introduction to linux kernel tcp/ip ptocotol stack
55 likes12,995 views
This document provides an introduction and overview of the networking code in the Linux kernel source tree. It discusses the different layers including link (L2), network (L3), and transport (L4) layers. It describes the input and output processing, device interfaces, traffic directions, and major developers for each layer. Config and benchmark tools are also mentioned. Resources for further learning about the Linux kernel networking code are provided at the end.
1 of 16
Downloaded 1,176 times













Recommended
DevConf 2014 Kernel Networking Walkthrough



DevConf 2014 Kernel Networking WalkthroughThomas Graf
?
This presentation features a walk through the Linux kernel networking stack covering the essentials and recent developments a developer needs to know. Our starting point is the network card driver as it feeds a packet into the stack. We will follow the packet as it traverses through various subsystems such as packet filtering, routing, protocol stacks, and the socket layer. We will pause here and there to look into concepts such as segmentation offloading, TCP small queues, and low latency polling. We will cover APIs exposed by the kernel that go beyond use of write()/read() on sockets and will look into how they are implemented on the kernel side.Understanding DPDK



Understanding DPDKDenys Haryachyy
?
1. DPDK achieves high throughput packet processing on commodity hardware by reducing kernel overhead through techniques like polling, huge pages, and userspace drivers.
2. In Linux, packet processing involves expensive operations like system calls, interrupts, and data copying between kernel and userspace. DPDK avoids these by doing all packet processing in userspace.
3. DPDK uses techniques like isolating cores for packet I/O threads, lockless ring buffers, and NUMA awareness to further optimize performance. It can achieve throughput of over 14 million packets per second on 10GbE interfaces.Introduction to DPDK



Introduction to DPDKKernel TLV
?
DPDK is a set of drivers and libraries that allow applications to bypass the Linux kernel and access network interface cards directly for very high performance packet processing. It is commonly used for software routers, switches, and other network applications. DPDK can achieve over 11 times higher packet forwarding rates than applications using the Linux kernel network stack alone. While it provides best-in-class performance, DPDK also has disadvantages like reduced security and isolation from standard Linux services.FD.IO Vector Packet Processing



FD.IO Vector Packet ProcessingKernel TLV
?
Kirill Tsym discusses Vector Packet Processing:
* Linux Kernel data path (in short), initial design, today's situation, optimization initiatives
* Brief overview of DPDK, Netmap, etc.
* Userspace Networking projects comparison: OpenFastPath, OpenSwitch, VPP.
* Introduction to VPP: architecture, capabilities and optimization techniques.
* Basic Data Flow and introduction to vectors.
* VPP Single and Multi-thread modes.
* Router and switch for namespaces example.
* VPP L4 protocol processing - Transport Layer Development Kit.
* VPP Plugins.
Kiril is a software developer at Check Point Software Technologies, part of Next Generation Gateway and Architecture team, developing proof of concept around DPDK and FD.IO VPP. He has years of experience in software, Linux kernel and networking development and has worked for Polycom, Broadcom and Qualcomm before joining Check Point.DPDK In Depth



DPDK In DepthKernel TLV
?
DPDK in depth
This document provides an overview of DPDK (Data Plane Development Kit):
1. DPDK is an open source project for data plane programming and network acceleration. It started at Intel in 2010 and is now maintained by the Linux Foundation.
2. DPDK provides poll mode drivers (PMDs), libraries, and sample applications for fast packet processing. It uses hugepages and avoids kernel involvement for high performance.
3. The document outlines several DPDK projects, libraries, PMDs, advantages and disadvantages, development process, and demonstrates a simple DPDK application (l2fwd) and the testpmd tool.Dpdk applications



Dpdk applicationsVipin Varghese
?
Here are some useful GDB commands for debugging:
- break <function> - Set a breakpoint at a function
- break <file:line> - Set a breakpoint at a line in a file
- run - Start program execution
- next/n - Step over to next line, stepping over function calls
- step/s - Step into function calls
- finish - Step out of current function
- print/p <variable> - Print value of a variable
- backtrace/bt - Print the call stack
- info breakpoints/ib - List breakpoints
- delete <breakpoint#> - Delete a breakpoint
- layout src - Switch layout to source code view
- layout asm - Switch layoutThe linux networking architecture



The linux networking architecturehugo lu
?
The document discusses Linux networking architecture and covers several key topics in 3 paragraphs or less:
It first describes the basic structure and layers of the Linux networking stack including the network device interface, network layer protocols like IP, transport layer, and sockets. It then discusses how network packets are managed in Linux through the use of socket buffers and associated functions. The document also provides an overview of the data link layer and protocols like Ethernet, PPP, and how they are implemented in Linux.LinuxCon 2015 Linux Kernel Networking Walkthrough



LinuxCon 2015 Linux Kernel Networking WalkthroughThomas Graf
?
This presentation features a walk through the Linux kernel networking stack for users and developers. It will cover insights into both, existing essential networking features and recent developments and will show how to use them properly. Our starting point is the network card driver as it feeds a packet into the stack. We will follow the packet as it traverses through various subsystems such as packet filtering, routing, protocol stacks, and the socket layer. We will pause here and there to look into concepts such as networking namespaces, segmentation offloading, TCP small queues, and low latency polling and will discuss how to configure them.Linux Network Stack



