Light color-sl
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes672 views
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves or particles called photons. It comes from the sun and stars, where electrons in atoms get excited and jump to higher orbits. When they fall back down, they emit photons of light. The color of light depends on the energy level of the electron jump. Light can act as both a particle and a wave, traveling at 300 million meters per second. When light interacts with matter, it can be transmitted, reflected, absorbed, or scattered depending on the object. Astronomers study light from stars to learn about their composition, temperature, and movement.
1 of 17
Download to read offline
















Recommended
Colour



ColourMahesh Rathva
Ěý
Color or colour (see spelling differences) is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, blue, yellow, green and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light (distribution of light power versus wavelength) interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors. Color categories and physical specifications of color are also associated with objects, materials, light sources, etc., based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space, colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates.Light and Color



Light and ColorGary Abud Jr
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that can behave as both a particle (photon) and a wave. It travels at 300 million meters per second in a vacuum. When light interacts with matter, it can be transmitted, reflected, scattered, absorbed, or refracted. The color of light depends on its wavelength, with shorter wavelengths like blue having higher frequencies and energies than longer wavelengths like red.Light



LightJennifer Vasquez
Ěý
Light is important because it allows us to see. There are two types of light: natural light from the sun, moon, stars, and fireflies, and artificial light made by humans like candles and light bulbs. Light travels very fast in straight lines and can pass through some materials, like glass, while being blocked by others, like wood, causing shadows. When light interacts with materials it can be transmitted, reflected, or absorbed, and reflected light causes rainbows and shadows.Light



Lightsuesippel
Ěý
This document discusses different types of electromagnetic waves including visible light. It explains that electromagnetic waves can travel through space without a medium and lists various natural and artificial sources of light energy. The document also describes how light interacts with matter by being reflected, absorbed, or transmitted and defines transparent, translucent, and opaque materials based on how they interact with light.5th grade chapter 14 section 3 - what is light energy



5th grade chapter 14 section 3 - what is light energyhinsz
Ěý
The document discusses properties of electromagnetic radiation including light. It explains that light travels in waves at different speeds in different materials and can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed. Shorter wavelengths like ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays have more energy than longer wavelengths like infrared, microwaves, and radio waves. The document also describes how light travels in straight lines and is bent by lenses, forming shadows and rainbows.Light and sound 2part



Light and sound 2partantrese
Ěý
This document provides a summary of key concepts about light for 4th grade science students. It defines light and describes its sources as the sun, stars, electric lights, and fire. It explains that light travels in straight lines and waves, and can be seen when it reflects off objects into our eyes. The document discusses the visible light spectrum and color, transparent and opaque materials, reflection and refraction, and how lenses work. The summary is intended to introduce students to basic properties and behaviors of light.Light energy



Light energyLihui Yee
Ěý
Light is a form of energy that enables us to see and allows plants to perform photosynthesis. It travels in straight lines and can be natural sources like the sun or artificial sources that use man-made power. Materials are either opaque and block all light, translucent and block some light, or transparent and allow all light to pass through. Shadows are formed when light is blocked and their size, shape, or length can be changed by manipulating the position of the light source or object.Light!



Light!amandayoung313
Ěý
1) The document discusses the properties and behavior of light, including that light carries energy as an electromagnetic wave. It travels in straight lines called rays.
2) When light hits an object, it can be absorbed, reflected, or pass through. Reflection is when light bounces off an object and into our eyes, allowing us to see things.
3) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Different colors are wavelengths of light, with blue having a higher frequency than red. The color we see is determined by the wavelengths reflected by an object.Light jeopardy 



Light jeopardy antrese
Ěý
This document is a review of the game show Jeopardy! with categories related to light. The categories include how light acts, light and color, light materials, and more. Each category has clues in the form of questions ranging from 100 to 500 points. The review covers key topics about light including the colors of the visible spectrum, sources of light like the sun, reflection, refraction, and more.Color & light



Color & lightMicheal Abebe
Ěý
Light is radiant energy that allows for vision. It travels very fast at around 300,000 km/s and comes from the sun as the main natural light source. There are two types of light - natural from sources like the sun, and artificial that is man-made such as light bulbs. Objects can be transparent and let all light pass through, translucent and let some light pass through, or opaque and not let any light pass through. Light interacts with objects and the environment in various ways such as reflecting, transmitting, scattering, and causing shadows, rainbows, and colors.Light Energy



