Lyophilization
- 1. Lyophilization Technology &Form Fill Seal Technology ïķ PREPARED BY: ï§ KISHAN RAM ï§ Dept. M.PHARM QA ïķ GUIDED BY: ï§ Mr. AJAY I. PATEL ï§ ASSISTANT- PROFESSOR ï§ BKMGPC RAJKOT
- 2. TABLE OF CONTENT : ïąLyophilization Technology ïą History ïą Objectives ïą Principle ïą Basic components of a Lyophilizer ïą Lyophilization process ïą Steps involved in Lyophilization ïąForm Fill Seal Technology ïąProcessing of FFS technology
- 3. ïą LYOPHILIZATION TECHNOLOGY: A stabilizing process in which a substance is first frozen and then the quantity of the solvent is reduced, first by sublimation (primary drying stage) and then desorption (secondary drying stage) to values that will no longer support biological activity or chemical reactions.
- 4. History ïFreeze drying was first actively developed during WORLD WAR II transport of serum. ïThe main aim was to store the products without refrigeration and to remove moisture from thermolabile compounds. ï Atlas in 1961 built 6 production freeze drying cabinet for Nestle group in Germany, Holland.
- 5. Objectives of Lyophilization process âĒTo preserve the biological activity of a product. âĒTo reduce the product weight to lower the transportation cost. âĒTo extend the shelf life or stability. âĒTo dry thermolabile materials. âĒTo eliminate the need for refrigerated storage. âĒTo get accurate, sterile dosing into the final product container.
- 6. Principle ï§ Lyophilization is carried out using a simple principle of physics sublimation. ï§ Lyophilization is performed at temperature and pressure conditions below the triple point, to enable sublimation of ice. ï§ The entire process is performed at low temperature and pressure by applying vacuum, hence is suited for drying of thermolabile compounds. ï§ The driving force is vapor pressure difference between the evaporating surface and the condenser.
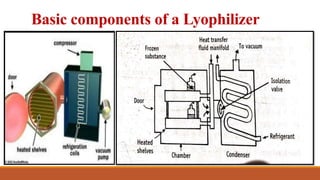
- 8. Basic components of a Lyophilizer
- 10. PROCESSING Fundamental process steps are: 1. Freezing: the product is frozen. This provides a necessary condition for low temperature 2. Vacuum: after freezing, the product is placed under vacuum. This enables the frozen solvent in the product to vaporize without passing through liquid phase, a process known as SUBLIMATION. 3. Heat: Heat is applied to the frozen product to accelerate sublimation. 4. Condensation: Low-temperature condenser plates remove the vaporized solvent from the vacuum chamber by converting it back to a solid. This completes the process.
- 11. STEPS INVOLVED IN LYOPHILIZATION FREEZING STAGE PRIMARY DRYING STAGE PACKING SECONDARY DRYING STAGE
- 12. 1.Freeze Drying âĒFreezing the product solution to a temperature below its eutectic temperature. âĒDecrease the shelf temperature to -50oc. âĒLow temperature and low atmospheric pressure are maintained. âĒFreons are used as refrigerant. âĒFormation of ice crystals occurs. âĒThe rate of ice crystallization define the freezing process and efficiency of primary drying.
- 13. 2.Primary Drying (Sublimation) âĒHeat is introduced from shelf to the product under graded control by electrical resistance coils or circulating silicone. âĒThe temperature and pressure should be below the triple point of water i.e., 0.0098°C and 4.58mmHg. âĒThe driving force is vapor pressure difference between the evaporating surface and the condenser. âĒEasily removes moisture up to 98% to 99%.
- 14. 3.Secondary Drying (Desorption) âĒThe temperature is raised to 50°C â 60°C and vacuum is lowered about 50mmHg. âĒBound water is removed. âĒRate of drying is low. âĒIt takes about 10-20 hrs.
- 15. 4.Packing âĒ After drying the vacuum is replaced by filtered dry air or nitrogen to establish atmospheric pressure âĒ Ampoules are sealed by either tip sealing or pull sealing method âĒ Vials and bottles are sealed with rubber closures and aluminum caps
- 16. Advantages of freeze drying over conventional drying Product quality Freeze drying Conventional drying Form of wet material to be dried Whole, liquids Pieces, powders Pieces Dry shape and form Maintained Shriveled Appearance Nearly same Shriveled color Maintained Faded Rehydration Fast Slow Heat exposure 0-150oC 200-300oC Oxygen exposure Very low High Retained volatiles Excellent Poor
- 17. Advantages of Lyophilization ï§Removal of water at low temperature ï§Thermolabile materials can be dried. ï§Compatible with aseptic operations ï§More precise fill weight control ï§Sterility can be maintained. ï§Reconstitution is easy
- 18. Disadvantages of Lyophilization ï§Many biological molecules are damaged by the stress associated with freezing, freeze-drying, or both. ï§The product is prone to oxidation, due to high porosity and large surface area. Therefore the product should be packed in vacuum or using inert gas or in a container impervious to gases ï§Cost may be an issue, depending on the product ï§Long time process
- 19. Common Lyophilized Products ïPharmaceuticals â large and small molecules ïBacteria ïViruses ïVaccines ïPlasma ïFruit ïCoffee ïFlowers etc.
- 20. ïForm fill seal (FFS) technology is an automated computer operated technology, to prepare sterile products. ïThe reason behind FFS technology is to reduce the contamination during production in a closed sterile chamber of a machine. ïThus there should be no personnel intervention so reduce the chances of contamination during the manufacturing of sterile products. Form Fill Seal Technology
- 23. Processing of FFS 1. Pre-sterilization of machine: carried out in 2 different phases âĶ Programmed in sequence âĶ H2O2 sterilization cycle 2. Production in aseptic chamber: which involves 3 steps âĶ Formation of container âĶ Filling of container with content âĶ Sealing of container 3.Post-production cleaning
- 24. Advantages of FFS Technology ï Bags made on FFS are less expensive than pre-made bags = âpay backâ ï Total automation - usually unattended, labour saving provides = âpay-backâ ï Consistent packing rate ï Compact (especially the Vertical FFS) ï Fast - increased production rate, reduced no. of shifts = âpay backâ ï Easy and quick to clean-out between production batches ï Fewer moving parts - especially Vertical FFS ï 'Onlineâ film printing provides readable bar code and product info
- 25. Disadvantages of FFS Technology ï Cannot handle paper. ï Cannot handle multi-ply packing materials. ï Not economical for packing low density, aerated powders ï Cannot remove âtrapped airâ very quickly or easily.
- 26. References 1. The science and practice of pharmacy by Remington, 21 edition, vol- 1. Pg 828-831. 2. The Theory And Practice of Industrial Pharmacy by Leon Lachmann, Herbert.A.Lieberman and Joseph I. Kanig, 1991. Pg 62-64, 672-674. 3. Pharmaceutical engeenering by CVS subhramanym, page no. 400-402 4. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences · January 2018 AN OUTLOOK TO FORM FILL SEAL TECHNOLOGY by Pratik Swarup Das and at all ,Volume 7, Issue 2, 290-295.