Linux Network StackAdrien Mahieux
?
- The document discusses Linux network stack monitoring and configuration. It begins with definitions of key concepts like RSS, RPS, RFS, LRO, GRO, DCA, XDP and BPF.
- It then provides an overview of how the network stack works from the hardware interrupts and driver level up through routing, TCP/IP and to the socket level.
- Monitoring tools like ethtool, ftrace and /proc/interrupts are described for viewing hardware statistics, software stack traces and interrupt information.DPDK KNI interface



DPDK KNI interfaceDenys Haryachyy
?
KNI (Kernel Network Interface) is one of the approach, used in DPDK, to connect its user space libs with the Linux kernel network stack.Dpdk performance



Dpdk performanceStephen Hemminger
?
FOSDEM15 SDN developer room talk
DPDK performance
How to not just do a demo with DPDK
The Intel DPDK provides a platform for building high performance Network Function Virtualization applications. But it is hard to get high performance unless certain design tradeoffs are made. This talk focuses on the lessons learned in creating the Brocade vRouter using DPDK. It covers some of the architecture, locking and low level issues that all have to be dealt with to achieve 80 Million packets per second forwarding.The TCP/IP Stack in the Linux Kernel



The TCP/IP Stack in the Linux KernelDivye Kapoor
?
The document discusses various data structures and functions related to network packet processing in the Linux kernel socket layer. It describes the sk_buff structure that is used to pass packets between layers. It also explains the net_device structure that represents a network interface in the kernel. When a packet is received, the interrupt handler will raise a soft IRQ for processing. The packet will then traverse various protocol layers like IP and TCP to be eventually delivered to a socket and read by a userspace application.DPDK in Containers Hands-on Lab



DPDK in Containers Hands-on LabMichelle Holley
?
This document provides an agenda and overview for a hands-on lab on using DPDK in containers. It introduces Linux containers and how they use fewer system resources than VMs. It discusses how containers still use the kernel network stack, which is not ideal for SDN/NFV usages, and how DPDK can be used in containers to address this. The hands-on lab section guides users through building DPDK and Open vSwitch, configuring them to work with containers, and running packet generation and forwarding using testpmd and pktgen Docker containers connected via Open vSwitch.Ovs dpdk hwoffload way to full offload



Ovs dpdk hwoffload way to full offloadKevin Traynor
?
This document discusses hardware offloading of VXLAN encapsulation and decapsulation in OVS-DPDK. It proposes representing virtual ports (vPorts) as tables to enable hardware offloading of VXLAN processing. Matching and actions on the vPort table would occur in hardware before decapsulation. Fallback processing using software would be used if full hardware offloading is not possible. The goal is to leverage intelligent NIC capabilities to accelerate VXLAN tunnel processing and improve performance for cloud, NFV, and storage workloads.FD.io Vector Packet Processing (VPP)



FD.io Vector Packet Processing (VPP)Kirill Tsym
?
This document provides an overview of Vector Packet Processing (VPP), an open source packet processing platform developed as part of the FD.io project. VPP is based on DPDK for high performance packet processing in userspace. It includes a full networking stack and can perform L2/L3 forwarding and routing at speeds of over 14 million packets per second on a single core. VPP processing is divided into individual nodes connected by a graph. Packets are passed between nodes as vectors to support batch processing. VPP supports both single and multicore modes using different threading models. It can be used to implement routers, switches, and other network functions and topologies.Linux Networking Explained



Linux Networking ExplainedThomas Graf
?
Linux offers an extensive selection of programmable and configurable networking components from traditional bridges, encryption, to container optimized layer 2/3 devices, link aggregation, tunneling, several classification and filtering languages all the way up to full SDN components. This talk will provide an overview of many Linux networking components covering the Linux bridge, IPVLAN, MACVLAN, MACVTAP, Bonding/Team, OVS, classification & queueing, tunnel types, hidden routing tricks, IPSec, VTI, VRF and many others.Ixgbe internals



Ixgbe internalsSUSE Labs Taipei
?
This document discusses the internals of the ixgbe driver, which is the Intel 10 Gigabit Ethernet driver for Linux. It describes how the driver handles transmission and reception of packets using ring buffers and NAPI. It also discusses how the driver supports eXpress Data Path (XDP) by using a separate ring for XDP packets and adjusting page reference counts to support XDP operations like redirection. Upcoming features that will improve XDP support for this driver are also mentioned.DPDK: Multi Architecture High Performance Packet Processing



DPDK: Multi Architecture High Performance Packet ProcessingMichelle Holley
?
What is DPDK? Why DPDK? How DPDK enhances OVS/NFV Infrastructure
Author: Muthurajan (M Jay) JayakumarFun with Network Interfaces



