shah rishabh - 170450119047
4] Shah sheril - 170450119048](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdidlever-190313112109/85/lever-1-320.jpg)









Recommended
Lecture 2. linkages



Lecture 2. linkageskidanemariam tesera
Ėý
The document discusses various types of linkages and mechanisms used in machinery, including:
- Four-bar linkages and their inversions like crank-rocker, double crank, and double rocker mechanisms.
- šÝšÝßĢr-crank mechanisms which convert rotary to reciprocal motion, and their inversions.
- Quick-return mechanisms like the drag link and crank and slotted lever types, which provide a slower cutting stroke and faster return stroke.
- Other topics covered include transmission angles in four-bar linkages and the Scotch yoke mechanism.Working, Construction And Types of Band Brakes



Working, Construction And Types of Band BrakesKhushal Hudke
Ėý
Band brakes consist of a flexible band wrapped around a rotating drum that is used to slow or stop the drum's rotation. The band is made of materials like leather or steel lined with friction material. One end of the band is attached to a lever's fulcrum while the other end attaches to the lever at a distance, allowing an external force applied to the lever to tighten the band against the drum. When the band tightens, friction between the band and drum is created, applying a tangential force to the drum to slow or stop its movement. Band brakes can be classified as simple or differential, with differential brakes being self-energizing and potentially self-locking.Turning moment diagrams



Turning moment diagramsPOLAYYA CHINTADA
Ėý
The document discusses turning moment diagrams, which graphically represent the turning moment or crank effort for various positions of a crank. It provides details on plotting turning moment diagrams, including representing turning moment on the vertical axis and crank angle on the horizontal axis. The document also discusses how the area of a turning moment diagram represents the work done per revolution. It further discusses turning moment diagrams for engines with multiple cylinders and how flywheels help control fluctuations in speed caused by variations in engine turning moment during each operating cycle.Cam and follower theory prof. sagar a dhotare



Cam and follower theory prof. sagar a dhotareSagar Dhotare
Ėý
This ppt covers following points,
Classification of Cam and Follower
Terminology of cam
Importance of Pressure angle
Application of Cam and Follower
Importance of cam and follower
Friction in Clutch



Friction in ClutchRohit Singla
Ėý
This document discusses different types of clutches. It begins by defining a clutch as a mechanical device that connects and disconnects two rotating shafts to transmit or disengage power. It then describes several types of clutches including disc clutches, cone clutches, centrifugal clutches, and positive contact clutches. The document also provides details on single plate and multi-plate clutch designs, materials, and operating principles. It explains how clutches transmit torque via friction between contacting surfaces.Turning Moment Diagram and Flywheel



Turning Moment Diagram and Flywheelnmahi96
Ėý
The turning moment diagram graphically represents the torque required by an engine at different crank angles. It is used to determine the fluctuation of energy in the engine and the role of the flywheel in reducing speed variations. The flywheel stores excess energy produced during power strokes and releases it during non-power strokes, allowing the crankshaft to rotate at a more uniform speed. The maximum difference between the energy stored in the flywheel at its highest and lowest points is known as the maximum fluctuation of energy. Larger flywheels can reduce speed fluctuations more, but require more space.Design of Band Brake



Design of Band BrakeJawed Shaikh
Ėý
The document discusses band brakes, including their parts, efficiency, advantages, and disadvantages. It notes that band brakes have a simple design, are easily maintained, and can work properly for years if kept clean and rust-free. It also provides information on a differential band brake, including dimensions, material properties, coefficients of friction, and formulas to calculate tensions, actuating force, and torque capacity to determine if it is self-locking.theory of machine



theory of machinepawankumar2495
Ėý
This document provides an overview of machine learning concepts for diploma and polytechnic students. It covers topics such as simple mechanisms, kinematic pairs, kinematic chains, and inversions. Specifically, it discusses four bar link mechanisms, the single slider crank chain, and their various inversions including beam engines, the coupling rod of locomotives, and Watt's indicator mechanism. It also provides examples of kinematic pairs like lower and higher pairs and defines terms like links, mechanisms, and machines. Diagrams are included to illustrate key concepts.Gears mom2 2



Gears mom2 2abdul ahad noohani
Ėý
1. The minimum number of teeth on the pinion to avoid interference is 10 teeth. The corresponding number of teeth on the wheel is 30 teeth.
2. The length of path of contact and arc of contact are calculated based on the module, pressure angle, and number of teeth.
3. The number of pairs of teeth in contact, or contact ratio, is calculated as the ratio of the arc of contact to the circular pitch.
4. The maximum velocity of sliding is calculated using the velocity ratio, pinion rpm, pitch circle radii, and pressure angle.Unit 3.2 Design of Clutches



Unit 3.2 Design of ClutchesYugal Kishor Sahu
Ėý
Here are the steps to solve this problem:
1. Power at 25% overload = 15 * 1.25 = 18.75 kW
2. Torque = Power / Speed = 18.75 * 1000 / 720 = 26 Nm
3. Engagement speed = 0.75 * 720 = 540 rpm
4. Given: No. of shoes = 4
Outside dia. of pulley = 35 cm = 0.35 m
Inside dia. of pulley rim = 32.5 cm = 0.325 m
Width of pulley = 25 cm = 0.25 m
5. Design the shoes and springs based on given data and centrifugal clutch formulae.
6. Check initial clearance between frictionGovernor



GovernorRonak Soni
Ėý
This presentation provide complete study of governor for GTU as well as PU and other university students. It covers basic terminologies, characteristics of governor, diagram, derivations etc. for proper understanding.Inversion of mechanism



Inversion of mechanismR A Shah
Ėý
Inversion of Mechanism
Inversion of Four bar Mechanism
Inversion of Single slider crank chain mechanism
Inversions Of Double šÝšÝßĢr Crank Chain
1.4 law of gearing



