Liquid Liquid Extraction
- 3. Why liquid-liquid extraction ÔÇó When difference in Boiling Point of two component is very low. ÔÇó For azeotropic mixtures. ÔÇó To avoid thermal decomposition. ÔÇó It consumes Lower Energy than the distillation. ÔÇó If proportion of one component is very less then other and it have high boiling point. 1- Separation is done according to different in solubility . 2- Problem with L-L extraction that we mix then we separate. IMP Notes:
- 4. What is liquid-liquid extraction Solvent Feed Raffinate Extract SeparationContact
- 5. What is liquid-liquid extraction As Inlet:  Solute + Inert  Solvent As Outlet: • Extract • Raffinate Each stage contain:  Contact  Separation
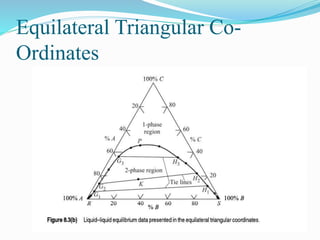
- 8. Types of ternary systems 1) Formation of one pair of partially soluble liquids. [closed ternary diagram] 2) Formation of two pair of partially soluble liquids. [open ternary diagram]
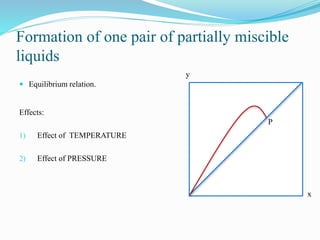
- 9. Formation of one pair of partially miscible liquids ÔÇ¢ AC&BC are completely soluble. ÔÇ¢ AB is partially soluble. ÔÇ¢ M will be separated to two compositions; N & L ÔÇ¢ If C is solvent for A so as C increases, L goes up till P(Plait Point) at which A,B & C become one phase. This is done due to the increase in mutual solubility between A&B. C BA P II I M N L
- 10. Formation of one pair of partially miscible liquids ÔÇó Equilibrium relation. Effects: 1) Effect of TEMPERATURE 2) Effect of PRESSURE x y P
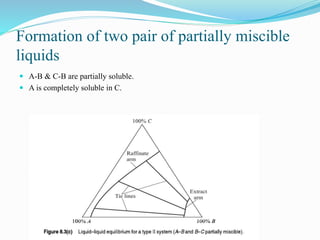
- 11. Formation of two pair of partially miscible liquids ÔÇó A-B & C-B are partially soluble. ÔÇó A is completely soluble in C.
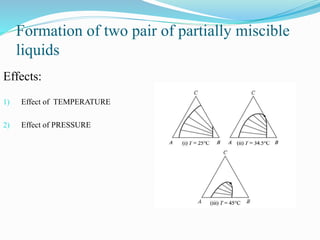
- 12. Formation of two pair of partially miscible liquids Effects: 1) Effect of TEMPERATURE 2) Effect of PRESSURE
- 13. Multi Component System ÔÇó In this type of system there are >=4 components in which 2 are solute and 2 are solvents. So it is known as multi component system. ÔÇó E.g: the distribution of formic acid and acetic acids between the partly soluble solvents water and carbon tetrachloride. But this type of system representation requires 3D graph which is very difficult to understand. So Generally it is not used.
- 14. Choice Of Solvent 1) Selectivity 2) Distribution Co-efficient 3) Insolubility of solvent 4) Recoverability 5) Density 6) Interfacial Tension 7) Chemical Reactivity 8) Viscosity, Vapor Pressure, Freezing Point 9) Non Toxic, Non Flammable, & low cost.