Fun with Network InterfacesKernel TLV
?
Agenda:
In this session, Shmulik Ladkani discusses the kernel's net_device abstraction, its interfaces, and how net-devices interact with the network stack. The talk covers many of the software network devices that exist in the Linux kernel, the functionalities they provide and some interesting use cases.
Speaker:
Shmulik Ladkani is a Tech Lead at Ravello Systems.
Shmulik started his career at Jungo (acquired by NDS/Cisco) implementing residential gateway software, focusing on embedded Linux, Linux kernel, networking and hardware/software integration.
51966 coffees and billions of forwarded packets later, with millions of homes running his software, Shmulik left his position as Jungo¡¯s lead architect and joined Ravello Systems (acquired by Oracle) as tech lead, developing a virtual data center as a cloud service. He's now focused around virtualization systems, network virtualization and SDN.Intel dpdk Tutorial



Intel dpdk TutorialSaifuddin Kaijar
?
DPDK greatly improves packet processing performance and throughput by allowing applications to directly access hardware and bypass kernel involvement. It can improve performance by up to 10 times, allowing over 80 Mbps throughput on a single CPU or double that with two CPUs. This enables telecom and networking equipment manufacturers to develop products faster and with lower costs. DPDK achieves these gains through techniques like dedicated core affinity, userspace drivers, polling instead of interrupts, and lockless synchronization.DPDK & Layer 4 Packet Processing



DPDK & Layer 4 Packet ProcessingMichelle Holley
?
Learn about Transport Layer Development Kit and let us accelerate beyond the Layer 2/Layer 3.
Author: Muthurajan (M Jay) JayakumarUserspace networking



Userspace networkingStephen Hemminger
?
Seven years ago at LCA, Van Jacobsen introduced the concept of net channels but since then the concept of user mode networking has not hit the mainstream. There are several different user mode networking environments: Intel DPDK, BSD netmap, and Solarflare OpenOnload. Each of these provides higher performance than standard Linux kernel networking; but also creates new problems. This talk will explore the issues created by user space networking including performance, internal architecture, security and licensing.Open vSwitch Offload: Conntrack and the Upstream Kernel



Open vSwitch Offload: Conntrack and the Upstream KernelNetronome
?
Offloading all or part of the Open vSwitch datapath to SmartNICs has been shown to not only release CPU resources on the server, but improve traffic processing performance. Recently steps have been made to support such offloading in the upstream Linux kernel. This has focused on creating an OVS datapath using the TC flower filter and utilizing the offload hooks already present here. This presentation focuses on how Connection Tracking (Conntrack) may fit into this model. It describes current work being undertaken with the Netfilter community to allow offloading of Conntrack entries. It continues to link this work with the offloading of Conntrack rules within OVS-TC.Meet cute-between-ebpf-and-tracing



Meet cute-between-ebpf-and-tracingViller Hsiao
?
This document discusses how eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) can be used for kernel tracing. It provides an overview of BPF and eBPF, how eBPF programs are compiled and run in the kernel, the use of BPF maps, and how eBPF enables new possibilities for dynamic kernel instrumentation through techniques like Kprobes and ftrace.TC Flower Offload



TC Flower OffloadNetronome
?
The TC Flower Classifier allows control of packets based on flows determined by matching of well-known packet fields and metadata. This is inspired by similar flow classification described by OpenFlow and implemented by Open vSwitch. Offload of the TC Flower classifier and related modules provides a powerful mechanism to both increase throughput and reduce CPU utilisation for users of such flow-based systems. This presentation will give an overview of the evolution of offload of the TC Flower classifier: where it came from, the current status and possible future directions.Understanding DPDK algorithmics



Understanding DPDK algorithmicsDenys Haryachyy
?
The document discusses algorithms used in the DPDK libraries for fast lookups. It describes the characteristics and usage of the hash, LPM, and ACL libraries. The hash library uses cuckoo hashing for tables like FDB and host tables. The LPM library uses a modified DIR-24-8-BASIC algorithm for IPv4 and IPv6 route tables. The ACL library classifies entries using techniques like scalar, SSE, and AVX2 based on multi-bit tries. Examples of lookups and inserts are provided for each library.Network Programming: Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK)



Network Programming: Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK)Andriy Berestovskyy
?
This presentation introduces Data Plane Development Kit overview and basics. It is a part of a Network Programming Series.
First, the presentation focuses on the network performance challenges on the modern systems by comparing modern CPUs with modern 10 Gbps ethernet links. Then it touches memory hierarchy and kernel bottlenecks.
The following part explains the main DPDK techniques, like polling, bursts, hugepages and multicore processing.
DPDK overview explains how is the DPDK application is being initialized and run, touches lockless queues (rte_ring), memory pools (rte_mempool), memory buffers (rte_mbuf), hashes (rte_hash), cuckoo hashing, longest prefix match library (rte_lpm), poll mode drivers (PMDs) and kernel NIC interface (KNI).
At the end, there are few DPDK performance tips.
Tags: access time, burst, cache, dpdk, driver, ethernet, hub, hugepage, ip, kernel, lcore, linux, memory, pmd, polling, rss, softswitch, switch, userspace, xeonIntel DPDK Step by Step instructions



