Levers in Physiotherapy
Download as PPTX, PDF38 likes62,615 views
1. A lever is a rigid bar that rotates around a fixed point called a fulcrum and is a simple machine that magnifies force and movement speed. 2. The three main components of a lever are the fulcrum, the effort arm where force is applied, and the resistance arm where the object to be moved is located. 3. There are three types of levers - first class levers have the fulcrum between the effort and resistance arms, second class levers have the resistance arm between the fulcrum and effort arm, and third class levers have the effort arm between the fulcrum and resistance arm.
1 of 29
Downloaded 85 times






















Recommended
Active movements



Active movementsDr Taimoor ul Hassan
╠²
This document discusses different types of voluntary movements used in physical therapy exercises. It classifies exercises as free, assisted, assisted-resisted, or resisted based on whether they involve gravity, external assistance, or resistance. Free exercises work against gravity alone and are used to improve relaxation, muscle tone, coordination, and confidence. They can help cure or rehabilitate patients, though some patients may be unable to perform them. The document outlines techniques for free exercises and their effects, including improved relaxation, joint mobility, muscle power, neuromuscular coordination, and confidence. It also describes circulatory and respiratory changes that occur with exercise like increased heart rate, blood flow, and respiration to meet tissue needs and regulate functions.ANATOMICAL PULLEYS.ppt



ANATOMICAL PULLEYS.pptSYED MASOOD
╠²
Anatomical pulleys in the hand redirect the pulling force of flexor tendons to provide precise control of finger movement. There are two types - annular pulleys, which are rings of connective tissue at the finger joints, and cruciate pulleys, which are smaller cross-shaped pulleys in between. Damage to the annular pulleys, especially the major A2 and A4 pulleys, can cause the tendon to be pulled away from the finger bone during movement, weakening grip. The pulley system enhances tendon power and allows normal range of motion in the fingers.ACTIVE MOVEMENTS.ppt



ACTIVE MOVEMENTS.pptTabassum Saher
╠²
This ppt is all about active movements of human body
Indications and contraindications are mentioned for the sameFluidotherapy



FluidotherapyFlorence Macwan
╠²
This document summarizes fluidotherapy, a dry heating modality. It transfers heat to the body through convection using a cabinet containing heated air and finely ground cellulose particles. This creates a fluid-like medium allowing limbs to float and exercises to be performed. Key effects include increased blood flow, pain relief and improved range of motion. It is used to treat distal extremities for conditions like pain, swelling and post-operative rehabilitation. Contraindications include fever, anesthesia or severe circulatory issues. Advantages include ease of use and allowing some active exercise in a comfortable, dry environment.Ultraviolet radiation in Physiotherapy



Ultraviolet radiation in PhysiotherapySreeraj S R
╠²
Ultraviolet radiation covers a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum between visible light and X-rays. It is divided into UVA, UVB, and UVC based on wavelength. UV is produced by mercury vapor lamps and fluorescent lamps and can cause both immediate and long term effects on skin like erythema, pigmentation, vitamin D production, and skin cancer. The dosage of UV exposure depends on the lamp output, distance from the skin, exposure time, and individual skin sensitivity. UV therapy is used to treat conditions like psoriasis, acne, and eczema.Glenohumeral joint-ppt.



Glenohumeral joint-ppt.Mohammad Akeel
╠²
The document discusses static and dynamic stability of the glenohumeral joint. Statically, the joint is stabilized by the humeral head resting in the glenoid fossa, creating negative pressure. The rotator cuff muscles and deltoid provide a vertical force to counteract gravity. Dynamically, the deltoid, rotator cuff, biceps and scapulohumeral rhythm work together to precisely guide humeral movement and stabilize the joint throughout its range of motion. Scapulohumeral rhythm involves greater scapular movement in the first 90 degrees of arm elevation compared to humeral movement.Faradic Foot Bath, Faradism Under Pressure, Faradism Under Tension, Stimulati...



Faradic Foot Bath, Faradism Under Pressure, Faradism Under Tension, Stimulati...Sreeraj S R
╠²
Low frequency stimulation, Faradic Foot Bath, Faradism Under Pressure, Faradism Under Tension, Stimulation to Pelvic Floor Muscles, PhysiotherapyBiomechanics of wrist complex



Biomechanics of wrist complexNeeti Christian
╠²
Biomwchanics of wrist and hand
- Kinematics and Kinetics of joints including flexion and extension mechanism
-Pathomechanics
- Prehension
-Functional position of wristS d curve



S d curvesanyal kumar
╠²
The document discusses strength duration curves, which plot the electrical stimuli needed to elicit a muscle contraction over a range of stimulus durations. It describes how to perform the test and interpret the results, including details on:
- Plotting S-D curves after 20 days post-injury to assess innervation status
- The typical shape of normal, denervated, and partially denervated curves
- Additional metrics that can be measured from S-D curves like rheobase and chronaxie
- Factors that can influence the curves and what different curve patterns indicateGalvanic current



Galvanic currentAVANIANBAN CHAKKARAPANI
╠²
This document discusses galvanic current and its use in stimulating denervated muscles. It defines galvanic current as a direct, unidirectional current that can cause pain due to its unidirectional nature. Interrupted galvanic current is introduced to overcome this by providing regular pauses in stimulation. Stimulating denervated muscles with galvanic current can help limit atrophy and edema until reinnervation occurs. Precautions must be taken when applying galvanic current due to potential dangers like burns or electric shock.Scapulohumeral rhythm ppt