Light EnergyElizabeth Nolen
Ěý
Light energy is electromagnetic radiation consisting of electrical and magnetic energy. It is emitted by electrons in objects and travels in waves across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption occurs when light is not reflected or transmitted by an object, with different colors absorbed and reflected. Reflection is when light bounces off a surface, like in mirrors. Transmission is when light passes through a medium without being absorbed or scattered. Refraction is the bending of light waves changing direction as they pass between substances. Scattering causes light to bounce off objects in many directions, as seen with the blue sky and halos around the sun.Light final for me



Light final for meMd EnaMul HaQ
Ěý
This document discusses various topics related to light, including:
- Natural light sources like the sun and artificial light sources.
- Light behaves as both a wave and particle. It carries energy and information.
- Light travels very fast at 300 million meters per second.
- The electromagnetic spectrum includes both visible and invisible light.
- Reflection, shadows, rainbows, and color are produced through light interactions.Light and Shadow



Light and ShadowYoshy Faweta
Ěý
Light travels in straight lines and can be reflected or refracted. There are three types of materials: transparent, translucent, and opaque. Shadows are formed when an object blocks light. The length and shape of a shadow depends on the position of the light source and object. An experiment was conducted to determine which material - transparent plastic, tissue paper, or black paper - makes the darkest shadow. Black paper produced the darkest shadow because it is opaque and does not let any light pass through.LIGHT 1



LIGHT 1isamadero79
Ěý
This document discusses light sources and how light travels. The main points are:
- The sun is our primary natural light source. Other light sources can be natural or man-made. The moon, water, and mirrors are not true light sources as they only reflect light.
- Light travels in straight lines. When it hits an opaque object, some light is absorbed and the rest is reflected. Transparent objects allow light to pass through, while translucent objects let some light pass through and reflect the rest.
- For us to see, light enters the eye and is focused on the retina. The retina sends this visual information to the brain via the optic nerve to be interpreted. Color is the result ofThe absorption and the selective refraction of light the color of objects



The absorption and the selective refraction of light the color of objectsTrần Thị Yến Xuân
Ěý
The document discusses the selective absorption and reflection of light and how it relates to color.
1) Light passing through a medium decreases in intensity exponentially with distance according to the absorption factor α, which depends on the wavelength of light.
2) Objects appear colored because they selectively absorb some wavelengths of visible light while reflecting or transmitting others.
3) The color of objects is due to their ability to selectively absorb and reflect certain wavelengths of visible light, making them appear that color.Light Energy



Light Energyblueroses0805
Ěý
The document discusses various properties of light. It explains that plants use light from the Sun to photosynthesize and make food. It also notes that the moon reflects light from the Sun, making it appear bright at night along with stars. Shadows are formed because light travels in straight lines, and their size and shape can change based on the position of the light source and object. Sunglasses help reduce glare by only allowing some light to pass through their lenses.Light Online



Light Onlineewingj
Ěý
Light is a form of electromagnetic energy that travels in waves at a speed of approximately 186,000 miles per second. It can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed when it interacts with different materials and surfaces. Visible light is made up of different wavelengths that correspond to the colors of the rainbow, with red having the longest wavelength and violet the shortest. Lenses and prisms can bend light through refraction, causing the different wavelengths to separate, which is how rainbows and spectrums are formed.Sources of Light



Sources of Lightblueroses0805
Ěý
This document discusses various sources of light and how light interacts with objects. It covers how light travels from sources to our eyes, how we see objects that are not light sources via light reflecting off of them, and how reflection works with both rough and shiny surfaces. It also explores color, how white light is composed of many colors, and how combining colors of light produces new colors.Light Lesson 1



Light Lesson 1dhmcmillan
Ěý
1. Light is a form of energy that travels away from a source in straight lines at a very high speed of 300,000 km/s.
2. Light has natural sources like the sun and stars, and artificial sources like candles, lamps, and flashlights that produce light when burning or heating.
3. Experiments showing light traveling through screens demonstrate that light travels in straight lines from its source.01 how does light travel



