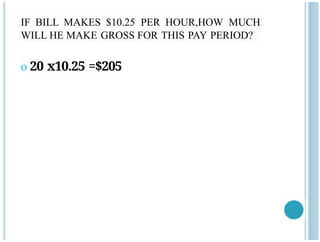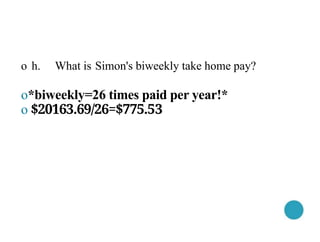Making an income.pptx .
- 2. INTRODUCTION,VOCABULARY,WAGES AND SALARIES o Who has had a job before? o How did you get paid? o Did you get paid overtime? o How did they determine how many hours they worked? o Did they have any deductions?Etc.
- 3. IN ALBERTA,THE CURRENT MINIMUM WAGE IS $15.00 PER HOUR. o Minimum wage is the minimum amount a worker MUST be paid an hour,as set out by the Provincial Government. o The minimum wage in BC is $17.40/hour.The minimum wage in Sask.is $15.00.The min. wage in Ontario is $17.20/hour. o why there might be differences in minimum wage across Canada?
- 4. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A SALARY AND A WAGE? o Salary - paid a fixed amount every pay period. This amount is determined usually in a contract which is signed before employment starts. o Advantages-paid the same amount every pay period,regardless of hours worked/holidays etc. o Disadvantage-not paid for any extra work you might do.
- 5. o Wage - paid a fixed amount PER HOUR worked during a certain pay period. o Advantages-paid for any extra hours you might work.Usually paid more per hour during certain times (for example,working on holidays, Sundays,evenings etc.) o Disadvantages-if you don't work,you don't get paid (for example,if you miss a day of work,or you work fewer hours in a week than normal).
- 6. o Gross Pay-the total amount of money earned in a pay period.AKA gross earnings.This is the amount you make BEFORE deductions.
- 7. A PAY STATEMENT IS A FORM AN EMPLOYER WILL GIVE YOU THAT SHOWS EARNINGS FOR A DEFINED PAY PERIOD. o A pay period could be weekly,bi-weekly, monthly,etc. o*weekly-once a week (paid 52 times per year) o*bi-weekly-every two weeks (paid 26 times/year) o*monthly-once a month (paid 12 times/year) o*semi-monthly-twice a month (paid 24 times/year) o*annually-one year (paid once a year)
- 8. *HOW DO WE DETERMINE THE MONTHLY,SEMI- MONTHLY,BI-WEEKLY AND WEEKLY PAY FOR A SALARY?* Ex.Brendan works at the Edmonton Journal.His annual salary is $35650. o Determine the following scenarios: o 12 pay periods per year: $35650/12=$2970.83 / month o Paid Semi-Monthly? o 24 pay periods per year:$35650124=$1485.42 twice a month o If Brendan is paid monthly,how much will he make
- 9. o Paid Bi-Weekly? o 26 pay periods per year:$35650/26=$1371.15 every two weeks o Paid Weekly? o 52 pay period per year:$35650/52 =$685.58
- 10. V§¯§¡§´ §¡§²§¦ §´§¯§¦ ADVANTAGES AND DIS§ÑD§µ§¡§®§´§¡§³§¦§Á §°§ß §¦§¡§³§¯ §²§¡§µ §²§¦§¦§À§°D?
- 11. *HOW DO WE DETERMINE THE GROSS PAY FOR WAGES? o EX: Morgan makes minimum wage.He works 35 hours one week.How much will his gross pay be for that week? o*Multiply the number of hours worked by the wage to get gross pay!* o 35 hours x$9.40/hour =$329.00 o*Always round MONEY to two decimal places!!!*
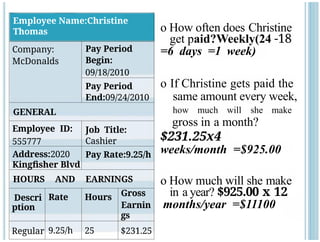
- 12. Employee Name:Christine Thomas Company: McDonalds Pay Period Begin: 09/18/2010 Pay Period End:09/24/2010 GENERAL Employee ID: 555777 Job Title: Cashier Address:2020 Kingfisher Blvd Pay Rate:9.25/h HOURS AND EARNINGS Descri ption Rate Hours Gross Earnin gs Regular 9.25/h 25 $231.25 o How often does Christine get paid?Weekly(24 -18 =6 days =1 week) o If Christine gets paid the same amount every week, how much will she make gross in a month? $231.25x4 weeks/month =$925.00 o How much will she make in a year? $925.00 x 12 months/year =$11100
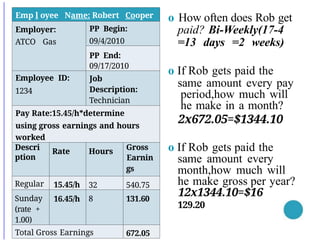
- 13. Emp l oyee Name: Robert Cooper Employer: ATCO Gas PP Begin: 09/4/2010 PP End: 09/17/2010 Employee ID: 1234 Job Description: Technician Pay Rate:15.45/h*determine using gross earnings and hours worked Descri ption Rate Hours Gross Earnin gs Regular 15.45/h 32 540.75 Sunday (rate + 1.00) 16.45/h 8 131.60 Total Gross Earnings 672.05 o How often does Rob get paid? Bi-Weekly(17-4 =13 days =2 weeks) o If Rob gets paid the same amount every pay period,how much will he make in a month? 2x672.05=$1344.10 o If Rob gets paid the same amount every month,how much will he make gross per year? 12x1344.10=$16 129.20
- 15. D§Ñ§å 2: §¯§à§Ú§£§Ù V§°§£§¬§¦D - §³§à§Ş§â§Ö§´§´§Ş§Ñ §´§ä§Ş§Ó §³§Ñ§Ó§â§Ó
- 17. FULL TIME VS PART TIME o Full Time -usually considered to be between 35-44 hours per week.Typically,full time results in 8 hour shifts per day,5 days a week. o Part Time -usually considered to be less than 35 hours a week.Typically,part time results in shifts less than 8 hours OR fewer days are worked per week. o Shift -the amount of time you work.