Intel DPDK Step by Step instructionsHisaki Ohara
?
The document provides step-by-step instructions for building and running Intel DPDK sample applications on a test environment with 3 virtual machines connected by 10G NICs. It describes compiling and running the helloworld, L2 forwarding, and L3 forwarding applications, as well as using the pktgen tool for packet generation between VMs to test forwarding performance. Key steps include preparing the Linux kernel for DPDK, compiling applications, configuring ports and MAC addresses, and observing packet drops to identify performance bottlenecks.Ccna Imp Guide



Ccna Imp Guideabhijitgnbbl
?
The document provides an overview of the OSI model, TCP/IP protocols, Cisco IOS modes, router components, cabling, router management, LAN switching concepts, IP addressing, routing protocols, and IPv6 migration methods. It summarizes key topics for the CCNA exam in 10 sentences or less per section.NUSE (Network Stack in Userspace) at #osio



NUSE (Network Stack in Userspace) at #osioHajime Tazaki
?
This document describes Network Stack in Userspace (NUSE), which implements a full network stack as a userspace library. NUSE aims to allow faster evolution of network stacks outside the kernel and enable network protocol personalization. It works by patching the Linux kernel to include a new architecture, implementing the network stack components as a userspace library, and hijacking POSIX socket calls to redirect them to the NUSE implementation. Performance tests show NUSE adding only small overhead compared to kernel implementations. NUSE can also integrate with the ns-3 network simulator to enable controllable and reproducible network simulations using real protocol implementations.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Linux Network Stack



Linux Network StackAdrien Mahieux
?
- The document discusses Linux network stack monitoring and configuration. It begins with definitions of key concepts like RSS, RPS, RFS, LRO, GRO, DCA, XDP and BPF.
- It then provides an overview of how the network stack works from the hardware interrupts and driver level up through routing, TCP/IP and to the socket level.
- Monitoring tools like ethtool, ftrace and /proc/interrupts are described for viewing hardware statistics, software stack traces and interrupt information.DPDK KNI interface



DPDK KNI interfaceDenys Haryachyy
?
KNI (Kernel Network Interface) is one of the approach, used in DPDK, to connect its user space libs with the Linux kernel network stack.Dpdk performance



Dpdk performanceStephen Hemminger
?
FOSDEM15 SDN developer room talk
DPDK performance
How to not just do a demo with DPDK
The Intel DPDK provides a platform for building high performance Network Function Virtualization applications. But it is hard to get high performance unless certain design tradeoffs are made. This talk focuses on the lessons learned in creating the Brocade vRouter using DPDK. It covers some of the architecture, locking and low level issues that all have to be dealt with to achieve 80 Million packets per second forwarding.The TCP/IP Stack in the Linux Kernel



The TCP/IP Stack in the Linux KernelDivye Kapoor
?
The document discusses various data structures and functions related to network packet processing in the Linux kernel socket layer. It describes the sk_buff structure that is used to pass packets between layers. It also explains the net_device structure that represents a network interface in the kernel. When a packet is received, the interrupt handler will raise a soft IRQ for processing. The packet will then traverse various protocol layers like IP and TCP to be eventually delivered to a socket and read by a userspace application.DPDK in Containers Hands-on Lab



DPDK in Containers Hands-on LabMichelle Holley
?
This document provides an agenda and overview for a hands-on lab on using DPDK in containers. It introduces Linux containers and how they use fewer system resources than VMs. It discusses how containers still use the kernel network stack, which is not ideal for SDN/NFV usages, and how DPDK can be used in containers to address this. The hands-on lab section guides users through building DPDK and Open vSwitch, configuring them to work with containers, and running packet generation and forwarding using testpmd and pktgen Docker containers connected via Open vSwitch.Ovs dpdk hwoffload way to full offload



Ovs dpdk hwoffload way to full offloadKevin Traynor
?
This document discusses hardware offloading of VXLAN encapsulation and decapsulation in OVS-DPDK. It proposes representing virtual ports (vPorts) as tables to enable hardware offloading of VXLAN processing. Matching and actions on the vPort table would occur in hardware before decapsulation. Fallback processing using software would be used if full hardware offloading is not possible. The goal is to leverage intelligent NIC capabilities to accelerate VXLAN tunnel processing and improve performance for cloud, NFV, and storage workloads.FD.io Vector Packet Processing (VPP)



FD.io Vector Packet Processing (VPP)Kirill Tsym
?
This document provides an overview of Vector Packet Processing (VPP), an open source packet processing platform developed as part of the FD.io project. VPP is based on DPDK for high performance packet processing in userspace. It includes a full networking stack and can perform L2/L3 forwarding and routing at speeds of over 14 million packets per second on a single core. VPP processing is divided into individual nodes connected by a graph. Packets are passed between nodes as vectors to support batch processing. VPP supports both single and multicore modes using different threading models. It can be used to implement routers, switches, and other network functions and topologies.Linux Networking Explained



Linux Networking ExplainedThomas Graf
?
Linux offers an extensive selection of programmable and configurable networking components from traditional bridges, encryption, to container optimized layer 2/3 devices, link aggregation, tunneling, several classification and filtering languages all the way up to full SDN components. This talk will provide an overview of many Linux networking components covering the Linux bridge, IPVLAN, MACVLAN, MACVTAP, Bonding/Team, OVS, classification & queueing, tunnel types, hidden routing tricks, IPSec, VTI, VRF and many others.Ixgbe internals