Scapulohumeral rhythm pptChristopher John
╠²
The document discusses the scapulohumeral rhythm, which is the coordinated movement between the glenohumeral joint and scapulothoracic joint during shoulder movement. Specifically, it notes that for every 2 degrees of shoulder abduction or flexion, the scapula upwardly rotates approximately 1 degree. This ratio maintains proper shoulder range of motion and prevents impingement. Clinical issues like frozen shoulder and scapular winging can result from impairments affecting the scapulothoracic joint.Contrast bath SRS



Contrast bath SRSSreeraj S R
╠²
Contrast bath therapy involves soaking an injured area in alternating hot and cold water baths to increase blood flow and decrease stiffness and pain. The physiological mechanism is that it induces vasodilation and vasoconstriction through changes in water temperature, pumping edema from the injured area. The procedure involves soaking in warm water for 10 minutes, cold water for 1 minute, repeating warm water for 4 minutes and cold water for 1 minute, ending in warm water for 4 minutes for a total time of 25 minutes. Contrast baths can treat injuries like sprains, strains and bruises by removing edema through changes in blood flow. Certain precautions should be taken for conditions like open wounds, pregnancy and impaired sensation.Kinetics and kinematics



Kinetics and kinematicsSana Rai
╠²
this presentation is about the basic information about the biomechanics which also include kinetics and kinematicsUltrasound therapy



Ultrasound therapyMuthuukaruppan
╠²
This document discusses ultrasound, including its physics, production, effects, and therapeutic uses. It defines ultrasound and discusses how it is produced using the piezoelectric effect. The main physical effects of ultrasound are heating, cavitation, acoustic streaming, and microstreaming. Thermally, ultrasound can increase tissue extensibility and reduce pain and muscle spasm. Non-thermally, it can increase membrane permeability and ion diffusion through cavitation. The document outlines appropriate ultrasound parameters and treatment techniques to maximize benefits and minimize risks.Active movements



Active movementsSunil kumar
╠²
This document discusses different types of exercises used in physiotherapy, including free exercises, assisted exercises, assisted-resisted exercises, and resisted exercises. It defines each type and describes techniques, effects, and uses. Free exercises use only voluntary muscle action and can be localised or general. Assisted exercises involve a therapist providing support and assistance during a movement. Assisted-resisted exercises combine assistance and resistance. Resisted exercises use forces like weights or elastic bands to oppose muscle movement. The document also covers types of resistance like weights, pulleys, springs, and water. It describes progression of resistance exercises by increasing weight, leverage, speed, or duration. Finally, it discusses reflex movements and specific reflexes like the stretch reflexResistance exercises



Resistance exercisesShiny Joseph
╠²
The document defines and describes various aspects of resistance exercises. It discusses types of muscle contractions like isotonic, isometric and eccentric. It explains principles of resistance training like overload and specificity. It describes adaptations to resistance training including neural, muscular and bone changes. Determinants of resistance training programs are outlined including intensity, time, volume and periodization. Guidelines for progressive resistance exercises and precautions are provided.Contrast Bath in Physiotherapy SRS 



Contrast Bath in Physiotherapy SRS Sreeraj S R
╠²
Contrast bath therapy involves soaking an injured area in alternating hot and cold water baths to increase blood flow and decrease joint stiffness. The temperature changes from hot to cold and back again produce a "pumping effect" that helps remove swelling through improved venous and lymphatic drainage. A full contrast bath treatment consists of soaking in warm water for 10 minutes, cold water for 1 minute, repeated three times, ending with warm water. Contrast baths can help relieve pain, stiffness and swelling through induced vasodilation and vasoconstriction of blood vessels.Ultrasound therapy



Ultrasound therapyAkshay Shetty
╠²
The document discusses ultrasound therapy, including its introduction, production, physiological effects, application techniques, methods, indications, and contraindications. Specifically, it explains that ultrasound therapy involves using high-frequency sound waves to treat soft tissue injuries and conditions. It describes how piezoelectric crystals or transducers are used to produce the therapeutic ultrasound and discusses direct contact and indirect immersion and bladder application as methods of delivery. The document also lists common uses of ultrasound therapy such as for soft tissue injuries, sprains, and arthritis, as well as who should avoid it like those with cancer lesions or metal implants.Paraffin Wax Bath



Paraffin Wax BathSreeraj S R
╠²
This document discusses paraffin wax bath therapy. It begins by explaining that paraffin wax is melted to around 40-44┬░C and applied to body parts for pain relief. It then describes the various components of a paraffin wax bath unit and different application methods such as dipping, immersion, and direct pouring. The physiological effects of heat are listed, along with common indications like pain, swelling, and adhesions. Contraindications include ischemia, hemorrhage, impaired sensation, and malignancy. Advantages include home use and molding to body contours, while disadvantages are limited areas of application and lack of temperature control once applied.Q angle (Quadriceps angle) Assessment 



Q angle (Quadriceps angle) Assessment Syed Adil
╠²
The document defines the Q-angle as the angle formed between a line from the ASIS to the midpoint of the patella and a line from the midpoint of the patella to the tibial tubercle. It represents the angle of pull of the quadriceps muscles. The normal range is 10-14 degrees for men and 15-23 degrees for women. Factors that can increase the Q-angle include muscle imbalances, tight iliotibial bands, genu valgum, medial femoral torsion, and lateral tibial rotation.Levers in human body



Levers in human bodyMohamed M. Elsaied
╠²
The document discusses levers in the human body. It defines levers as rigid bars that rotate around a fulcrum or axis. There are three classes of levers - first class has the fulcrum between the effort and resistance arms, second class has the resistance arm between the effort and fulcrum, and third class has the effort arm between the fulcrum and resistance. Examples of each class in the human body include the head lifting muscles using the atlas joint as a first class lever, the Achilles tendon acting as a second class lever, and the bicep muscle bending the elbow as a third class lever. Levers in the body allow for increased power, distance, speed, and precision ofTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)



Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)Saurab Sharma
╠²
Saurab Sharma presented on Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS). The objectives were to understand TENS theory, application techniques, uses, electrode placement, and precautions. TENS delivers electricity across the skin to activate nerves and provides pain relief for acute, chronic non-malignant, and palliative malignant pain. Different application techniques include high frequency, low frequency, brief intense, burst mode, and modulated TENS. Common uses are postoperative, labor, musculoskeletal, and neuropathic pain. Electrodes are placed over painful sites and precautions taken with pacemakers, malignancy, and skin conditions.Resistance exercise



Resistance exerciseSubhanjan Das
╠²
The document defines various terms related to resistance exercise such as resisted exercise, strength, power, endurance, isometric muscle work, isotonic muscle work, and types of muscle contractions. It describes the principles of resistance exercise including overload, SAID, reversibility, and individual variability. It discusses ranges of muscle work, group actions of muscles, and indications for resistance exercise. Overall, the document provides an overview of key concepts in resistance training.Goniometry.ppt uche



Goniometry.ppt ucheOduenyi Christian Onyeka.BMR(PT)
╠²
The document discusses goniometry, which is the measurement of joint angles using a goniometer. It outlines what goniometry is, the importance and types of goniometers, how to measure range of motion for various joints including the shoulder, wrist, hip and hand, and considerations for validity and reliability when performing goniometric measurements. Proper procedures and positioning for accurate goniometric assessment of different joints are described.Cryotherapy



CryotherapyFlorence Macwan
╠²
Cryotherapy involves applying cold to the body for therapeutic purposes. It uses cooling agents like ice, frozen gel, or vapocoolant sprays. The cold induces vasoconstriction which reduces blood flow, lowering metabolic rate and inhibiting inflammation. It also increases pain threshold and reduces muscle spasm. Cryotherapy can relieve pain, reduce swelling and spasticity, facilitate muscle contraction, and promote tissue repair. Contraindications include cardiac conditions, peripheral nerve injury, and cold sensitivity. Common application techniques are ice towels, ice packs, immersion, and ice cube massage.FARADIC CURRENT.pptx



FARADIC CURRENT.pptxPriyankaBhusal2
╠²
A faradic current is a short duration interrupted direct current with a pulse duration of 0.1-1 ms and frequency of 50-100 Hz. It produces a biphasic, asymmetrical and spiked waveform. Faradic currents are used to produce near normal tetanic-like muscle contractions and relaxations. When applied to nerves and muscles, it causes sensory stimulation, muscle contraction, reduced swelling and pain, and increased metabolism. Faradic current is indicated for muscle reeducation, maintaining range of motion, loosening adhesions, and replacing orthosis. It involves placing electrodes on muscles or nerve trunks and gradually increasing and decreasing intensity to cause contraction and relaxation.Passive movements



Passive movementsRAJESH MANI
╠²
Passive movement involves moving a body part without active muscle contraction. There are several types: relaxed passive movements where a therapist smoothly moves a joint within its pain-free range; accessory movements which are small rotational or gliding motions in a joint; and passive manual techniques like joint mobilizations and manipulations. Controlled stretching can also be applied to tight muscles and tissues. Passive movements help maintain range of motion, prevent adhesions, reduce swelling, and stretch contracted structures. They are important for patients who cannot actively move due to injury or condition.BIOMECHANICS OF ELBOW COMPLEX



BIOMECHANICS OF ELBOW COMPLEXMuhammadasif909
╠²
The elbow complex is designed to provide mobility and stability for the hand. It consists of three joints - the humeroulnar joint between the humerus and ulna, the humeroradial joint between the humerus and radius, and the superior and inferior radioulnar joints. These joints allow for flexion-extension, pronation, and supination movements. The elbow is stabilized by ligaments and muscles like the biceps brachi, triceps, and pronators. Common problems affecting the elbow include tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, nursemaid's elbow, and cubital tunnel syndrome.Presentation of lever by Rahul Sharma.pptx



Presentation of lever by Rahul Sharma.pptxvishalboh89
╠²
This presentation is about lever and it's types and about its function LEVERS 1.ppt



LEVERS 1.pptKaushik Patel
╠²
A lever is a rigid bar that moves around a fixed point called a fulcrum. Effort is applied at one point to act on a weight or resistance at another point. There are three types of levers - first order has the fulcrum between the effort and resistance points, second order has the resistance point between the effort and fulcrum, and third order has the effort point between the resistance and fulcrum. Levers provide mechanical advantage by multiplying effort, with greater advantage when the effort arm is longer than the resistance arm. Examples of levers in the body and used in tools/structures are also provided.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
S d curve



S d curvesanyal kumar
╠²
The document discusses strength duration curves, which plot the electrical stimuli needed to elicit a muscle contraction over a range of stimulus durations. It describes how to perform the test and interpret the results, including details on:
- Plotting S-D curves after 20 days post-injury to assess innervation status
- The typical shape of normal, denervated, and partially denervated curves
- Additional metrics that can be measured from S-D curves like rheobase and chronaxie
- Factors that can influence the curves and what different curve patterns indicateGalvanic current



Galvanic currentAVANIANBAN CHAKKARAPANI
╠²
This document discusses galvanic current and its use in stimulating denervated muscles. It defines galvanic current as a direct, unidirectional current that can cause pain due to its unidirectional nature. Interrupted galvanic current is introduced to overcome this by providing regular pauses in stimulation. Stimulating denervated muscles with galvanic current can help limit atrophy and edema until reinnervation occurs. Precautions must be taken when applying galvanic current due to potential dangers like burns or electric shock.Scapulohumeral rhythm ppt