01 how does light travelMs Yam
Ěý
1) Light travels much faster than sound, so we see lightning before hearing thunder. When a starting pistol fires, we see the smoke before hearing the bang.
2) Light travels extremely fast at around 300,000 kilometers per second, and can circle the Earth 8 times in one second.
3) Light reaches the moon in 1.3 seconds, the nearest star other than the sun in 8.5 minutes, but reaches Pluto and the sun almost instantly.Ch.12.less.12.how does light travel and interact with matter



Ch.12.less.12.how does light travel and interact with matterReem Bakr
Ěý
This document summarizes key concepts about how light travels and interacts with matter in 3 paragraphs or less:
Light travels from the sun to earth at a distance of 90 million miles. It is made up of electric and magnetic waves that can pass through a vacuum faster than other materials. The speed and wavelength of light determines how it interacts with different transparent, translucent, or opaque materials by passing through, reflecting, or forming shadows on them. When light changes mediums it bends, as seen when a spoon appears bent in a glass of water, in a phenomenon called refraction. Light and sound daily power point



Light and sound daily power pointcbelldes
Ěý
1. The document discusses key concepts about light and sound including that light travels in straight lines while sound travels as waves through matter.
2. Key terms are defined such as reflection, refraction, transparent and opaque objects.
3. The document also explores how lenses work, specifically that convex lenses magnify objects while concave lenses make objects appear smaller.Characteristic Of light and Visible Spectrum



Characteristic Of light and Visible SpectrumKathNiel Bernadilla
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that stimulates sight and makes objects visible. It is classified based on how it interacts with different materials. Transparent materials allow light to pass through clearly, translucent materials allow some light to pass through, and opaque materials do not allow any light to pass through. The visible light spectrum refers to the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum detectable by the human eye, ranging from infrared to violet. Within this spectrum, colors are arranged from long to short wavelengths as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.Properties of light



Properties of lightKABILESH RAMAR
Ěý
This document discusses various properties and behaviors of light, including reflection, refraction, diffraction, and how light interacts with materials and objects. It notes that light travels in straight lines, is faster than sound, allows us to see by reflecting into our eyes, and causes shadows when blocked by objects. The document also addresses how light can be absorbed or reflected by objects and that the color of an object is determined by the dominant frequency of the light.Light - Physics



Light - PhysicsRising Fighters
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that allows us to see. It can travel without a medium and includes visible light. The sun, flames, and light bulbs are luminous as they produce their own light, while objects like the moon reflect light and are non-luminous. Materials can be opaque and block light, transparent and let light pass through clearly, or translucent and let some light pass through blurring images. Shadows are formed when an opaque object blocks light, which travels in straight lines. Solar and lunar eclipses occur due to the alignment of the sun, earth, and moon. A pinhole camera uses a small opening to project an image using the principle that light travels in straight lines.Light - Part -1 



Light - Part -1 Imaginative Brain Science
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the key topics covered in a 6th grade science chapter on light. The chapter will cover the basic concepts of light, including sources of light, luminous and non-luminous bodies, transparency, translucency and opacity. It will also cover the properties of light rays, beams of light, rectilinear propagation, and applications like pinhole cameras and shadow formation. Specific types of shadows like umbra and penumbra will be defined. Finally, the chapter will discuss natural eclipses like lunar and solar eclipses.Light and sound



Light and soundluisagema
Ěý
1) Light travels in straight lines and much faster than sound.
2) We see objects because they reflect light into our eyes, and shadows are formed when light is blocked.
3) Reflection, refraction, and the splitting of white light into colors are described. Filters can be used to block certain colors of light.Light



LightMakati Science High School
Ěý
The document discusses the nature and properties of light. It explains that early scientists like Newton and Huygens disagreed on whether light behaved as a particle or wave, but Maxwell later proposed light has a dual nature. The document also discusses common light sources like the sun and artificial sources like bulbs. It describes how these sources transform other forms of energy into light. Additionally, it explains properties of light such as traveling in straight lines and casting shadows due to its high fixed speed.Meetali



MeetaliCute Girl
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that travels in straight lines and can act as both a particle and a wave. It comes from the sun and stars as atoms emit photons of light when electrons jump to different orbits and then fall back to their original orbits. The color of the light depends on the size of the jump between electron orbits, with bigger jumps producing higher energy and shorter wavelengths like blue light.Light Properties