Ixgbe internalsSUSE Labs Taipei
?
This document discusses the internals of the ixgbe driver, which is the Intel 10 Gigabit Ethernet driver for Linux. It describes how the driver handles transmission and reception of packets using ring buffers and NAPI. It also discusses how the driver supports eXpress Data Path (XDP) by using a separate ring for XDP packets and adjusting page reference counts to support XDP operations like redirection. Upcoming features that will improve XDP support for this driver are also mentioned.DPDK: Multi Architecture High Performance Packet Processing



DPDK: Multi Architecture High Performance Packet ProcessingMichelle Holley
?
What is DPDK? Why DPDK? How DPDK enhances OVS/NFV Infrastructure
Author: Muthurajan (M Jay) JayakumarFun with Network Interfaces



Fun with Network InterfacesKernel TLV
?
Agenda:
In this session, Shmulik Ladkani discusses the kernel's net_device abstraction, its interfaces, and how net-devices interact with the network stack. The talk covers many of the software network devices that exist in the Linux kernel, the functionalities they provide and some interesting use cases.
Speaker:
Shmulik Ladkani is a Tech Lead at Ravello Systems.
Shmulik started his career at Jungo (acquired by NDS/Cisco) implementing residential gateway software, focusing on embedded Linux, Linux kernel, networking and hardware/software integration.
51966 coffees and billions of forwarded packets later, with millions of homes running his software, Shmulik left his position as Jungo¡¯s lead architect and joined Ravello Systems (acquired by Oracle) as tech lead, developing a virtual data center as a cloud service. He's now focused around virtualization systems, network virtualization and SDN.Intel dpdk Tutorial



Intel dpdk TutorialSaifuddin Kaijar
?
DPDK greatly improves packet processing performance and throughput by allowing applications to directly access hardware and bypass kernel involvement. It can improve performance by up to 10 times, allowing over 80 Mbps throughput on a single CPU or double that with two CPUs. This enables telecom and networking equipment manufacturers to develop products faster and with lower costs. DPDK achieves these gains through techniques like dedicated core affinity, userspace drivers, polling instead of interrupts, and lockless synchronization.DPDK & Layer 4 Packet Processing



DPDK & Layer 4 Packet ProcessingMichelle Holley
?
Learn about Transport Layer Development Kit and let us accelerate beyond the Layer 2/Layer 3.
Author: Muthurajan (M Jay) JayakumarUserspace networking



Userspace networkingStephen Hemminger
?
Seven years ago at LCA, Van Jacobsen introduced the concept of net channels but since then the concept of user mode networking has not hit the mainstream. There are several different user mode networking environments: Intel DPDK, BSD netmap, and Solarflare OpenOnload. Each of these provides higher performance than standard Linux kernel networking; but also creates new problems. This talk will explore the issues created by user space networking including performance, internal architecture, security and licensing.Open vSwitch Offload: Conntrack and the Upstream Kernel



Open vSwitch Offload: Conntrack and the Upstream KernelNetronome
?
Offloading all or part of the Open vSwitch datapath to SmartNICs has been shown to not only release CPU resources on the server, but improve traffic processing performance. Recently steps have been made to support such offloading in the upstream Linux kernel. This has focused on creating an OVS datapath using the TC flower filter and utilizing the offload hooks already present here. This presentation focuses on how Connection Tracking (Conntrack) may fit into this model. It describes current work being undertaken with the Netfilter community to allow offloading of Conntrack entries. It continues to link this work with the offloading of Conntrack rules within OVS-TC.Meet cute-between-ebpf-and-tracing



Meet cute-between-ebpf-and-tracingViller Hsiao
?
This document discusses how eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) can be used for kernel tracing. It provides an overview of BPF and eBPF, how eBPF programs are compiled and run in the kernel, the use of BPF maps, and how eBPF enables new possibilities for dynamic kernel instrumentation through techniques like Kprobes and ftrace.TC Flower Offload



TC Flower OffloadNetronome
?
The TC Flower Classifier allows control of packets based on flows determined by matching of well-known packet fields and metadata. This is inspired by similar flow classification described by OpenFlow and implemented by Open vSwitch. Offload of the TC Flower classifier and related modules provides a powerful mechanism to both increase throughput and reduce CPU utilisation for users of such flow-based systems. This presentation will give an overview of the evolution of offload of the TC Flower classifier: where it came from, the current status and possible future directions.Understanding DPDK algorithmics



Understanding DPDK algorithmicsDenys Haryachyy
?
The document discusses algorithms used in the DPDK libraries for fast lookups. It describes the characteristics and usage of the hash, LPM, and ACL libraries. The hash library uses cuckoo hashing for tables like FDB and host tables. The LPM library uses a modified DIR-24-8-BASIC algorithm for IPv4 and IPv6 route tables. The ACL library classifies entries using techniques like scalar, SSE, and AVX2 based on multi-bit tries. Examples of lookups and inserts are provided for each library.Network Programming: Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK)