1.4 law of gearingKiran Wakchaure
Ėý
This document discusses the law of gearing in three main points:
1) The common normal at the point of contact between gear teeth must always pass through the pitch point. This is the fundamental condition for designing gear teeth profiles.
2) The angular velocity ratio between two gears must remain constant throughout meshing.
3) The angular velocity ratio is inversely proportional to the ratio of the distances of the pitch point P from the gear centers O1 and O2. The common normal intersecting the line of centers at P divides the center distance inversely proportional to the angular velocity ratio.Momentum & Collisions



Momentum & CollisionsTimothy Welsh
Ėý
This document provides an overview of momentum and collisions in physics. It defines momentum as the product of an object's mass and velocity, and explains how momentum can be changed through the application of an impulse, which is the product of force and time. The document also discusses conservation of momentum, stating that the total momentum of a system is always conserved during collisions or interactions. Several examples of collision calculations are worked through, including explosions, "hit and stick" collisions, and "hit and rebound" collisions.Clutches



Clutchesparth98796
Ėý
- Clutches are used to connect or disconnect a driving shaft from a driven shaft. They allow transmission of power from one shaft to another that needs to be started or stopped frequently.
- There are two main types of clutches: positive clutches and friction clutches. Cone clutches are a type of friction clutch with conical working surfaces.
- Torque transmission in clutches is calculated using either a uniform pressure theory or uniform wear theory. These theories make assumptions about the pressure distribution across the clutch plates or cones.Kinemetic chains, Pairs, Joints, Four bar Mechanisms (KOM)



Kinemetic chains, Pairs, Joints, Four bar Mechanisms (KOM)University of Windsor
Ėý
Basic Definitions and ideas about KOM, Overview of types of joints, links, motions, mechanisms with diagrams and suitable figures. Turning Moment Diagram and Flywheel



Turning Moment Diagram and FlywheelRonak Soni
Ėý
This presentation gives you basic concept of turning moment diagram used for I.C. Engine and usefulness of flywheel.Porter Governor



Porter GovernorPrem Kumar Soni
Ėý
Porter Governor is a modification of Watt Governor with central load attached to the sleeve. This load moves up and down the central spindle. The additional force increases the speed of revolution required to enable the balls to rise to any predetermined level.Machine Design Belts



Machine Design BeltsMayank Bhatia
Ėý
This document provides an overview of belt drives for power transmission. It defines a belt as a flexible loop used to link rotating shafts. Belts transmit power efficiently and can accommodate shafts that are not axially aligned. The document outlines the advantages of belts, such as being cheap, vibration-free, and tolerant of misalignment. It also notes some disadvantages like varying angular velocity. Different types of belts are described, including flat belts, V-belts, timing belts, and others. Key factors in belt selection and design are also summarized.Lesson 14-idlers-and-pulleys



Lesson 14-idlers-and-pulleysmkpq pasha
Ėý
This document discusses idlers and pulleys used in conveyor systems. It describes different types of idlers like carry idlers and return idlers, and their purposes in shaping the belt load and supporting the belt. It discusses CEMA classifications for idlers and common idler diameters. It also describes factors involved in selecting idlers like idler load, belt tension, and misalignment load. For pulleys, it discusses types like drum and wing pulleys and their purpose in transmitting power and changing belt direction. It covers CEMA duty classifications and describes pulley lagging used to increase traction. The document concludes with discussing belt tensions at different locations and how to select pulley diameter based on wrap angle and belt tension.Belt drive. ppt



Belt drive. pptSadia Textile
Ėý
Like Comment and download
Belt is a Flexible Mechanical element
that transmit power from one shaft to another
Belt is a Flexible Mechanical element
that transmit power from one shaft to another
Gear Train
Ex: Automobile, engines etc.
Chain Drive
Ex : Bi-cycle , Motor cycle etc.
Belt Drive
Ex: Rice mills, sewing machine etc.
Rope Drive
Ex: lift, crane etctransmission.pdf



transmission.pdfhalilyldrm13
Ėý
The document discusses vehicle resistance and gear boxes. It describes the main types of resistance that affect vehicle motion including air resistance, rolling resistance, and gradient resistance. It then discusses different types of gear boxes including sliding mesh gear boxes, constant mesh gear boxes, and synchromesh gear boxes. Sliding mesh gear boxes have gears that can slide into mesh, constant mesh gear boxes always have gears meshed but use dog clutches to engage different gears, and synchromesh gear boxes first synchronize the speed of gears before engaging them using synchronizers.Types of Dynamometers



Types of DynamometersHarsh Pathak
Ėý
Introduction of dynamomter which is mention below:
Absorption dynamometer
Prony brake dynamometer
Rope brake dynamometer
Transmission dynamometer
Belt transmission dynamometer
Epicyclic dynamometer
Torsion dynamometer
V belt drives



V belt drivesabdul ahad noohani
Ėý
V-belts are used to transmit power between pulleys in factories and workshops. They are made of fabric, cords, and rubber molded into a trapezoidal shape to fit into the V-grooved pulleys. The belts grip the pulleys through a wedging action caused by the 30-40 degree V-groove. Clearance is provided at the bottom of the groove to prevent wear from making the groove narrower. The driving tension ratio between pulleys depends on factors like the groove angle and coefficient of friction between the belt and groove.Governor



Governorankit ramdin
Ėý
This document discusses various types of governors used to regulate engine speed. It describes centrifugal governors that use rotating balls to control engine speed based on centrifugal force. Specific governors discussed include the Watt, Porter, Proell, Hartnell, Hartung, Wilson-Hartnell, and Pickering governors. Equations are provided for each governor relating factors like ball mass, radius of rotation, spring stiffness, and centrifugal force to the governor's operation and ability to control engine speed under varying loads.Velocity and Acceleration analysis in kinematics of mechanism