Scapulohumeral rhythm pptChristopher John
╠²
The document discusses the scapulohumeral rhythm, which is the coordinated movement between the glenohumeral joint and scapulothoracic joint during shoulder movement. Specifically, it notes that for every 2 degrees of shoulder abduction or flexion, the scapula upwardly rotates approximately 1 degree. This ratio maintains proper shoulder range of motion and prevents impingement. Clinical issues like frozen shoulder and scapular winging can result from impairments affecting the scapulothoracic joint.Contrast bath SRS



Contrast bath SRSSreeraj S R
╠²
Contrast bath therapy involves soaking an injured area in alternating hot and cold water baths to increase blood flow and decrease stiffness and pain. The physiological mechanism is that it induces vasodilation and vasoconstriction through changes in water temperature, pumping edema from the injured area. The procedure involves soaking in warm water for 10 minutes, cold water for 1 minute, repeating warm water for 4 minutes and cold water for 1 minute, ending in warm water for 4 minutes for a total time of 25 minutes. Contrast baths can treat injuries like sprains, strains and bruises by removing edema through changes in blood flow. Certain precautions should be taken for conditions like open wounds, pregnancy and impaired sensation.Kinetics and kinematics



Kinetics and kinematicsSana Rai
╠²
this presentation is about the basic information about the biomechanics which also include kinetics and kinematicsUltrasound therapy



Ultrasound therapyMuthuukaruppan
╠²
This document discusses ultrasound, including its physics, production, effects, and therapeutic uses. It defines ultrasound and discusses how it is produced using the piezoelectric effect. The main physical effects of ultrasound are heating, cavitation, acoustic streaming, and microstreaming. Thermally, ultrasound can increase tissue extensibility and reduce pain and muscle spasm. Non-thermally, it can increase membrane permeability and ion diffusion through cavitation. The document outlines appropriate ultrasound parameters and treatment techniques to maximize benefits and minimize risks.Active movements



Active movementsSunil kumar
╠²
This document discusses different types of exercises used in physiotherapy, including free exercises, assisted exercises, assisted-resisted exercises, and resisted exercises. It defines each type and describes techniques, effects, and uses. Free exercises use only voluntary muscle action and can be localised or general. Assisted exercises involve a therapist providing support and assistance during a movement. Assisted-resisted exercises combine assistance and resistance. Resisted exercises use forces like weights or elastic bands to oppose muscle movement. The document also covers types of resistance like weights, pulleys, springs, and water. It describes progression of resistance exercises by increasing weight, leverage, speed, or duration. Finally, it discusses reflex movements and specific reflexes like the stretch reflexResistance exercises



Resistance exercisesShiny Joseph
╠²
The document defines and describes various aspects of resistance exercises. It discusses types of muscle contractions like isotonic, isometric and eccentric. It explains principles of resistance training like overload and specificity. It describes adaptations to resistance training including neural, muscular and bone changes. Determinants of resistance training programs are outlined including intensity, time, volume and periodization. Guidelines for progressive resistance exercises and precautions are provided.Contrast Bath in Physiotherapy SRS 



Contrast Bath in Physiotherapy SRS Sreeraj S R
╠²
Contrast bath therapy involves soaking an injured area in alternating hot and cold water baths to increase blood flow and decrease joint stiffness. The temperature changes from hot to cold and back again produce a "pumping effect" that helps remove swelling through improved venous and lymphatic drainage. A full contrast bath treatment consists of soaking in warm water for 10 minutes, cold water for 1 minute, repeated three times, ending with warm water. Contrast baths can help relieve pain, stiffness and swelling through induced vasodilation and vasoconstriction of blood vessels.Ultrasound therapy



Ultrasound therapyAkshay Shetty
╠²
The document discusses ultrasound therapy, including its introduction, production, physiological effects, application techniques, methods, indications, and contraindications. Specifically, it explains that ultrasound therapy involves using high-frequency sound waves to treat soft tissue injuries and conditions. It describes how piezoelectric crystals or transducers are used to produce the therapeutic ultrasound and discusses direct contact and indirect immersion and bladder application as methods of delivery. The document also lists common uses of ultrasound therapy such as for soft tissue injuries, sprains, and arthritis, as well as who should avoid it like those with cancer lesions or metal implants.Paraffin Wax Bath



Paraffin Wax BathSreeraj S R
╠²
This document discusses paraffin wax bath therapy. It begins by explaining that paraffin wax is melted to around 40-44┬░C and applied to body parts for pain relief. It then describes the various components of a paraffin wax bath unit and different application methods such as dipping, immersion, and direct pouring. The physiological effects of heat are listed, along with common indications like pain, swelling, and adhesions. Contraindications include ischemia, hemorrhage, impaired sensation, and malignancy. Advantages include home use and molding to body contours, while disadvantages are limited areas of application and lack of temperature control once applied.Q angle (Quadriceps angle) Assessment 



Q angle (Quadriceps angle) Assessment Syed Adil
╠²
The document defines the Q-angle as the angle formed between a line from the ASIS to the midpoint of the patella and a line from the midpoint of the patella to the tibial tubercle. It represents the angle of pull of the quadriceps muscles. The normal range is 10-14 degrees for men and 15-23 degrees for women. Factors that can increase the Q-angle include muscle imbalances, tight iliotibial bands, genu valgum, medial femoral torsion, and lateral tibial rotation.Levers in human body



Levers in human bodyMohamed M. Elsaied
╠²
The document discusses levers in the human body. It defines levers as rigid bars that rotate around a fulcrum or axis. There are three classes of levers - first class has the fulcrum between the effort and resistance arms, second class has the resistance arm between the effort and fulcrum, and third class has the effort arm between the fulcrum and resistance. Examples of each class in the human body include the head lifting muscles using the atlas joint as a first class lever, the Achilles tendon acting as a second class lever, and the bicep muscle bending the elbow as a third class lever. Levers in the body allow for increased power, distance, speed, and precision ofTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)



Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)Saurab Sharma
╠²
Saurab Sharma presented on Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS). The objectives were to understand TENS theory, application techniques, uses, electrode placement, and precautions. TENS delivers electricity across the skin to activate nerves and provides pain relief for acute, chronic non-malignant, and palliative malignant pain. Different application techniques include high frequency, low frequency, brief intense, burst mode, and modulated TENS. Common uses are postoperative, labor, musculoskeletal, and neuropathic pain. Electrodes are placed over painful sites and precautions taken with pacemakers, malignancy, and skin conditions.Resistance exercise



Resistance exerciseSubhanjan Das
╠²
The document defines various terms related to resistance exercise such as resisted exercise, strength, power, endurance, isometric muscle work, isotonic muscle work, and types of muscle contractions. It describes the principles of resistance exercise including overload, SAID, reversibility, and individual variability. It discusses ranges of muscle work, group actions of muscles, and indications for resistance exercise. Overall, the document provides an overview of key concepts in resistance training.Goniometry.ppt uche



Goniometry.ppt ucheOduenyi Christian Onyeka.BMR(PT)
╠²
The document discusses goniometry, which is the measurement of joint angles using a goniometer. It outlines what goniometry is, the importance and types of goniometers, how to measure range of motion for various joints including the shoulder, wrist, hip and hand, and considerations for validity and reliability when performing goniometric measurements. Proper procedures and positioning for accurate goniometric assessment of different joints are described.Cryotherapy



CryotherapyFlorence Macwan
╠²
Cryotherapy involves applying cold to the body for therapeutic purposes. It uses cooling agents like ice, frozen gel, or vapocoolant sprays. The cold induces vasoconstriction which reduces blood flow, lowering metabolic rate and inhibiting inflammation. It also increases pain threshold and reduces muscle spasm. Cryotherapy can relieve pain, reduce swelling and spasticity, facilitate muscle contraction, and promote tissue repair. Contraindications include cardiac conditions, peripheral nerve injury, and cold sensitivity. Common application techniques are ice towels, ice packs, immersion, and ice cube massage.FARADIC CURRENT.pptx



FARADIC CURRENT.pptxPriyankaBhusal2
╠²
A faradic current is a short duration interrupted direct current with a pulse duration of 0.1-1 ms and frequency of 50-100 Hz. It produces a biphasic, asymmetrical and spiked waveform. Faradic currents are used to produce near normal tetanic-like muscle contractions and relaxations. When applied to nerves and muscles, it causes sensory stimulation, muscle contraction, reduced swelling and pain, and increased metabolism. Faradic current is indicated for muscle reeducation, maintaining range of motion, loosening adhesions, and replacing orthosis. It involves placing electrodes on muscles or nerve trunks and gradually increasing and decreasing intensity to cause contraction and relaxation.Passive movements



Passive movementsRAJESH MANI
╠²
Passive movement involves moving a body part without active muscle contraction. There are several types: relaxed passive movements where a therapist smoothly moves a joint within its pain-free range; accessory movements which are small rotational or gliding motions in a joint; and passive manual techniques like joint mobilizations and manipulations. Controlled stretching can also be applied to tight muscles and tissues. Passive movements help maintain range of motion, prevent adhesions, reduce swelling, and stretch contracted structures. They are important for patients who cannot actively move due to injury or condition.BIOMECHANICS OF ELBOW COMPLEX



BIOMECHANICS OF ELBOW COMPLEXMuhammadasif909
╠²
The elbow complex is designed to provide mobility and stability for the hand. It consists of three joints - the humeroulnar joint between the humerus and ulna, the humeroradial joint between the humerus and radius, and the superior and inferior radioulnar joints. These joints allow for flexion-extension, pronation, and supination movements. The elbow is stabilized by ligaments and muscles like the biceps brachi, triceps, and pronators. Common problems affecting the elbow include tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, nursemaid's elbow, and cubital tunnel syndrome.Similar to Levers in Physiotherapy (20)
Presentation of lever by Rahul Sharma.pptx



Presentation of lever by Rahul Sharma.pptxvishalboh89
╠²
This presentation is about lever and it's types and about its function LEVERS 1.ppt



LEVERS 1.pptKaushik Patel
╠²
A lever is a rigid bar that moves around a fixed point called a fulcrum. Effort is applied at one point to act on a weight or resistance at another point. There are three types of levers - first order has the fulcrum between the effort and resistance points, second order has the resistance point between the effort and fulcrum, and third order has the effort point between the resistance and fulcrum. Levers provide mechanical advantage by multiplying effort, with greater advantage when the effort arm is longer than the resistance arm. Examples of levers in the body and used in tools/structures are also provided.LEVER,PULLEY AND SPRING LEVER. ppt .pptx



LEVER,PULLEY AND SPRING LEVER. ppt .pptxbharti pawar
╠²
This document discusses levers and how they are used in the human body. It defines a lever as a rigid bar that moves about a fixed point called a fulcrum. In the body, bones act as levers and joints act as fulcrums. Movement is created by two forces - resistance (R), the opposing force, and effort (E), the action force. There are three types of levers - first, second, and third order. First order levers provide mechanical advantage when the fulcrum is closer to the weight than the effort. Second order levers always provide mechanical advantage. Mechanical advantage is the ratio of weight to effort and allows less effort to be used to lift a weight.LEVERS ppt.pptx



LEVERS ppt.pptxNijal parmar
╠²
it is about different types of lever system in our body and how movements can be varied based on the lever systemKinetics 2009 Lecture 2with Torque Joke Not To Post