Light Propertiesdscfall2012
Ěý
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that can be described as a stream of massless particles called photons traveling in wave-like patterns. Electromagnetic radiation includes visible light as well as other wavelengths and includes properties like wavelength, frequency, and speed. Light travels in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, and separated into colors using a prism. The sky appears blue during the day due to scattering of blue light by dust in the atmosphere.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Light jeopardy 



Light jeopardy antrese
Ěý
This document is a review of the game show Jeopardy! with categories related to light. The categories include how light acts, light and color, light materials, and more. Each category has clues in the form of questions ranging from 100 to 500 points. The review covers key topics about light including the colors of the visible spectrum, sources of light like the sun, reflection, refraction, and more.Color & light



Color & lightMicheal Abebe
Ěý
Light is radiant energy that allows for vision. It travels very fast at around 300,000 km/s and comes from the sun as the main natural light source. There are two types of light - natural from sources like the sun, and artificial that is man-made such as light bulbs. Objects can be transparent and let all light pass through, translucent and let some light pass through, or opaque and not let any light pass through. Light interacts with objects and the environment in various ways such as reflecting, transmitting, scattering, and causing shadows, rainbows, and colors.Light Energy



Light EnergyElizabeth Nolen
Ěý
Light energy is electromagnetic radiation consisting of electrical and magnetic energy. It is emitted by electrons in objects and travels in waves across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption occurs when light is not reflected or transmitted by an object, with different colors absorbed and reflected. Reflection is when light bounces off a surface, like in mirrors. Transmission is when light passes through a medium without being absorbed or scattered. Refraction is the bending of light waves changing direction as they pass between substances. Scattering causes light to bounce off objects in many directions, as seen with the blue sky and halos around the sun.Light final for me



Light final for meMd EnaMul HaQ
Ěý
This document discusses various topics related to light, including:
- Natural light sources like the sun and artificial light sources.
- Light behaves as both a wave and particle. It carries energy and information.
- Light travels very fast at 300 million meters per second.
- The electromagnetic spectrum includes both visible and invisible light.
- Reflection, shadows, rainbows, and color are produced through light interactions.Light and Shadow



Light and ShadowYoshy Faweta
Ěý
Light travels in straight lines and can be reflected or refracted. There are three types of materials: transparent, translucent, and opaque. Shadows are formed when an object blocks light. The length and shape of a shadow depends on the position of the light source and object. An experiment was conducted to determine which material - transparent plastic, tissue paper, or black paper - makes the darkest shadow. Black paper produced the darkest shadow because it is opaque and does not let any light pass through.LIGHT 1



LIGHT 1isamadero79
Ěý
This document discusses light sources and how light travels. The main points are:
- The sun is our primary natural light source. Other light sources can be natural or man-made. The moon, water, and mirrors are not true light sources as they only reflect light.
- Light travels in straight lines. When it hits an opaque object, some light is absorbed and the rest is reflected. Transparent objects allow light to pass through, while translucent objects let some light pass through and reflect the rest.
- For us to see, light enters the eye and is focused on the retina. The retina sends this visual information to the brain via the optic nerve to be interpreted. Color is the result ofThe absorption and the selective refraction of light the color of objects



The absorption and the selective refraction of light the color of objectsTrần Thị Yến Xuân
Ěý
The document discusses the selective absorption and reflection of light and how it relates to color.
1) Light passing through a medium decreases in intensity exponentially with distance according to the absorption factor α, which depends on the wavelength of light.
2) Objects appear colored because they selectively absorb some wavelengths of visible light while reflecting or transmitting others.
3) The color of objects is due to their ability to selectively absorb and reflect certain wavelengths of visible light, making them appear that color.Light Energy



Light Energyblueroses0805
Ěý
The document discusses various properties of light. It explains that plants use light from the Sun to photosynthesize and make food. It also notes that the moon reflects light from the Sun, making it appear bright at night along with stars. Shadows are formed because light travels in straight lines, and their size and shape can change based on the position of the light source and object. Sunglasses help reduce glare by only allowing some light to pass through their lenses.Light Online