Velocity and Acceleration analysis in kinematics of mechanismDr.R. SELVAM
Ėý
This document provides an overview of topics related to velocity and acceleration analysis of mechanisms using graphical methods. It discusses analyzing the velocity and acceleration of links in four-bar mechanisms, slider-crank mechanisms, and other simple mechanisms using vector polygons. It also covers determining the relative velocity and acceleration of particles on common links and separate links, as well as the Coriolis component of acceleration, angular velocity, angular acceleration of links, and velocity of rubbing.Gear Drives for Diploma Students first and second Year



Gear Drives for Diploma Students first and second YearMechTech3
Ėý
Here is the PPT on the Gear Drives for Diploma Students of first and second year. Based on Mechanical Engineering diploma. The data for PPT is collected From book so don,t worry about PPT.Ppt mech 5sem_dom



Ppt mech 5sem_domvbrayka
Ėý
This document discusses dynamics of machinery and includes sections on force analysis, balancing, and free vibration. The force analysis section covers static and dynamic force analysis, D'Alembert's principle, and analyzing forces in reciprocating engines. The balancing section discusses static and dynamic balancing of rotating and reciprocating masses. Methods for balancing single, multi-cylinder, and V-engines are presented. The free vibration section introduces concepts of vibration systems including degrees of freedom, undamped and damped free vibration, and natural frequencies of single and multi-rotor shaft systems. Sample problems are provided on balancing multiple rotating masses and analyzing the vibration of a spring-mass system.Presentation on module 2 lecture 2.pptx



Presentation on module 2 lecture 2.pptxAnantaKumarNandi
Ėý
A rocker arm transfers radial movement from a cam lobe into linear movement to open a poppet valve. One end of the rocker arm is raised and lowered by the rotating camshaft lobe, while the other end presses down on the valve stem to open the valve. When the camshaft lobe permits the outside of the arm to return, the inside rises and allows the valve spring to close the valve. The rocker arm is designed to withstand bending loads and is usually an I-section. Design considerations include the ratio of pin lengths to diameters, permissible bearing pressures, boss and eye diameters relative to pin diameters, and roller diameter.Design of lever (machine design & industrial drafting )



Design of lever (machine design & industrial drafting )Digvijaysinh Gohil
Ėý
This document provides information on the design of levers, including rocker arms, bell crank levers, and safety valve levers. It discusses the key lever components like the fulcrum, effort arm, and load arm. It describes how to calculate mechanical advantage, leverage, and determine the necessary effort. The procedures for designing the fulcrum pin, boss diameter, and lever cross-section are also outlined. Design examples are provided for a rocker arm, bell crank lever, and safety valve lever. The document contains the essential steps, formulas, and considerations for properly sizing and designing lever mechanisms.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Gears mom2 2



Gears mom2 2abdul ahad noohani
Ėý
1. The minimum number of teeth on the pinion to avoid interference is 10 teeth. The corresponding number of teeth on the wheel is 30 teeth.
2. The length of path of contact and arc of contact are calculated based on the module, pressure angle, and number of teeth.
3. The number of pairs of teeth in contact, or contact ratio, is calculated as the ratio of the arc of contact to the circular pitch.
4. The maximum velocity of sliding is calculated using the velocity ratio, pinion rpm, pitch circle radii, and pressure angle.Unit 3.2 Design of Clutches



Unit 3.2 Design of ClutchesYugal Kishor Sahu
Ėý
Here are the steps to solve this problem:
1. Power at 25% overload = 15 * 1.25 = 18.75 kW
2. Torque = Power / Speed = 18.75 * 1000 / 720 = 26 Nm
3. Engagement speed = 0.75 * 720 = 540 rpm
4. Given: No. of shoes = 4
Outside dia. of pulley = 35 cm = 0.35 m
Inside dia. of pulley rim = 32.5 cm = 0.325 m
Width of pulley = 25 cm = 0.25 m
5. Design the shoes and springs based on given data and centrifugal clutch formulae.
6. Check initial clearance between frictionGovernor



GovernorRonak Soni
Ėý
This presentation provide complete study of governor for GTU as well as PU and other university students. It covers basic terminologies, characteristics of governor, diagram, derivations etc. for proper understanding.Inversion of mechanism



Inversion of mechanismR A Shah
Ėý
Inversion of Mechanism
Inversion of Four bar Mechanism
Inversion of Single slider crank chain mechanism
Inversions Of Double šÝšÝßĢr Crank Chain
1.4 law of gearing



1.4 law of gearingKiran Wakchaure
Ėý
This document discusses the law of gearing in three main points:
1) The common normal at the point of contact between gear teeth must always pass through the pitch point. This is the fundamental condition for designing gear teeth profiles.
2) The angular velocity ratio between two gears must remain constant throughout meshing.
3) The angular velocity ratio is inversely proportional to the ratio of the distances of the pitch point P from the gear centers O1 and O2. The common normal intersecting the line of centers at P divides the center distance inversely proportional to the angular velocity ratio.Momentum & Collisions



Momentum & CollisionsTimothy Welsh
Ėý
This document provides an overview of momentum and collisions in physics. It defines momentum as the product of an object's mass and velocity, and explains how momentum can be changed through the application of an impulse, which is the product of force and time. The document also discusses conservation of momentum, stating that the total momentum of a system is always conserved during collisions or interactions. Several examples of collision calculations are worked through, including explosions, "hit and stick" collisions, and "hit and rebound" collisions.Clutches



Clutchesparth98796
Ėý
- Clutches are used to connect or disconnect a driving shaft from a driven shaft. They allow transmission of power from one shaft to another that needs to be started or stopped frequently.
- There are two main types of clutches: positive clutches and friction clutches. Cone clutches are a type of friction clutch with conical working surfaces.
- Torque transmission in clutches is calculated using either a uniform pressure theory or uniform wear theory. These theories make assumptions about the pressure distribution across the clutch plates or cones.Kinemetic chains, Pairs, Joints, Four bar Mechanisms (KOM)