Network Programming: Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK)Andriy Berestovskyy
?
This presentation introduces Data Plane Development Kit overview and basics. It is a part of a Network Programming Series.
First, the presentation focuses on the network performance challenges on the modern systems by comparing modern CPUs with modern 10 Gbps ethernet links. Then it touches memory hierarchy and kernel bottlenecks.
The following part explains the main DPDK techniques, like polling, bursts, hugepages and multicore processing.
DPDK overview explains how is the DPDK application is being initialized and run, touches lockless queues (rte_ring), memory pools (rte_mempool), memory buffers (rte_mbuf), hashes (rte_hash), cuckoo hashing, longest prefix match library (rte_lpm), poll mode drivers (PMDs) and kernel NIC interface (KNI).
At the end, there are few DPDK performance tips.
Tags: access time, burst, cache, dpdk, driver, ethernet, hub, hugepage, ip, kernel, lcore, linux, memory, pmd, polling, rss, softswitch, switch, userspace, xeonIntel DPDK Step by Step instructions



Intel DPDK Step by Step instructionsHisaki Ohara
?
The document provides step-by-step instructions for building and running Intel DPDK sample applications on a test environment with 3 virtual machines connected by 10G NICs. It describes compiling and running the helloworld, L2 forwarding, and L3 forwarding applications, as well as using the pktgen tool for packet generation between VMs to test forwarding performance. Key steps include preparing the Linux kernel for DPDK, compiling applications, configuring ports and MAC addresses, and observing packet drops to identify performance bottlenecks.Similar to introduction to linux kernel tcp/ip ptocotol stack (20)
Ccna Imp Guide



Ccna Imp Guideabhijitgnbbl
?
The document provides an overview of the OSI model, TCP/IP protocols, Cisco IOS modes, router components, cabling, router management, LAN switching concepts, IP addressing, routing protocols, and IPv6 migration methods. It summarizes key topics for the CCNA exam in 10 sentences or less per section.NUSE (Network Stack in Userspace) at #osio



NUSE (Network Stack in Userspace) at #osioHajime Tazaki
?
This document describes Network Stack in Userspace (NUSE), which implements a full network stack as a userspace library. NUSE aims to allow faster evolution of network stacks outside the kernel and enable network protocol personalization. It works by patching the Linux kernel to include a new architecture, implementing the network stack components as a userspace library, and hijacking POSIX socket calls to redirect them to the NUSE implementation. Performance tests show NUSE adding only small overhead compared to kernel implementations. NUSE can also integrate with the ns-3 network simulator to enable controllable and reproducible network simulations using real protocol implementations.Network



Networkrumoorthyit
?
The document discusses several key functions and design goals of the network layer in internet architecture. It covers routing algorithms like distance vector and link state routing, as well as routing protocols like RIP. It also provides an overview of the TCP/IP protocol stack and some of its core components like IP, ICMP, TCP and UDP.???????? 2 ????????



???????? 2 ????????natnathapong
?
This document provides an overview of the TCP/IP model and its layers:
1. It describes the 7 layers of the TCP/IP model from the physical layer up to the application layer.
2. It explains some of the key protocols used at each layer, including IP, TCP, UDP, FTP, and HTTP.
3. It provides brief histories of TCP/IP and how it emerged from ARPANET in the 1960s to become the fundamental protocol of the Internet.OSI layers



OSI layersAhmed Elnaggar
?
This document discusses reference models for computer networks, including the OSI model and TCP/IP model. It provides details on each of the seven layers of the OSI model, including the layer name and number, example protocols, and key functions. It notes that the OSI model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization while TCP/IP was initially designed by the U.S. Department of Defense. It concludes that it will use the hybrid reference model as the framework.The Osi Model And Layers



The Osi Model And LayersKathleenSSmith
?
The OSI model defines a standard framework for how applications can communicate over a network through 7 layers of abstraction: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. Each layer has a specific purpose and set of protocols to convert data between layers, establish connections, route packets, ensure reliable and secure delivery of data, and interface with applications. The layers work together to take a message from an application, convert it to bits for transmission over a physical medium, and reconstruct it back to a message at the destination.Dc fabric path



Dc fabric pathASHISH SEHGAL
?
FabricPath is a Layer 2 technology from Cisco that provides multi-path Ethernet capabilities and eliminates the need for Spanning Tree Protocol. It combines the benefits of Layer 2 switching with greater scalability, availability, and loop prevention capabilities. FabricPath adds routing-like capabilities to Layer 2 switching such as all active links, fast convergence, and built-in loop avoidance mechanisms.FD.io - The Universal Dataplane



FD.io - The Universal DataplaneOpen Networking Summit
?
Ed Warnicke's talk at Open Networking Summit.
All Open Source Networking project depend on having access to a Universal Dataplane that is:
Able to they deployment models: Bare Metal/Embedded/Cloud/Containers/NFVi/VNFs
High performance
Feature Rich
Open with Broad Community support/participation
FD.io provides all of this and more. Come learn more about FD.io and how you can begin using it.
Cisco crs1



Cisco crs1wjunjmt
?
The document provides an overview of the Cisco CRS-1 router. It discusses the router's distributed architecture with multiple line cards and a high-speed fabric. The fabric uses a multi-stage Benes switch design to provide multiple paths between cards. Each line card contains specialized silicon that can process packets at wire speed through independent packet processing engines. The router is designed to scale routing capacity and features through this distributed and programmable hardware architecture.Tempesta FW: a FrameWork and FireWall for HTTP DDoS mitigation and Web Applic...