Light Onlineewingj
Ěý
Light is a form of electromagnetic energy that travels in waves at a speed of approximately 186,000 miles per second. It can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed when it interacts with different materials and surfaces. Visible light is made up of different wavelengths that correspond to the colors of the rainbow, with red having the longest wavelength and violet the shortest. Lenses and prisms can bend light through refraction, causing the different wavelengths to separate, which is how rainbows and spectrums are formed.Sources of Light



Sources of Lightblueroses0805
Ěý
This document discusses various sources of light and how light interacts with objects. It covers how light travels from sources to our eyes, how we see objects that are not light sources via light reflecting off of them, and how reflection works with both rough and shiny surfaces. It also explores color, how white light is composed of many colors, and how combining colors of light produces new colors.Light Lesson 1



Light Lesson 1dhmcmillan
Ěý
1. Light is a form of energy that travels away from a source in straight lines at a very high speed of 300,000 km/s.
2. Light has natural sources like the sun and stars, and artificial sources like candles, lamps, and flashlights that produce light when burning or heating.
3. Experiments showing light traveling through screens demonstrate that light travels in straight lines from its source.01 how does light travel



01 how does light travelMs Yam
Ěý
1) Light travels much faster than sound, so we see lightning before hearing thunder. When a starting pistol fires, we see the smoke before hearing the bang.
2) Light travels extremely fast at around 300,000 kilometers per second, and can circle the Earth 8 times in one second.
3) Light reaches the moon in 1.3 seconds, the nearest star other than the sun in 8.5 minutes, but reaches Pluto and the sun almost instantly.Ch.12.less.12.how does light travel and interact with matter



Ch.12.less.12.how does light travel and interact with matterReem Bakr
Ěý
This document summarizes key concepts about how light travels and interacts with matter in 3 paragraphs or less:
Light travels from the sun to earth at a distance of 90 million miles. It is made up of electric and magnetic waves that can pass through a vacuum faster than other materials. The speed and wavelength of light determines how it interacts with different transparent, translucent, or opaque materials by passing through, reflecting, or forming shadows on them. When light changes mediums it bends, as seen when a spoon appears bent in a glass of water, in a phenomenon called refraction. Light and sound daily power point



Light and sound daily power pointcbelldes
Ěý
1. The document discusses key concepts about light and sound including that light travels in straight lines while sound travels as waves through matter.
2. Key terms are defined such as reflection, refraction, transparent and opaque objects.
3. The document also explores how lenses work, specifically that convex lenses magnify objects while concave lenses make objects appear smaller.Characteristic Of light and Visible Spectrum



Characteristic Of light and Visible SpectrumKathNiel Bernadilla
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that stimulates sight and makes objects visible. It is classified based on how it interacts with different materials. Transparent materials allow light to pass through clearly, translucent materials allow some light to pass through, and opaque materials do not allow any light to pass through. The visible light spectrum refers to the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum detectable by the human eye, ranging from infrared to violet. Within this spectrum, colors are arranged from long to short wavelengths as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.Properties of light



Properties of lightKABILESH RAMAR
Ěý
This document discusses various properties and behaviors of light, including reflection, refraction, diffraction, and how light interacts with materials and objects. It notes that light travels in straight lines, is faster than sound, allows us to see by reflecting into our eyes, and causes shadows when blocked by objects. The document also addresses how light can be absorbed or reflected by objects and that the color of an object is determined by the dominant frequency of the light.Light - Physics



Light - PhysicsRising Fighters
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that allows us to see. It can travel without a medium and includes visible light. The sun, flames, and light bulbs are luminous as they produce their own light, while objects like the moon reflect light and are non-luminous. Materials can be opaque and block light, transparent and let light pass through clearly, or translucent and let some light pass through blurring images. Shadows are formed when an opaque object blocks light, which travels in straight lines. Solar and lunar eclipses occur due to the alignment of the sun, earth, and moon. A pinhole camera uses a small opening to project an image using the principle that light travels in straight lines.Light - Part -1 



Light - Part -1 Imaginative Brain Science
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the key topics covered in a 6th grade science chapter on light. The chapter will cover the basic concepts of light, including sources of light, luminous and non-luminous bodies, transparency, translucency and opacity. It will also cover the properties of light rays, beams of light, rectilinear propagation, and applications like pinhole cameras and shadow formation. Specific types of shadows like umbra and penumbra will be defined. Finally, the chapter will discuss natural eclipses like lunar and solar eclipses.Light and sound