Kinemetic chains, Pairs, Joints, Four bar Mechanisms (KOM)University of Windsor
Ėý
Basic Definitions and ideas about KOM, Overview of types of joints, links, motions, mechanisms with diagrams and suitable figures. Turning Moment Diagram and Flywheel



Turning Moment Diagram and FlywheelRonak Soni
Ėý
This presentation gives you basic concept of turning moment diagram used for I.C. Engine and usefulness of flywheel.Porter Governor



Porter GovernorPrem Kumar Soni
Ėý
Porter Governor is a modification of Watt Governor with central load attached to the sleeve. This load moves up and down the central spindle. The additional force increases the speed of revolution required to enable the balls to rise to any predetermined level.Machine Design Belts



Machine Design BeltsMayank Bhatia
Ėý
This document provides an overview of belt drives for power transmission. It defines a belt as a flexible loop used to link rotating shafts. Belts transmit power efficiently and can accommodate shafts that are not axially aligned. The document outlines the advantages of belts, such as being cheap, vibration-free, and tolerant of misalignment. It also notes some disadvantages like varying angular velocity. Different types of belts are described, including flat belts, V-belts, timing belts, and others. Key factors in belt selection and design are also summarized.Lesson 14-idlers-and-pulleys



Lesson 14-idlers-and-pulleysmkpq pasha
Ėý
This document discusses idlers and pulleys used in conveyor systems. It describes different types of idlers like carry idlers and return idlers, and their purposes in shaping the belt load and supporting the belt. It discusses CEMA classifications for idlers and common idler diameters. It also describes factors involved in selecting idlers like idler load, belt tension, and misalignment load. For pulleys, it discusses types like drum and wing pulleys and their purpose in transmitting power and changing belt direction. It covers CEMA duty classifications and describes pulley lagging used to increase traction. The document concludes with discussing belt tensions at different locations and how to select pulley diameter based on wrap angle and belt tension.Belt drive. ppt



Belt drive. pptSadia Textile
Ėý
Like Comment and download
Belt is a Flexible Mechanical element
that transmit power from one shaft to another
Belt is a Flexible Mechanical element
that transmit power from one shaft to another
Gear Train
Ex: Automobile, engines etc.
Chain Drive
Ex : Bi-cycle , Motor cycle etc.
Belt Drive
Ex: Rice mills, sewing machine etc.
Rope Drive
Ex: lift, crane etctransmission.pdf



transmission.pdfhalilyldrm13
Ėý
The document discusses vehicle resistance and gear boxes. It describes the main types of resistance that affect vehicle motion including air resistance, rolling resistance, and gradient resistance. It then discusses different types of gear boxes including sliding mesh gear boxes, constant mesh gear boxes, and synchromesh gear boxes. Sliding mesh gear boxes have gears that can slide into mesh, constant mesh gear boxes always have gears meshed but use dog clutches to engage different gears, and synchromesh gear boxes first synchronize the speed of gears before engaging them using synchronizers.Types of Dynamometers



Types of DynamometersHarsh Pathak
Ėý
Introduction of dynamomter which is mention below:
Absorption dynamometer
Prony brake dynamometer
Rope brake dynamometer
Transmission dynamometer
Belt transmission dynamometer
Epicyclic dynamometer
Torsion dynamometer
V belt drives



V belt drivesabdul ahad noohani
Ėý
V-belts are used to transmit power between pulleys in factories and workshops. They are made of fabric, cords, and rubber molded into a trapezoidal shape to fit into the V-grooved pulleys. The belts grip the pulleys through a wedging action caused by the 30-40 degree V-groove. Clearance is provided at the bottom of the groove to prevent wear from making the groove narrower. The driving tension ratio between pulleys depends on factors like the groove angle and coefficient of friction between the belt and groove.Governor



Governorankit ramdin
Ėý
This document discusses various types of governors used to regulate engine speed. It describes centrifugal governors that use rotating balls to control engine speed based on centrifugal force. Specific governors discussed include the Watt, Porter, Proell, Hartnell, Hartung, Wilson-Hartnell, and Pickering governors. Equations are provided for each governor relating factors like ball mass, radius of rotation, spring stiffness, and centrifugal force to the governor's operation and ability to control engine speed under varying loads.Velocity and Acceleration analysis in kinematics of mechanism



Velocity and Acceleration analysis in kinematics of mechanismDr.R. SELVAM
Ėý
This document provides an overview of topics related to velocity and acceleration analysis of mechanisms using graphical methods. It discusses analyzing the velocity and acceleration of links in four-bar mechanisms, slider-crank mechanisms, and other simple mechanisms using vector polygons. It also covers determining the relative velocity and acceleration of particles on common links and separate links, as well as the Coriolis component of acceleration, angular velocity, angular acceleration of links, and velocity of rubbing.Gear Drives for Diploma Students first and second Year



Gear Drives for Diploma Students first and second YearMechTech3
Ėý
Here is the PPT on the Gear Drives for Diploma Students of first and second year. Based on Mechanical Engineering diploma. The data for PPT is collected From book so don,t worry about PPT.Ppt mech 5sem_dom



Ppt mech 5sem_domvbrayka
Ėý
This document discusses dynamics of machinery and includes sections on force analysis, balancing, and free vibration. The force analysis section covers static and dynamic force analysis, D'Alembert's principle, and analyzing forces in reciprocating engines. The balancing section discusses static and dynamic balancing of rotating and reciprocating masses. Methods for balancing single, multi-cylinder, and V-engines are presented. The free vibration section introduces concepts of vibration systems including degrees of freedom, undamped and damped free vibration, and natural frequencies of single and multi-rotor shaft systems. Sample problems are provided on balancing multiple rotating masses and analyzing the vibration of a spring-mass system.Similar to lever (20)
Presentation on module 2 lecture 2.pptx