Kinetics 2009 Lecture 2with Torque Joke Not To PostPam Kasyan
╠²
The document discusses various biomechanical concepts related to movement and forces in the musculoskeletal system. It defines scalar and vector quantities, describes different types of motion including translation and rotation. It also covers lever systems, the three classes of levers, mechanical advantage, torque, moment arms, and types of muscle contraction including isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions.levers in human body.pptx



levers in human body.pptxVinodBaithaVinodSir
╠²
Understanding the concept of levers and their types can be highly beneficial to people in various ways. use of lever in sports.



use of lever in sports.VinodBaithaVinodSir
╠²
Its a sports biomechanics topic in which students will know about levers and how its work in human body.Joint biomechanics 



Joint biomechanics Lennard Funk
╠²
Torque = Force x Force Arm
= Resistance x Resistance Arm
= 45 kg x 0.25 m
= 11.25 Nm
So the force needed is 11.25 N
Therefore, the torque needed is 1.125 Nm (11.25 N x 0.1 m)Levers.pptx



Levers.pptxsachinchaudhary158
╠²
IN BIOMECHANICS, LEVERS ARE THE MAINSTAY OF THE MOVEMENT. THE LEVERS ARE CLASSIFIED AS FIRST ORDER, SECOND ORDER AND THIRD ORDER LEVERS RESPECTIVELY. OF THESE SECOND ORDER LEVER IS OF MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE AND THIRD ORDER LEVER IS OF MECHANICAL DISADVANTAGE.Levers assignment 



Levers assignment Smitha D
╠²
This document discusses parallel force systems and the three classes of levers. It defines parallel force systems as existing when two or more parallel forces act on a lever at some distance from each other and the axis of rotation. It then defines the three classes of levers - first, second, and third - based on the relative positions of the effort force, resistance force, and fulcrum. Examples are provided for each class of lever, including seesaws, wheelbarrows, and human movements like nodding the head. The classes are distinguished by whether the effort arm is greater than, less than, or equal to the resistance arm.TYPES OF LEVER



TYPES OF LEVERDr. Darshan Parmar
╠²
The document discusses the concept of a lever and its types. A lever is a rigid bar that pivots around a fixed point called the fulcrum. There are three types of levers - first, second, and third order. The first order lever has the fulcrum between the effort and weight points. The second order lever has the weight between the effort and fulcrum. The third order lever has the effort between the fulcrum and weight. Examples of each type in the human body and common objects are provided.LEVERS & LEVERS OF THE BODY



LEVERS & LEVERS OF THE BODYRAJESH MANI
╠²
The document discusses the three types of levers found in the human body - 1st, 2nd, and 3rd order levers. A 1st order lever provides stability with or without mechanical advantage, such as when nodding the head. A 2nd order lever is the lever of power, with the fulcrum between the effort and weight, like when standing on the toes. A 3rd order lever has a mechanical disadvantage but provides speed and range of motion, like when flexing the elbow. Examples of each type of lever are described.inbound2772655900034201706.pdf lever system in human body



inbound2772655900034201706.pdf lever system in human bodyBenzonLouVillarin
╠²
Lever system in human bodyLevers 



Levers Samiksha Sathe
╠²
This presentation discusses levers and their application in physiotherapy. It begins with definitions of a lever as a rigid bar that can rotate around a fixed point called a fulcrum. There are three orders of levers - first order has the fulcrum between the effort and weight, second order has the weight between the effort and fulcrum, and third order has the effort between the weight and fulcrum. Examples of each order are given from the human body. Mechanical advantage is explained as the ratio of weight to effort. Levers in the body allow movement through muscular contraction acting as effort at attachment points. Understanding levers informs strengthening exercises by adjusting resistance or leverage.5. inertia, friction, levers



5. inertia, friction, leversDr. M Farrukh Shahzad
╠²
This document discusses key concepts in kinesiology including inertia, friction, and levers. It defines inertia as the resistance of a body to changes in its motion or rest. Friction is defined as the force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact. Levers are described as rigid bars that rotate around a fixed point called a fulcrum. There are three classes of levers defined by the relative positions of the fulcrum, effort, and weight. Mechanical advantage is gained when the effort arm is longer than the weight arm, allowing a smaller force to overcome a larger load.LEVER ACTION.pptx



LEVER ACTION.pptxDIVINE SPORTS ACADEMY
╠²
The document defines a lever as a mechanical device that produces a turning motion around a fixed point called a fulcrum. It describes the three parts of a lever as the rigid bar, fulcrum, and force/resistance. There are three types (orders) of levers - first order levers have the fulcrum between the force and resistance, second order levers have the resistance between the fulcrum and force, and third order levers have the force between the fulcrum and resistance. Examples of each type are given from both machines and the human body. Levers provide advantages by increasing speed, range, power, or mechanical advantage.Lever system - Exercise therapy