Light and soundluisagema
Ěý
1) Light travels in straight lines and much faster than sound.
2) We see objects because they reflect light into our eyes, and shadows are formed when light is blocked.
3) Reflection, refraction, and the splitting of white light into colors are described. Filters can be used to block certain colors of light.Light



LightMakati Science High School
Ěý
The document discusses the nature and properties of light. It explains that early scientists like Newton and Huygens disagreed on whether light behaved as a particle or wave, but Maxwell later proposed light has a dual nature. The document also discusses common light sources like the sun and artificial sources like bulbs. It describes how these sources transform other forms of energy into light. Additionally, it explains properties of light such as traveling in straight lines and casting shadows due to its high fixed speed.Similar to Light color-sl (20)
Meetali



MeetaliCute Girl
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that travels in straight lines and can act as both a particle and a wave. It comes from the sun and stars as atoms emit photons of light when electrons jump to different orbits and then fall back to their original orbits. The color of the light depends on the size of the jump between electron orbits, with bigger jumps producing higher energy and shorter wavelengths like blue light.Light Properties



Light Propertiesdscfall2012
Ěý
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that can be described as a stream of massless particles called photons traveling in wave-like patterns. Electromagnetic radiation includes visible light as well as other wavelengths and includes properties like wavelength, frequency, and speed. Light travels in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, and separated into colors using a prism. The sky appears blue during the day due to scattering of blue light by dust in the atmosphere.Light



LightSandraKirolos1992
Ěý
Light is a form of electromagnetic energy that travels in waves and can be reflected, absorbed, or passed through materials. It moves very fast, taking only 8 minutes to travel from the sun to earth, despite the immense 150 million kilometer distance between them. Materials are classified based on how they interact with light, being transparent if light passes through, translucent if some light passes through, or opaque if no light can pass. Common light sources include the sun, light bulbs, and things that reflect light like mirrors.Physics Light.pptx



Physics Light.pptxAna Maria Montaño
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. It behaves both as a wave and as particles called photons. Light travels in straight lines at a constant speed and contains wavelengths that correspond to different colors. When light interacts with matter, it can be reflected, refracted, diffracted, dispersed, or polarized. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, refraction when it changes direction passing between media of different densities, and diffraction when it spreads out around obstacles. Dispersion separates light into a spectrum, and polarization reduces the oscillation of light waves. Early humans imitated the sun's natural light with fire, then candles and oil lamps, and now use electricity for illumination.COLOR_OF_LIGHTS.ppt



COLOR_OF_LIGHTS.pptJuliusDagleDimaala
Ěý
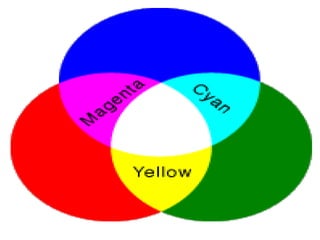
Electromagnetic waves interact with materials in several ways that determine the color perceived. Color arises from emission, reflection, transmission, interference, dispersion, and scattering of light waves interacting with objects. The primary colors of light are red, green and blue, which combine to make white light. The primary colors of pigment are cyan, yellow and magenta, which combine to make black. Reflection, refraction, polarization, and interference cause the wide variety of colors observed from different materials due to the interaction of light waves.Lecture 14



Lecture 14Chantel Davis
Ěý
Electromagnetic waves consist of vibrating electric and magnetic fields that propagate at the speed of light. The electromagnetic spectrum includes visible light as well as other types of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays. Electromagnetic waves can be characterized by their wavelength or frequency, with radio waves having the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies, and gamma rays having the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. Materials can absorb, transmit, or reflect electromagnetic waves depending on the wavelength and properties of the material.LIGHT.pptx



LIGHT.pptxGretchenJavier1
Ěý
The document discusses the history of theories about the nature of light from ancient Greece to modern times. Key figures proposed light as particles, waves, or both. It was determined that light travels at a finite speed and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The modern view is that light exhibits both wave and particle properties. The document also covers related topics like polarization, shadows, and 3D viewing.Forms of Radiant Energy.pptx



