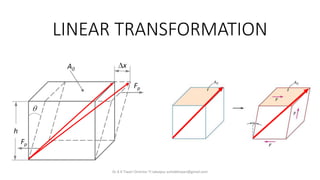
LINEAR TRANSFORMATION22.pptx
- 1. LINEAR TRANSFORMATION Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 2. ŌĆó A linear equation is an equation that has one or more variables having degree one. ŌĆó Matrix multiplication method and gaussian elimination method are two methods to solve linear equations using matrices. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com Ax=b
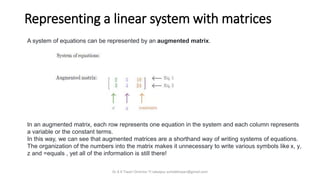
- 3. Representing a linear system with matrices A system of equations can be represented by an augmented matrix. In an augmented matrix, each row represents one equation in the system and each column represents a variable or the constant terms. In this way, we can see that augmented matrices are a shorthand way of writing systems of equations. The organization of the numbers into the matrix makes it unnecessary to write various symbols like x, y, z and =equals , yet all of the information is still there! Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 4. Which system is represented by the augmented matrix? Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 5. LINEAR SYSTEM ŌĆó principle of superposition ŌĆó Homogeneity: A system is said to be homogeneous, if we multiply input with some constant A then the output will also be multiplied by the same value of constant (i.e. A). ŌĆó Additivity: Suppose we have a system S and we are giving the input to this system as a1 for the first time and we are getting the output as b1 corresponding to input a1. On the second time we are giving input a2 and correspond to this we are getting the output as b2. ŌĆó Now suppose this time we are giving input as a summation of the previous inputs (i.e. a1 + a2) and corresponding to this input suppose we are getting the output as (b1 + b2) then we can say that system S is following the property of additivity. S Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 6. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 7. 1.A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers while a vector is a mathematical quantity that has magnitude and direction. 2.A vector and a matrix are both represented by a letter with a vector typed in boldface with an arrow above it to distinguish it from real numbers while a matrix is typed in an upper- case letter. 3.Vectors are used in geometry to simplify certain 3D problems while matrices are key tools used in linear algebra. 4.A vector is an array of numbers with a single index while a matrix is an array of numbers with two indices. 5.While a vector is used to represent magnitude and direction, a matrix is used to represent linear transformations and keep track of coefficients in linear equations. P = xi + yj + zk. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 8. Vectors are a collection of components which are related to a set of basis vectors basis vectors x^ and y^ for the basis vectors along the xŌłÆaxis and yŌłÆaxis respectively. vectors as points in space, assuming the tail is always at the origin and the head is at the specified point. Vector as column matrices Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 9. THIS MATRIX HAS 3 VECTORS Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
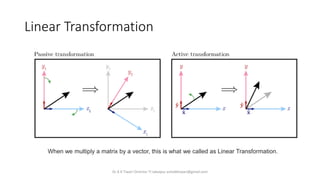
- 10. Linear Transformation When we multiply a matrix by a vector, this is what we called as Linear Transformation. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 11. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
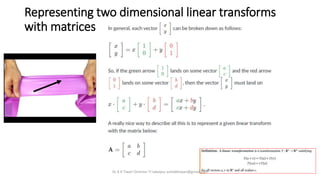
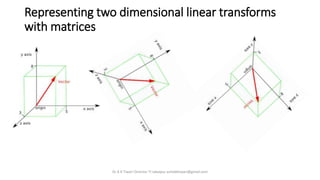
- 12. Representing two dimensional linear transforms with matrices Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 13. Representing three dimensional linear transforms with matrices Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 14. Representing two dimensional linear transforms with matrices Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 15. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 16. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 17. (eigen- meaning own, belonging to oneself, in German) ŌĆó The eigenvectors are the directions in which the matrix acts solely as a scaling transformation, and the eigenvalues are the corresponding scale factors. ŌĆó eigenvectors of a matrix are those direction in the space that after the matrix operating on them, they supply the same direction with some coefficient of proportionality between "old" and "new" direction that are eigenvalues. ŌĆó The eigen functions represent stationary states of the system i.e. the system can achieve that state under certain conditions and eigenvalues represent the value of that property of the system in that stationary state. ŌĆó the eigenvectors are the special directions where the linear operator A simply acts through scaling. ŌĆó Each Eigenvalue has a set of eigenvectors. ŌĆó Eigenvalues and eigenvectors are linearly dependent Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com
- 18. Eigenvalue =2 , eigenvector P = 2 2 Same direction Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com EXPAND 2 times
- 19. Dr A K Tiwari Director TI Jabalpur ashokktiwari@gmail.com