Tempesta FW: a FrameWork and FireWall for HTTP DDoS mitigation and Web Applic...Alexander Krizhanovsky
?
Tempesta FW is an open source framework for building high performance intelligent DDoS mitigation systems and web application firewalls. It directly embeds into the Linux TCP/IP stack and uses a just-in-time domain specific language to efficiently process and filter traffic at layers 3 through 7. This allows for fine-grained rule filtering, acceleration of web applications to mitigate DDoS attacks, and caching of content for improved performance. Tempesta aims to overcome limitations of traditional web servers and firewalls through its synchronous socket processing, fast HTTP parsing, generic finite state machine, and in-memory persistent database.Wireshark



Wiresharkbtohara
?
This document provides an introduction to the packet analysis tool Wireshark. It introduces key people involved in Wireshark including creator Gerald Combs and trainer Laura Chappell. It reviews common network protocols like Ethernet, IP, TCP and TCP/IP. It provides an overview of how to use Wireshark including capturing packets, filtering displays, saving files and more. The document concludes with resources for learning more about Wireshark and guides for certification.Tcp and introduction to protocol



Tcp and introduction to protocolSripati Mahapatra
?
The document discusses several networking protocols including TCP/IP, Netware, IEEE 802 standards, IPX, UDP, IP, ARP, SMTP, POP, IMAP and more. It provides information on what each protocol is used for, such as IP being used for addressing, routing packet selection, and fragmentation. It also compares the OSI model, DoD model and TCP/IP protocol suite.Tcpandintroductiontoprotocol 150618054958-lva1-app6892



Tcpandintroductiontoprotocol 150618054958-lva1-app6892Saumendra Pradhan
?
The document discusses several networking protocols including TCP/IP, Netware, IEEE 802 standards, IPX, UDP, IP, ARP, SMTP, POP, IMAP and more. It provides information on what each protocol is used for, such as IP being used for addressing, routing packet selection, and fragmentation. It also compares the OSI model, DoD model and TCP/IP protocol suite, noting similarities and differences between the layers and protocols of each.Ccent notes part 1



Ccent notes part 1ahmady
?
The document provides notes on networking fundamentals from CCENT/CCNA ICND1 Official Exam Certification Guide. It discusses the TCP/IP and OSI networking models, including their layers and functions. It also covers fundamentals of local area networks (LANs) such as Ethernet standards, speeds, cable types and maximum lengths. Common Ethernet standards include 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX and 1000BASE-T.End to End Convergence



End to End ConvergenceSkillFactory
?
§±§â§Ö§Ù§Ö§ß§ä§Ñ§è§Ú§ñ §Õ§Ý§ñ §Õ§à§Ü§Ý§Ñ§Õ§Ñ, §ã§Õ§Ö§Ý§Ñ§ß§ß§à§Ô§à §Ó §â§Ñ§Þ§Ü§Ñ§ç §Ü§à§ß§æ§Ö§â§Ö§ß§è§Ú§Ú Juniper New Network Day 01.01.2014.
§¥§à§Ü§Ý§Ñ§Õ§é§Ú§Ü -- Product Line Manager §Ü§à§Þ§á§Ñ§ß§Ú§Ú Juniper §¥§Þ§Ú§ä§â§Ú§Û §º§à§Ü§Ñ§â§Ö§Ó.
§£§Ú§Õ§Ö§à§Ù§Ñ§á§Ú§ã§î §ï§ä§à§Ô§à §Õ§à§Ü§Ý§Ñ§Õ§Ñ §ã §à§ß§Ý§Ñ§Û§ß-§ä§â§Ñ§ß§ã§Ý§ñ§è§Ú§Ú §Ü§à§ß§æ§Ö§â§Ö§ß§è§Ú§Ú §Ó§í §Þ§à§Ø§Ö§ä§Ö §å§Ó§Ú§Õ§Ö§ä§î §Ù§Õ§Ö§ã§î: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R2groq4YMaQ
MPLS Deployment Chapter 1 - Basic



MPLS Deployment Chapter 1 - BasicEricsson
?
Tutorial about MPLS Implementation with Cisco Router, this first of two chapter discuss about What is MPLS, Network Design, P, PE, and CE Router Description, Case Study of IP MPLS Implementation, IP and OSPF Routing ConfigurationTCP/IP Basics



TCP/IP BasicsSMC Networks Europe
?
The document discusses TCP/IP networking fundamentals including:
- The TCP/IP protocol suite model with layers for internet, transport, and applications.
- Key protocols like IP, TCP, UDP that operate at each layer.
- IP addressing and routing protocols like RIP and OSPF.
- Network applications that use TCP/IP like HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS.
- Networking services like DHCP, NAT, and firewalls.
- Emerging technologies like IPv6 that expand addressing and add new features.Networking revolution



Networking revolutionNahian Chowdhury
?
Networking revolution in last 6-7 years. This document shows the very brief of high level concept in changing Networking technology from legacy networking to future ideas. ??????????????????????? 2 ????????