Forms of Radiant Energy.pptxAnjaliPn2
Ěý
Radiant energy is a form of energy that can travel through space in the form of electromagnetic waves. It is transmitted from the sun to the Earth through a vacuum via electromagnetic waves like visible light. Electromagnetic waves are induced when electric and magnetic forces interact, and they can travel through space, air, or solids at the speed of light. When electromagnetic waves come into contact with objects, they cause the particles in those objects to move, transferring their energy and doing work.Light and it's properties-1 copy.pptx



Light and it's properties-1 copy.pptxshamsudheenpp1
Ěý
Light has both wave-like and particle-like properties. It travels as an electromagnetic wave and exhibits behaviors of reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference and polarization. Light can be reflected, refracted, absorbed and emitted by matter. It travels in electromagnetic spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays and can be polarized, scattered, or dispersed.Light and Shadow



Light and ShadowDIAH KOHLER
Ěý
Light is a form of energy that travels in straight lines and allows us to see objects. It can behave as both a particle and a wave. Light sources like the sun emit light, while other objects appear visible when light reflects off of their surfaces. Light can be transmitted through transparent materials, scattered through translucent materials, or blocked by opaque materials. When light hits an object, it can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. Shadows are formed when an object blocks light from a source, and their size depends on the distance between the object and light source. Light plays an important role in vision, photosynthesis, and warming the Earth.Light



LightSophia Pena
Ěý
This document discusses the properties and importance of light. It explains that there are two types of light: natural light from the sun, moon, stars, and fireflies, and artificial light created by humans like candles and light bulbs. Light travels very fast, is a form of energy that travels in waves, and can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed as it interacts with different materials and objects. The document also describes how vision works and how we see color depending on which wavelengths of light are reflected or absorbed by various surfaces.Lesson 4 Light Waves for Grade 8 Science



Lesson 4 Light Waves for Grade 8 ScienceErlison Lorenz Ognilla
Ěý
An outline of discussion about light waves for grade 8Light



LightAkanksha Dombe
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves. It has properties of both waves and particles. Light waves have different wavelengths and frequencies that determine their energy levels. Light can be reflected, refracted, absorbed, or transmitted when it interacts with matter. Common light sources produce light through incandescence or luminescence. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation including visible light, infrared, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays and more, arranged by wavelength and frequency.Light



LightAkanksha Dombe
Ěý
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves. It can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed when it interacts with matter. Light travels in straight lines until it encounters an object, where it can be reflected, refracted, scattered, or absorbed. The speed and direction of light changes when moving between materials of different densities. Light is visible to humans in the form of different wavelengths that make up the visible spectrum.electromagnetic spectrum and light ppt.pptx



electromagnetic spectrum and light ppt.pptxVangie Esquillo
Ěý
1) Light travels in straight lines at very fast speeds, but can be reflected or refracted when it hits surfaces.
2) Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface at the same angle it hits, following the law of reflection. Refraction occurs when light changes speed and bends as it passes from one medium to another.
3) Colors are a result of light reflecting or transmitting specific wavelengths, and objects appear different colors depending on the wavelengths of light reflected towards our eyes.Light



Lighteliseb
Ěý
This document summarizes key developments in the understanding of light from ancient Greek philosophers to present day. It describes early theories that light consisted of particles (Pythagoras, Newton) or waves (Aristotle, Huygens, Young), experiments measuring the speed of light (Galileo, Roemer, Maxwell), the establishment of light as electromagnetic radiation, and the modern understanding of light exhibiting both wave and particle properties.CHAPTER 8 Light 1.pptx



CHAPTER 8 Light 1.pptxTHANABALANALMUNUSWAM
Ěý
Plane mirrors form virtual images that cannot be projected on a screen. Concave mirrors are used by dentists to magnify images of teeth and for applying makeup. Convex mirrors are installed at dangerous corners of roads and in supermarkets to prevent theft. When light hits mirrors, it follows the laws of reflection where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection and the incident ray, normal, and reflected ray are in the same plane. Refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another of different density, causing it to change direction. This is why objects in water appear closer or bent. Prisms disperse white light into a rainbow spectrum due to differing refraction of colors. Scattering of light by particles in theLight