Lever system - Exercise therapyRohini Surti
╠²
This document defines and provides examples of the three classes of lever systems in the body. A lever system uses a rigid bar (lever) and fulcrum to amplify force. The three parts are the effort, load, and fulcrum. The first class lever has the fulcrum between the effort and load, like the head nodding. The second class lever has the load between the effort and fulcrum, like plantarflexion of the foot. The third class lever has the effort between the load and fulcrum, like the elbow joint. Lever systems increase resistance and speed of movement through mechanical advantage.biomechanics.ppt



biomechanics.pptSwatiTiwari865509
╠²
This document discusses basic biomechanics concepts including mechanics, kinematics, kinetics, and how the musculoskeletal system functions as a series of simple machines. It describes how levers, wheels, and axles are used to create mechanical advantages that enhance force, range of motion, or speed of movement. It provides examples of the three classes of levers and how the relationship between the force arm, axis, and resistance arm determines torque requirements.biomechanics.ppt



biomechanics.pptVikasYedida
╠²
This document discusses basic biomechanics concepts including mechanics, kinematics, kinetics, and how the musculoskeletal system functions as a series of simple machines. It describes how levers, wheels, and axles are used to create mechanical advantages that enhance force, range of motion, or speed of movement. It provides examples of the three classes of levers and how torque is calculated based on the force, force arm, and resistance arm. Increasing the force arm or decreasing the resistance arm reduces the torque required to overcome a given resistance.biomechanics.ppt



biomechanics.pptjenifer60
╠²
This document discusses basic biomechanics concepts including mechanics, kinematics, kinetics, and how the musculoskeletal system functions as a series of simple machines. It describes how levers, wheels, and axles are used to create mechanical advantages that enhance force, range of motion, or speed of movement. Specifically, it defines the three classes of levers and provides examples of how varying the force arm and resistance arm can increase or decrease the amount of torque required to move a given resistance.Recently uploaded (20)
psychosomaticdisorder and it's physiotherapy management



psychosomaticdisorder and it's physiotherapy managementDr Shiksha Verma (PT)
╠²
Psychosomatic disorder Dr. Jaymee ShellŌĆÖs Perspective on COVID-19



Dr. Jaymee ShellŌĆÖs Perspective on COVID-19Jaymee Shell
╠²
Dr. Jaymee Shell views the COVID-19 pandemic as both a crisis that exposed weaknesses and an opportunity to build stronger systems. She emphasizes that the pandemic revealed critical healthcare inequities while demonstrating the power of collaboration and adaptability.
Shell highlights that organizations with gender-diverse executive teams are 25% more likely to experience above-average profitability, positioning diversity as a business necessity rather than just a moral imperative. She notes that the pandemic disproportionately affected women of color, with one in three women considering leaving or downshifting their careers.
To combat inequality, Shell recommends implementing flexible work policies, establishing clear metrics for diversity in leadership, creating structured virtual collaboration spaces, and developing comprehensive wellness programs. For healthcare providers specifically, she advocates for multilingual communication systems, mobile health units, telehealth services with alternatives for those lacking internet access, and cultural competency training.
Shell emphasizes the importance of mental health support through culturally appropriate resources, employee assistance programs, and regular check-ins. She calls for diverse leadership teams that reflect the communities they serve and community-centered care models that address social determinants of health.
In her words: "The COVID-19 pandemic didn't create healthcare inequalities ŌĆō it illuminated them." She urges building systems that reach every community and provide dignified care to all.One Health Rabies Control in Indonesia_APCAT meeting May 2022.pptx



One Health Rabies Control in Indonesia_APCAT meeting May 2022.pptxWahid Husein
╠²
What is FAO doing to support rabies control programmes in Indonesia using One Health approachCharacteristics and Criteria of Good Research.pptx



Characteristics and Criteria of Good Research.pptxDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
╠²
Characteristics and Criteria of Good ResearchRenal Physiology - Regulation of GFR and RBF



Renal Physiology - Regulation of GFR and RBFMedicoseAcademics
╠²
1. Explain the physiological control of glomerular filtration and renal blood flow
2. Describe the humoral and autoregulatory feedback mechanisms that mediate the autoregulation of renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptx



Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptxDr Punith Kumar
╠²
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing clinical microbiology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, automating workflows, and improving patient outcomes. This presentation explores the key applications of AI in microbial identification, antimicrobial resistance detection, and laboratory automation. Learn how machine learning, deep learning, and data-driven analytics are transforming the field, leading to faster and more efficient microbiological diagnostics. Whether you're a researcher, clinician, or healthcare professional, this presentation provides valuable insights into the future of AI in microbiology.ISO 14155 Clinical investigation of medical devices for human subjects- Good ...



ISO 14155 Clinical investigation of medical devices for human subjects- Good ...ketakeephadnis
╠²
Clinical investigation of medical devices for human subjects- Good clinical practices Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Co-Chairs and Presenters, Gerald Appel, MD, and Dana V. Rizk, MD, discuss kidney disease in this CME activity titled ŌĆ£Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Pathway Therapies.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/48UHvVM. CME credit will be available until February 25, 2026.Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy | Causes, Risks & Management



Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy | Causes, Risks & ManagementDr.Laxmi Agrawal Shrikhande
╠²
Explore the impact of thyroid disorders in pregnancy, including causes, risks, diagnosis, and management strategies to ensure maternal and fetal health.Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptx



Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptxMohamadAlhes
╠²
Neurological complications of inflective endocarditis Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptx



Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptxKafrELShiekh University
╠²
Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.plant fibres and surgical dressing. method of preparation



plant fibres and surgical dressing. method of preparationchandaniprasad
╠²
Surgical dressing- The word surgical dressing is used to include all the materials
either used alone or in combination to cover the wound.Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes status_Dr Ahmed Al Montasir_f...



Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes status_Dr Ahmed Al Montasir_f...zilkerapurbo
╠²
Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes statusIMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINE



IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINERelianceNwosu
╠²
This presentation emphasizes the role of immunodiagnostics and Immunotherapy. Research Problems - Nursing Research....