??????????????????????? 2 ????????Thitinan607
?
The document discusses the seven-layer OSI model and describes the four layers of the TCP/IP model. It explains that the physical layer deals with transmitting raw bits of data over a communication channel. The network layer is responsible for packetizing and routing data across multiple networks. The transport layer establishes connections between applications on different hosts, providing reliable data streams. The application layer supports protocols for common network functions such as file transfer, email, and the web.2 130704230920-phpapp02



2 130704230920-phpapp02Anupon Chaipitaksombat
?
The document discusses the seven-layer OSI model and describes the four layers of the TCP/IP model. It explains that the physical layer deals with transmitting raw bits of data over a communication channel. The internet layer is responsible for packet switching across network connections. The transport layer establishes communication channels for applications and uses either TCP or UDP. The application layer supports protocols like HTTP, FTP, and SMTP that are commonly used in networking.Tempesta FW: a FrameWork and FireWall for HTTP DDoS mitigation and Web Applic...



Tempesta FW: a FrameWork and FireWall for HTTP DDoS mitigation and Web Applic...Alexander Krizhanovsky
?
introduction to linux kernel tcp/ip ptocotol stack
- 1. Introduction to Linux Kernel TCP/IP procotol stack µñÁº ºËÐÄϵͳ·þÎñÆ÷ƽ̨×é diaoliang@taobao.com simohayha.bobo@gmail.com http://www.pagefault.info 2011/01/15
- 2. Agenda Introduction Networking code in the Linux kernel tree L2 (Link Layer) L3 (Network Layer) L4 (Transport Layer) Config and benchmark tools Resource
- 3. Introduction Source http://git.kernel.org/ net-next-2.6 and net-2.6 Developer Alan Cox, David Miller, Eric Dumazet, Patrick Mchardy etc. Traffic directions input , forward and output Layer L2(Link Layer)/L3(Network Layer)/L4(Transport Layer) Device interface PCI/PCI-E
- 4. Networking code in the Linux kernel tree Net-Kernel source tree
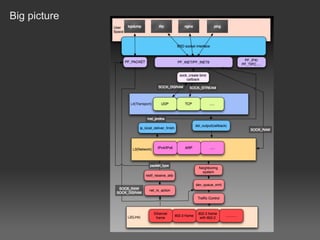
- 5. Big picture
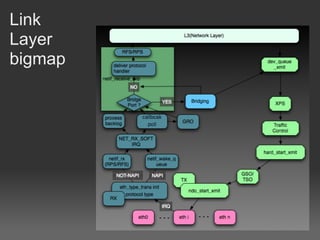
- 6. Link layer Frame type 802.3/802.2/802.2-SNAP/Ethernet Input Driver NAPI Poll + Interrupt Soft interrupt GRO feed packet to network stack RPS/RFS make steer in SMP Protocol handler use eth_type_trans Packet_type list
- 7. Link layer Output Traffic Control Soft interrupt Transmit SKB Scatter/Gather DMA Free skb XPS multiqueue avoid cache line bouncing improve locality Bridge Virtual device, must bind one or more real device Spanning Tree Protocol
- 9. Network Layer(IP) Input Protocol handler net_protocol array defragment Hashtable Each IP packet being defragmented save in a list stored in kernel memory until they are totally processed Output fragment MTU Scatter/Gather IO udp neighboring
- 10. Network Layer(IP) Forward process ip option igonore defragmentation Router Alert option Route Forwarding Information Base(routing table) cache Netfilter HOOK point NF_IP_LOCAL_OUT/ NF_IP_LOCAL_IN etc.. Management Long-living IP peer information AVL tree IP statistics per cpu data ipstats_mib /proc/net/snmp
- 12. Transport Layer (tcp) Init bind callback (sock_create) Three handshrek accept queue syn table create new socket fd and change state Manage socket inet_ehash_bucket TCP_ESTABLISHED <= sk->sk_state < TCP_CLOSE inet_bind_hashbucket local binding port info listening_hash socket in TCP_LISTEN state
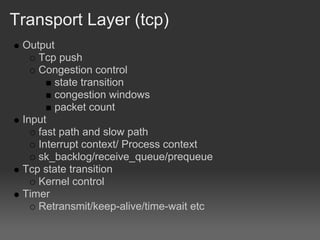
- 13. Transport Layer (tcp) Output Tcp push Congestion control state transition congestion windows packet count Input fast path and slow path Interrupt context/ Process context sk_backlog/receive_queue/prequeue Tcp state transition Kernel control Timer Retransmit/keep-alive/time-wait etc
- 14. TCP Bigmap
- 15. Config and Benchmark Tools Ethtool offload fetures Benchmark and test tools Netperf/pktgen Mpstat/tcpstat Proc FileSystem /proc/net /proc/sys/net ipv4 core Sys FileSystem /sys/class/net/ethx
- 16. Resource http://kernelnewbies.org http://kernel.org http://www.kernelplanet.org https://lkml.org http://vger.kernel.org/vger-lists.html http://www.pagefault.info/?tag=kernel