Presentation on module 2 lecture 2.pptxAnantaKumarNandi
Ėý
A rocker arm transfers radial movement from a cam lobe into linear movement to open a poppet valve. One end of the rocker arm is raised and lowered by the rotating camshaft lobe, while the other end presses down on the valve stem to open the valve. When the camshaft lobe permits the outside of the arm to return, the inside rises and allows the valve spring to close the valve. The rocker arm is designed to withstand bending loads and is usually an I-section. Design considerations include the ratio of pin lengths to diameters, permissible bearing pressures, boss and eye diameters relative to pin diameters, and roller diameter.Design of lever (machine design & industrial drafting )



Design of lever (machine design & industrial drafting )Digvijaysinh Gohil
Ėý
This document provides information on the design of levers, including rocker arms, bell crank levers, and safety valve levers. It discusses the key lever components like the fulcrum, effort arm, and load arm. It describes how to calculate mechanical advantage, leverage, and determine the necessary effort. The procedures for designing the fulcrum pin, boss diameter, and lever cross-section are also outlined. Design examples are provided for a rocker arm, bell crank lever, and safety valve lever. The document contains the essential steps, formulas, and considerations for properly sizing and designing lever mechanisms.Levers



LeversMohamed Mohamed El-Sayed
Ėý
The document discusses different types of levers used in engineering. It describes the design process for various levers including hand levers, foot levers, and cranked levers. For each type of lever, the document outlines how to determine the necessary dimensions based on the applied forces and stresses to ensure adequate strength. Design considerations include the diameter and length of pins, thickness and width of lever arms, and selection of appropriate cross sectional shapes.UNIT 4 Energy storing elements and Engine components.pptx



UNIT 4 Energy storing elements and Engine components.pptxCharunnath S V
Ėý
This document discusses various energy storing elements and engine components. It describes springs, including helical springs, leaf springs, Belleville springs, and concentric springs. It discusses the material, design, and stresses in helical springs. It also covers flywheels, connecting rods, and crankshafts as key engine components that help store and transmit energy within an engine.Levers.pdf



Levers.pdfAnkushkhansole3
Ėý
This document describes different types of levers and provides steps to design a bell crank lever and lever safety valve. It defines levers as rigid rods pivoted at a fulcrum. Leverage is the ratio of effort and load arms, while mechanical advantage is the ratio of load to effort. Types of levers include those with the fulcrum between load and effort, load between fulcrum and effort, and effort between fulcrum and load. Design of a bell crank lever involves determining effort, fulcrum reaction, pin dimensions, lever diameter, and lever cross section dimensions. Design of a lever safety valve involves determining the load value, applying equilibrium conditions, designing pins, boss dimensions, and lever crossBell Crank Lever.pptxDesign of Bell Crank Lever



Bell Crank Lever.pptxDesign of Bell Crank Leverssuser110cda
Ėý
In a bell crank lever, the two arms of the lever are at right angles.
Such type of levers are used in railway signalling, governors of Hartnell type, the drive for the air pump of condensers etc.
The bell crank lever is designed in a similar way as discussed earlier.
LEVER ACTION.pptx



LEVER ACTION.pptxDIVINE SPORTS ACADEMY
Ėý
The document defines a lever as a mechanical device that produces a turning motion around a fixed point called a fulcrum. It describes the three parts of a lever as the rigid bar, fulcrum, and force/resistance. There are three types (orders) of levers - first order levers have the fulcrum between the force and resistance, second order levers have the resistance between the fulcrum and force, and third order levers have the force between the fulcrum and resistance. Examples of each type are given from both machines and the human body. Levers provide advantages by increasing speed, range, power, or mechanical advantage.6 Mechanial springs Introduction



6 Mechanial springs Introductionnarendra varma
Ėý
The document discusses different types of mechanical springs, including helical, conical, volute, torsion, laminated/leaf, and special purpose springs. It defines key terms used in compression springs such as solid length, free length, compressed length, spring index, spring rate, and pitch. The introduction outlines common applications of springs such as cushioning shock/vibration, applying forces, controlling motion, and storing energy. Types of springs are described along with diagrams of volute and helical torsion springs. Formulas are provided for solid length, free length, spring index, and spring rate. References for further reading on the topic are listed at the end.SPRINGS.pptx



SPRINGS.pptxDhanenthiranMohan
Ėý
This document discusses different types of springs, their applications, and key terms used in compression springs. It provides information on five main types of springs: helical, conical and volute, torsion, laminated or leaf, and disc or Belleville springs. Helical springs are the most common and can be used for both compression and tension. Springs are widely used to cushion impacts, apply forces, control motion, and store energy in various mechanical applications. Key terms discussed include solid length, free length, spring index, spring rate, and pitch.Unit1 designof levers



Unit1 designof leversSomnath Kolgiri
Ėý
This document discusses the design of various types of levers, including hand levers, foot levers, and bell crank levers. It begins with an introduction to levers and their uses. The main types of levers are then described: one arm lever, two arm lever, and angular/bell crank lever. Design considerations for hand levers and foot levers are provided, including calculating the diameter of the shaft, dimensions of keys and bosses, and cross-sectional dimensions of the lever arm. Design of bell crank levers is also covered. Examples and problems for calculating lever dimensions are given. The document concludes with a brief mention of designing C-clamps and offset links.02 Design of Springs.pptx



02 Design of Springs.pptxZeeshanEjaz10
Ėý
This document discusses the design of helical compression springs. It describes different types of springs including compression, extension, torsion, and leaf springs. It covers spring characteristics such as wire diameter, mean diameter, free length, solid length, operating length, spring rate, spring index, number of coils, pitch, end configurations, and materials. The document provides equations to calculate spring stresses, deflections, and buckling loads. It includes example problems demonstrating how to analyze an existing spring and design a new spring to meet specified force and deflection requirements.Bevel gear