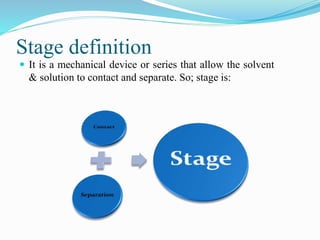
- 15. Stage definition ÔÇó It is a mechanical device or series that allow the solvent & solution to contact and separate. So; stage is:
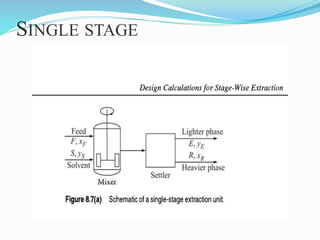
- 16. SINGLE STAGE
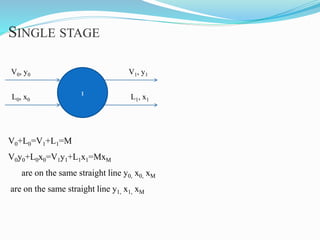
- 17. 1 V0, y0 L1, x1L0, x0 V1, y1 V0+L0=V1+L1=M V0y0+L0x0=V1y1+L1x1=MxM are on the same straight line y0, x0, xM are on the same straight line y1, x1, xM SINGLE STAGE
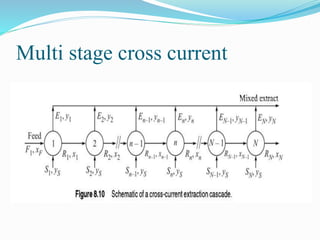
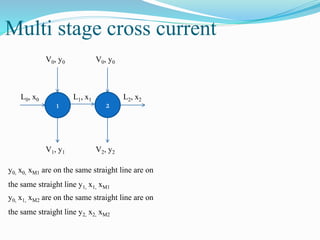
- 18. Multi stage cross current
- 19. Multi stage cross current 1 2 L0, x0 L1, x1 L2, x2 V0, y0 V0, y0 V2, y2V1, y1 y0, x0, xM1 are on the same straight line are on the same straight line y1, x1, xM1 y0, x1, xM2 are on the same straight line are on the same straight line y2, x2, xM2
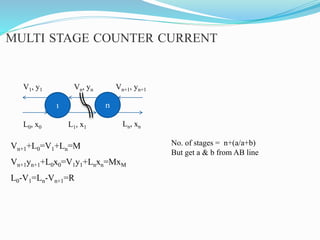
- 20. MULTI STAGE COUNTER CURRENT 1 n L0, x0 L1, x1 Ln, xn V1, y1 Vn, yn Vn+1, yn+1 Vn+1+L0=V1+Ln=M Vn+1yn+1+L0x0=V1y1+Lnxn=MxM L0-V1=Ln-Vn+1=R No. of stages = n+(a/a+b) But get a & b from AB line
- 21. EQUIPMENT: ÔÇó Different mechanical devices are used in liquid-liquid extraction such as: 1. The simplest is a mixer/settler, or decanter, in which the two liquid phases are separated. 2. Plate towers, packed towers, and mechanically agitated mixers (rotating disk contactors)
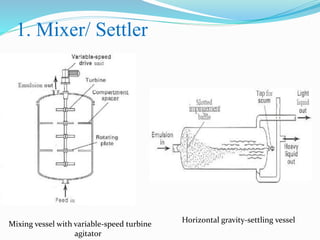
- 23. 1. Mixer/ Settler Mixing vessel with variable-speed turbine agitator Horizontal gravity-settling vessel
- 24. Types of Impeller In Mixer
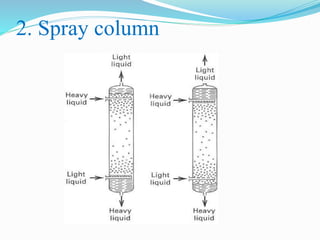
- 25. 2. Spray column
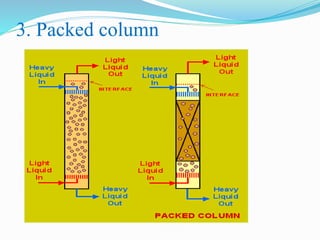
- 26. 3. Packed column
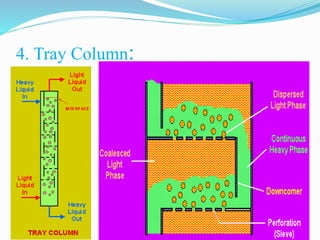
- 27. 4. Tray Column:





![Types of ternary systems
1) Formation of one pair of partially soluble liquids.
[closed ternary diagram]
2) Formation of two pair of partially soluble liquids.
[open ternary diagram]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masstransfer-1-170805114109/85/Liquid-Liquid-Extraction-8-320.jpg)