Research Problems - Nursing Research....Dr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
╠²
Research Problems - Nursing ResearchDigestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing Students



Digestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing StudentsViresh Mahajani
╠²
This educational PowerPoint presentation is designed to equip GNM students with a solid understanding of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. It explores the anatomical structures, physiological processes, and clinical significance of these vital organs. Key topics include:
Liver functions: detoxification, metabolism, and bile synthesis.
Gallbladder: bile storage and release.
Pancreas: exocrine and endocrine functions, including digestive enzyme and hormone production. This presentation is ideal for GNM students seeking a clear and concise review of these important digestive system components."Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptx



Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptxWahid Husein
╠²
A decade of rabies control programmes in Bali with support from FAO ECTAD Indonesia with Mass Dog Vaccination, Integrated Bite Case Management, Dog Population Management, and Risk Communication as the backbone of the programmesNeurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptx



Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptxdribnibrahem164
╠²
neurological complications of infective endocarditisAdvancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Levers in Physiotherapy
- 1. 1 LEVERS LEVERS ’éĢDEFINATION ’éĢ COMPONENTS OF LEVER ’éĢTYPES OF LEVER ’éĢEXAMPLES
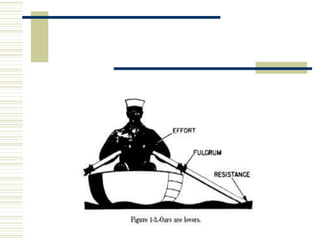
- 2. 2 LEVERS LEVER ’üĘ LEVER is a rigid bar that rotates around a fix ed point called fulcrum(F). ’üĘ It is simple machine which magnifies the for ce and speed of movement. Rigid Bar Fulcrum
- 3. 3 LEVERS Component of Lever ’üĘ Fulcrum ŌĆō It is represented by the joint or is a point on the axis about which the rigid mass rotates. ’üĘ Effort Arm ŌĆō Effort (E) is the point where muscle is attached to the bone. It includes all parts of the rigid mass between the fulcrum and the point at which en ergy is applied to the rigid bar. EF RF F EA RA
- 4. 4 LEVERS ’üĘ Resistance Arm ŌĆō Resistance ( R ) is the poin t where object is held. ’üĘ RA includes all parts of the rigid mass betwe en the fulcrum and the point at which energy is applied to the object to be moved by the le ver.
- 5. 5 LEVERS Levers in Human Body Fulcrum Effort Force Resistance Force Muscle Force Joint Gravity/Weight
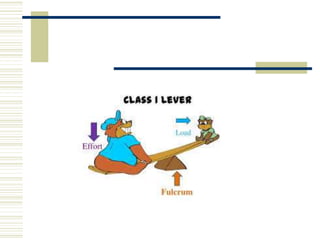
- 6. 6 LEVERS TYPES OF LEVER ’üĘ Mainly three: 1.First Class Lever 2.Second Class Lever 3.Third Class Lever
- 7. 7 LEVERS First Class Lever EA RA F EA RA ’üĘ In this F lies in between the point of applic ation of Effort and the point of application of Resistance.
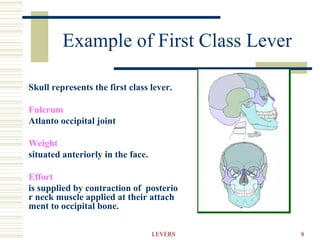
- 8. 8 LEVERS Example of First Class Lever Skull represents the first class lever. Fulcrum Atlanto occipital joint Weight situated anteriorly in the face. Effort is supplied by contraction of posterio r neck muscle applied at their attach ment to occipital bone.
- 9. 9 LEVERS Second Class Lever ’üĘ In this the RF has a point of application betw een the F and the point of application of the EF. (EA>RA) EF RF F EA RA
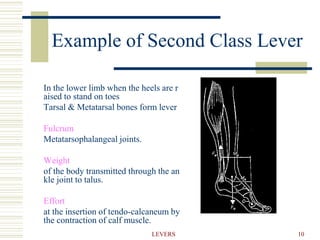
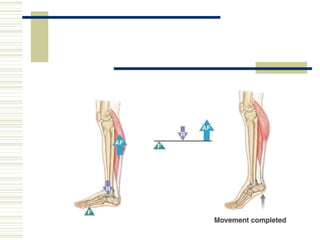
- 10. 10 LEVERS Example of Second Class Lever In the lower limb when the heels are r aised to stand on toes Tarsal & Metatarsal bones form lever Fulcrum Metatarsophalangeal joints. Weight of the body transmitted through the an kle joint to talus. Effort at the insertion of tendo-calcaneum by the contraction of calf muscle.
- 11. 11 LEVERS Third Class Lever ’üĘ In this the EF has a point of application betw een the F and the point of application of the RF. (RA>EA) EF RF F EA RA
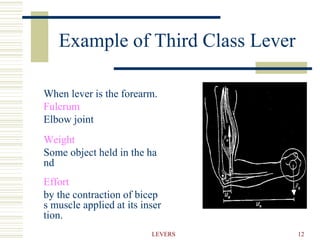
- 12. 12 LEVERS Example of Third Class Lever When lever is the forearm. Fulcrum Elbow joint Weight Some object held in the ha nd Effort by the contraction of bicep s muscle applied at its inser tion.
- 13. 13 LEVERS MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE ( M Ad) ’üĘ It is a measure of the efficiency of the lever. ’é¦ M Ad = EA / RA ’üĘ Whenever MA is > than one, the magnitude of the effort force can be smaller than the ma gnitude of resistance. I.e smaller effort is req uired to overcome a large resistance.
- 14. 14 LEVERS ’üĘ In all 2nd class lever, the MA of the lever is g reater than than one as EA > RA. ’üĘ In our body majority are 3rd class levers. Mechanical advantage < 1.
- 15. 15 LEVERS Uses of Lever ’üĘ By learning the concepts of various type s of lever these principles can be applied in almost all aspects of therapy. ’üĘ To make exercise more resistive long le ver arm can be selected. Contrary in the beginning short lever arm is preferred.