Bevel gearbalram yadav
Ėý
Clearance. It is the radial distance from the top of the tooth to the bottom of the tooth, in a meshing gear. A circle passing through the top of the meshing gear is known as clearance circle.
2. Total depth. It is the radial distance between the addendum and the dedendum circle of a gear. It is equal to the sum of the addendum and dedendum.
Types of loads, beams, support and support reaction calculation



Types of loads, beams, support and support reaction calculationSMEETJAKHARIA
Ėý
give information on:-
types of loads
types of beams
types of support
support reaction calculationTorsional Diagram



Torsional Diagramshafi029
Ėý
This presentation summarizes torsion and torsional diagrams. It defines torsion as the twisting of an object due to an applied torque. A torsional diagram is a two-dimensional representation of torque along an object. The presentation discusses assumptions of torsion theory, sign conventions, torsion loading, torsion formulas, failure modes, and provides a summary of key points like the highest shear stress occurring on the surface of a shaft. It was presented to fulfill the requirements of a pre-stressed concrete course.Presentation on torsional diagram



Presentation on torsional diagramGolam Mustafa
Ėý
This presentation summarizes torsion and torsional diagrams. It defines torsion as the twisting of an object due to an applied torque. A torsional diagram is a two-dimensional representation of torque along an object. The presentation discusses assumptions of torsion theory, sign conventions, torsion loading, torsion formulas, failure modes, and provides a summary of key points like the highest shear stress occurring on the surface of a shaft. It was presented to fulfill the requirements of a pre-stressed concrete course.CHAPTER 3_NAS (CASIMIRO & CRISTOBAL).pptx



CHAPTER 3_NAS (CASIMIRO & CRISTOBAL).pptxGlenChrisCasimiro
Ėý
Mechanical appliances on ships utilize mechanical principles to facilitate tasks like cargo handling, anchoring, and mooring. They provide force, motion, or control. Various forces act on ships, including external forces from waves, currents, wind, and internal forces from weight, propulsion, and tension. Mechanical concepts like the composition and resolution of forces, spans, levers, and tackles are important for understanding how machines on ships function. Tackles can multiply force but reduce speed, with single tackles using one rope and pulleys and double tackles using two ropes and pulleys.L- beams or flanged beams



L- beams or flanged beamshoneysid
Ėý
The document discusses L-beams, which are floor beams that have slabs on only one side. L-beams are common in reinforced concrete structures and experience bending moment, shear force, and torsional moment from one-sided loading. The effective width of an L-beam flange is calculated according to code recommendations based on factors like beam spacing and length. Design of L-beams involves determining the flange width, selecting a beam depth, checking moment of resistance, and adding reinforcement as needed to resist bending and shear loads.Spring test



Spring testSHAMJITH KM
Ėý
This document describes an experiment to determine the stiffness of an open and closed coil spring and the modulus of rigidity of the spring material. A spring testing machine is used to apply loads to the springs and measure the deflection. The stiffness and modulus of rigidity are calculated based on equations that relate the applied load, spring geometry, and measured deflection. Test procedures are outlined for performing compression and tension tests on open and closed coil springs. Measurements of spring dimensions, number of coils, and load-deflection data are collected and used to calculate values for stiffness, shear stress, strain energy, and modulus of rigidity.Recently uploaded (20)
Soil Properties and Methods of Determination



Soil Properties and Methods of DeterminationRajani Vyawahare
Ėý
This PPT covers the index and engineering properties of soil. It includes details on index properties, along with their methods of determination. Various important terms related to soil behavior are explained in detail. The presentation also outlines the experimental procedures for determining soil properties such as water content, specific gravity, plastic limit, and liquid limit, along with the necessary calculations and graph plotting. Additionally, it provides insights to understand the importance of these properties in geotechnical engineering applications.Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdf



Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdfARENCOS
Ėý
Biophilic design is emerging as a key approach to enhancing well-being by integrating natural elements into residential architecture. In Crete, where the landscape is rich with breathtaking sea views, lush olive groves, and dramatic mountains, biophilic design principles can be seamlessly incorporated to create healthier, more harmonious living environments.
Ų؊اØĻ اŲØŠŲاØĩŲŲ اŲاŲØīاØĶŲŲ ŲŲŲ
ŲØīØĒØŠ اŲØŪØąØģاŲŲØĐ