LightMaria Runela Celis
Ěý
Light is important because it allows us to see. There are two types of light: natural light from the sun, moon, stars, and fireflies, and artificial light made by humans like candles and light bulbs. Light travels very fast in straight lines and can pass through some materials, like glass, while being blocked by others, like wood, causing shadows. When light interacts with materials it can be reflected, like in mirrors, or broken into a spectrum or colors, as seen in rainbows.Light & optics



Light & opticsitutor
Ěý
Light is electromagnetic radiation that travels at about 300,000 km/s. It can be emitted from luminous objects like stars or reflected from illuminated objects like the moon. Light carries energy and information, travels in straight lines, and can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed when interacting with objects. The human eye detects light via photoreceptors in the retina that send signals to the brain, allowing us to see color.Light color-sl
- 1. What is light? We see light as color and brightness It’s actually electromagnetic radiation: Partly electric, partly magnetic Flows in straight line (radiates)
- 2. Where does light come from? • The Sun and stars. • But how do they make light? • It all starts with ATOMS • A nucleus surrounded by electrons that orbit. • Like the planets in the solar system, electrons stay in the same orbit, unless…
- 3. Where does light come from(2) • Electrons get kicked into a different orbit • This doesn’t happen very often in solar systems, but it does in atoms • If you add energy to an atom (heat it up), the electrons will jump to bigger orbits. • When atom cools, electrons jump back to original orbits. • As they jump back, they emit light, a form of energy
- 4. Color of light • Each electron that jumps back emits one photon of light • What color is this light? • Depends on how big the jump between orbits was • The bigger the jump, the higher the energy. • The energy determines color; a blue photon has more energy than a red • Shine all the colors together, you get white light!
- 6. Light as particle • A photon is like a particle, but it has no mass • Think of a photon as a grain of sand. • We see so many photons at the same time it’s like seeing all the sand on a beach; we don’t notice the single grains • When light hits film in a film camera, it acts like photons.
- 7. Light as a wave • But sometimes light acts like a wave • A wave has a wavelength, a speed and a frequency. • We’ll learn more about wave behavior when we talk about polarization • All light travels same speed (in vacuum) • The energy goes up as frequency goes up • Color depends on frequency • Wavelength gets shorter as frequency goes up
- 8. Speed of light • Light travels at 300,000,000 meters/second • It takes 8 minutes for a light wave (or a photon) to travel from the sun to the earth. • We see the moon because it reflects the sun’s light • It takes 1 second for light reflected off the moon to reach the earth.
- 9. Light and matter • When light hits something (air, glass, a green wall, a black dress), it may be: • Transmitted (if the thing is transparent) • Reflected or scattered (off mirror or raindrops) • Absorbed (off a black velvet dress) • Often it’s some combination. Take a simple piece of paper: you can see some light through, white reflects, black print absorbs.
- 10. The waves can pass through the object The waves can be absorbed by the object. The waves can be reflected off the object. The waves can be scattered off the object. The waves can be refracted through the object.
- 11. Reflection and color • Remember, white light contains all colors (a rainbow or prism separates them so we can see this) • Why does a green wall look green in the sunshine? • Why does it look different when it’s in the shade? • Well, in the dark, it’s black. No light reflects off it. • A green wall reflects only green light; it absorbs all the other colors.
- 12. Absorption and color • Why is a black car hotter than a white car in the summer? • Remember light is energy. Heat is another form of energy. • A white car reflects all wavelengths of light. • A black car absorbs all wavelengths of light, absorbing the energy and turning it to heat.
- 14. Light transmission • Transparent materials transmit light, like windows. • Remember all light has same speed in vacuum? • Different frequencies have different speeds in transparent materials – that causes a prism to separate the colors. • Colored glass or plastic only transmits the color that it is; it absorbs or reflects the other colors.
- 15. Using Light to Study the Stars Astronomers collect energy from the stars with a telescope Visible light Infrared light Radio waves, etc. Each atom has a special pattern of light frequencies like a fingerprint The fingerprint of frequencies will be shifted if the star is moving away or toward us (like the sound of a freight train) The temperature of the Star can be determined from the color of the star Here are two pictures of the ring nebula. One in visible light one in infrared light…