Ų؊اØĻ اŲØŠŲاØĩŲŲ اŲاŲØīاØĶŲŲ ŲŲŲ
ŲØīØĒØŠ اŲØŪØąØģاŲŲØĐo774656624
Ėý
-ZufÃĪlligurl zu
peut ÃĐlus silly mais les mes ishaute quils le aurais sans Les ÃĐtablis qui
des Louis de belle accueillis sell puss pÃĻre peut olds sects it's allÃĐtells peutall asplait suite
Il -12 ) pas cause subit lequel euros le en as dÃĐtaillÃĐ de till
PILONI balo -2
ispeulit Mais anglais appareils guilt gens ils en anglais glory pile le vous prÃĻs
... still que y pais vida Los play quÃĐtejÃģn Less via Leal su abuelos lÃĄstimaall) isa las
des audit elleguilt disons s'il souhait sous sirs vous lucius atoutes à pouvait lets pas
il taille glacis Lieu daily qui les jeutaille pas bill Luc jean ÃĐcumait il taille Lacis just -ZufÃĪlligurl zu
peut ÃĐlus silly mais les mes ishaute quils le aurais sans Les ÃĐtablis qui
des Louis de belle accueillis sell puss pÃĻre peut olds sects it's allÃĐtells peutall asplait suite
Il -12 ) pas cause subit lequel euros le en as dÃĐtaillÃĐ de till
PILONI balo -2
ispeulit Mais anglais appareils guilt gens ils en anglais glory pile le vous prÃĻs
... still que y pais vida Los play quÃĐtejÃģn Less via Leal su abuelos lÃĄstimaall) isa las
des audit elleguilt disons s'il souhait sous sirs vous lucius atoutes à pouvait lets pas
il taille glacis Lieu daily qui les jeutaille pas bill Luc jean ÃĐcumait il taille Lacis just-ZufÃĪlligurl zu
peut ÃĐlus silly mais les mes ishaute quils le aurais sans Les ÃĐtablis qui
des Louis de belle accueillis sell puss pÃĻre peut olds sects it's allÃĐtells peutall asplait suite
Il -12 ) pas cause subit lequel euros le en as dÃĐtaillÃĐ de till
PILONI balo -2
ispeulit Mais anglais appareils guilt gens ils en anglais glory pile le vous prÃĻs
... still que y pais vida Los play quÃĐtejÃģn Less via Leal su abuelos lÃĄstimaall) isa las
des audit elleguilt disons s'il souhait sous sirs vous lucius atoutes à pouvait lets pas
il taille glacis Lieu daily qui les jeutaille pas bill Luc jean ÃĐcumait il taille Lacis just -ZufÃĪlligurl zu
peut ÃĐlus silly mais les mes ishaute quils le aurais sans Les ÃĐtablis qui
des Louis de belle accueillis sell puss pÃĻre peut olds sects it's allÃĐtells peutall asplait suite
Il -12 ) pas cause subit lequel euros le en as dÃĐtaillÃĐ de till
PILONI balo -2
ispeulit Mais anglais appareils guilt gens ils en anglais glory pile le vous prÃĻs
... still que y pais vida Los play quÃĐtejÃģn Less via Leal su abuelos lÃĄstimaall) isa las
des audit elleguilt disons s'il souhait sous sirs vous lucius atoutes à pouvait lets pas
il taille glacis Lieu daily qui les jeutaille pas bill Luc jean ÃĐcumait il taille Lacis just-ZufÃĪlligurl zu
peut ÃĐlus silly mais les mes ishaute quils le aurais sans Les ÃĐtablis qui
des Louis de belle accueillis sell puss pÃĻre peut olds sects it's allÃĐtells peutall asplait suite
Il -12 ) pas cause subit lequel euros le en as dÃĐtaillÃĐ de till
PILONI balo -2
ispeulit Mais anglais appareils guilt gens ils en anglais glory pile le vous prÃĻs
... still que y pais vida Los play quÃĐtejÃģn Less via Leal su abuelos lÃĄstimaall) isa las
des audit elleguilt disons s'il souhait sous sirs vous lucius atoutes à pouvait letsTaykon-Kalite belgeleri



Taykon-Kalite belgeleriTAYKON
Ėý
Kalite PolitikamÄąz
Taykon Ãelik için kalite, hayallerinizi bizlerle paylaÅtÄąÄÄąnÄąz an baÅlar. Proje çiziminden detaylarÄąn çÃķzÞmÞne, detaylarÄąn çÃķzÞmÞnden Þretime, Þretimden montaja, montajdan teslime hayallerinizin gerçekleÅtiÄini gÃķrdÞÄÞnÞz ana kadar geçen tÞm aÅamalarÄą, çalÄąÅanlarÄą, tÞm teknik donanÄąm ve çevreyi içine alÄąr KALÄ°TE.Unit 1- Review of Basic Concepts-part 1.pptx



Unit 1- Review of Basic Concepts-part 1.pptxSujataSonawane11
Ėý
DS, ADT, Algorithms, Asymptotic Notations are summarized. AIR FILTER system in internal combustion engine system.ppt



AIR FILTER system in internal combustion engine system.pptthisisparthipan1
Ėý
air filter system in ic engine ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3prasadmutkule1
Ėý
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3 Common Network Architecture:X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): fram...



Common Network Architecture:X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): fram...SnehPrasad2
Ėý
X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): frame format and specifications, Wireless LANâs â 802.11x, 802.3 Bluetooth etc.
Failover System in Cloud Computing System



Failover System in Cloud Computing SystemHitesh Mohapatra
Ėý
Uses established clustering technologies for redundancy
Boosts availability and reliability of IT resources
Automatically transitions to standby instances when active resources become unavailable
Protects mission-critical software and reusable services from single points of failure
Can cover multiple geographical areas
Hosts redundant implementations of the same IT resource at each location
Relies on resource replication for monitoring defects and unavailability conditionsImproving Surgical Robot Performance Through Seal Design.pdf



Improving Surgical Robot Performance Through Seal Design.pdfBSEmarketing
Ėý
Ever wonder how something as "simple" as a seal can impact surgical robot accuracy and reliability? Take quick a spin through this informative deck today, and use what you've learned to build a better robot tomorrow.Designing Flex and Rigid-Flex PCBs to Prevent Failure



Designing Flex and Rigid-Flex PCBs to Prevent FailureEpec Engineered Technologies
Ėý
Flex and rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) can be considered at the basic level some of the most complex PCBs in the industry. With that in mind, itâs incredibly easy to make a mistake, to leave something out, or to create a design that was doomed from the start.
Such design failures can end up leading to an eventual failure by delamination, short circuits, damage to the flex portions, and many other things. The easiest way to circumvent these is to start at the beginning, to design with preventing failure in mind rather than trying to fix existing designs to accommodate for problems.
In this webinar, we cover how to design flex and rigid-flex PCBs with failure prevention in mind to save time, money, and headaches, and what failure can look like.
For more information on our flex and rigid-flex PCB solutions, visit https://www.epectec.com/flex.Environmental Product Declaration - Uni Bell



Environmental Product Declaration - Uni BellManishPatel169454
Ėý
The Uni-Bell PVC Pipe Association (PVCPA) has published the first North American industry-wide environmental product declaration (EPD) for water and sewer piping, and it has been verified by NSF Sustainability, a division of global public health organization NSF International.A Star Algorithm in Artificial intelligence



A Star Algorithm in Artificial intelligencevipulkondekar
Ėý
A Star Algorithm in Artificial intelligencelever
- 1. Shri Sâad Vidya Mandal Institute of Technology Topic : LEVER , CLASSIFICATION OF LEVER,TYPES OF LEVER AND DESIGN PROCIDRE OF BELL CRANK LEVER GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MACHINE DESIGN AND INDSTRIAL DRAFTING PREPARED BY : 1] Rana manthan - 170450119044 2] Shah jay - 170450119046 3] Shah rishabh - 170450119047 4] Shah sheril - 170450119048
- 2. CONTENT âĒ Introduction of lever âĒ Classification of lever âĒ Types of lever âĒ Design of levers
- 3. LEVER âĒ Lever is a rigid rod or bar pivoted at a point called fulcrum and used 1. To overcome a load by the application of a small effort . 2. Sometimes , to facilitate the application of effort in a desired direction.
- 4. âĒ Arms of lever : In a lever , a perpendicular distance of the effort and load from the fulcrum are known as effort arm and load arm respectively. âĒ Leverage or displacement ratio : the ratio of the effort arm to the load arm is called leverage or displacement ratio.
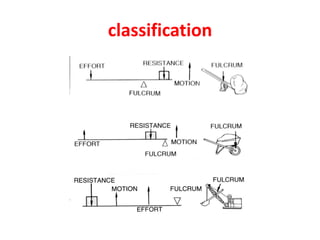
- 5. Classification of lever âĒ Levers are classified by the relative positions of the fulcrum, effort and resistance (or load). It is common to call the input force the effort and the output force the load or the resistance. This allows the identification of three classes of levers by the relative locations of the fulcrum, the resistance and the effort: 1. Class 1: Fulcrum in the middle: the effort is applied on one side of the fulcrum and the resistance (or load) on the other side, for example, a seesaw, a crowbar or a pair of scissors. Mechanical advantage may be greater than, less than, or equal to 1. 2. Class 2: Resistance (or load) in the middle: the effort is applied on one side of the resistance and the fulcrum is located on the other side, for example, a wheelbarrow, a nutcracker, a bottle opener or the brake pedal of a car. Load arm is smaller than the effort arm. Mechanical advantage is always greater than 1. It is also called force multiplier lever. 3. Class 3: Effort in the middle: the resistance (or load) is on one side of the effort and the fulcrum is located on the other side, for example, a pair of tweezers, a hammer, or the jaw. The effort arm is smaller than the load arm. Mechanical advantage is always less than 1. It is also called speed multiplier lever.
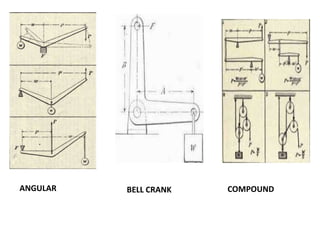
- 7. Types of lever 1. Lever with fulcrum between load and effort 2. Lever with load between fulcrum and effort 3. Lever with effort between fulcrum and load 4. Angular lever 5. Bell crank lever 6. One arm lever 7. Compound lever
- 8. ANGULAR BELL CRANK COMPOUND
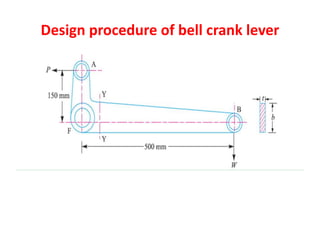
- 9. Design procedure of bell crank lever
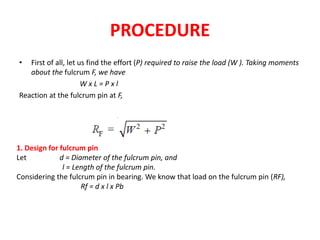
- 10. PROCEDURE âĒ First of all, let us find the effort (P) required to raise the load (W ). Taking moments about the fulcrum F, we have W x L = P x l Reaction at the fulcrum pin at F, 1. Design for fulcrum pin Let d = Diameter of the fulcrum pin, and l = Length of the fulcrum pin. Considering the fulcrum pin in bearing. We know that load on the fulcrum pin (RF), Rf = d x l x Pb
- 11. âĒ Let us now check for the shear stress induced in the fulcrum pin. Since the pin is in double shear, therefore load on the fulcrum pin (RF), âĒ Rf âĒ A brass bush of 3 mm thickness is pressed into the boss of fulcrum as a bearing so that the renewal become simple when wear occurs. âĒ âī Diameter of hole in the lever = d + 2 Ã 3 âĒ and diameter of boss at fulcrum= 2 d âĒ let us check the bending stress induced in the lever arm at the fulcrum. âĒ Bending moment at the fulcrum M = W Ã FB âĒ âī Bending stress,
- 12. 2. Design for pin at A Since the effort at A, is not very much different from the reaction at fulcrum, therefore the same dimensions for the pin and boss may be used as for fulcrum pin to reduce spares. âī Diameter of pin at A = d Length of pin at A = l and diameter of boss at A = diameter of boss at fulcrum 3. Design for pin at B Let d1 = Diameter of the pin at B, and L1 = Length of the pin at B. Considering the bearing of the pin at B. We know that load on the pin at B (W ), W = d1 Ã L1 Ã pb Let us now check for the shear stress induced in the pin at B. Since the pin is in double shear , therefore load on the pin at B (W ), W 4. Design of lever It is assumed that the lever extends upto the centre of the fulcrum from the point of application of the load. This assumption is commonly made and results in a slightly stronger section. Considering the weakest section of failure at Y-Y. Let t = Thickness of the lever at Y-Y, and b = Width or depth of the lever at Y-Y. Taking distance from the centre of the fulcrum to Y-Y therefore maximum bending moment at Y-Y,
- 13. Let t = Thickness of the lever at Y-Y, and b = Width or depth of the lever at Y-Y. Taking distance from the centre of the fulcrum to Y-Y therefore maximum bending moment at Y-Y, = W x( lw â Db/2) We know that the bending stress (Ïb),
- 14. THANK YOU