- 18. GETTING PAID WITH A WAGE-HOW ARE THE HOURS YOU WORK TRACKED? o Punch cards-at the start and end of every shift,you insert a card into a machine that will record the date and time.This card is then later used to calculate the number of hours worked during a pay period. o Time Card (Personal) -you may have to manually record the time you start and end each shift.Sometimes this is called"logged hours". o Time Card (Pay Roll) -you may work for a company where a person logs your hours for you.It will be your responsibility to inform them of any extra hours you work,or any shifts you miss.
- 19. 24 HOUR TIME -MOST JOBS WILL USE 24 HOUR(INSTEAD OF 12 HOUR)TIME.To DETERMINE THE TIME,SUBTRACT 12. o Remember,in 12 hour time,the morning is am, and the afternoon/evening is pm o Ex.What time is 13:05?13-12 =1:05 pm o What time is 22:45?22-12 =10:45 pm o What time is 02:50?=2:50 am
- 20. hours have you worked? o 1st add minutes to the start time to match the minutes of the end time o 9:30+20 minutes =9:50 o 2nd subtract the hours:14-9=5 hours o 3rd combine hours and minutes =5 hours +20 minutes. HOW DO WE DETERMINE THE NUMBER OF HOURS WORKED? o For example,you work from 9:30-14:50.How many
- 21. o Employers don't usually pay for every minute of work.Typically you will get paid for every quarter hour you work.Round to the nearest quarter (0,15,30,45) o 20 minutes-closest to 15 minutes. o What part of an hour is 15 minutes? o x/1=15/60 =0.25 o 4th Add hours and parts of an hour together: 5+0.25=5.25 hours.
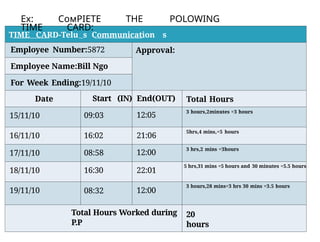
- 22. . TIME CARD-Telu s Communication s Employee Number:5872 Approval: Employee Name:Bill Ngo For Week Ending:19/11/10 Date Start (IN) End(OUT) Total Hours 15/11/10 09:03 12:05 3 hours,2minutes =3 hours 16/11/10 16:02 21:06 5hrs,4 mins,=5 hours 17/11/10 08:58 12:00 3 hrs,2 mins =3hours 18/11/10 16:30 22:01 5 hrs,31 mins =5 hours and 30 minutes =5.5 hours 19/11/10 08:32 12:00 3 hours,28 mins=3 hrs 30 mins =3.5 hours Total Hours Worked during P.P §¦§ç: §³§à§Ş§²?§¦§´§¦ §´§¯§¦ POLOWING TI§®§¦ CARD: 20 hours
- 23. IF BILL MAKES $10.25 PER HOUR,HOW MUCH WILL HE MAKE GROSS FOR THIS PAY PERIOD? o 20 x10.25 =$205
- 24. Da§å 3: §°§ä§ß§Ö§£ WAYS TO EARN - PIECEWORK AND COMMISSION
- 25. SALARY AND WAGE AREN'T THE ONLY WAYS TO EARN AN INCOME.OTHER WAYS INCLUDE: o Self employment-a person who works for themselves rather than for an employer. o Piecework-when someone is paid a set rate for an amount produced o Commission-an amount (usually a percentage) paid to someone for a business transaction o Contract-a legal agreement that outlines terms, conditions and payments for work to be done
- 26. o Brainstorm as a class examples of occupations for each vocabulary words above.Also,brainstorm advantages and disadvantages of being self employed.
- 27. PIECEWORK o Ex.Michelle is an Artisan-a craftsperson who specializes in decorative arts.She makes pottery bowls. She sells large bowls for $45.00 and medium bowls for $35.00.One weekend at a farmers market she sells 11 medium and 8 large bowls.How much does she make? o*Multiply price by quantity,then add totals together* $45x8=$360 $35x 11=$365 Total:$745
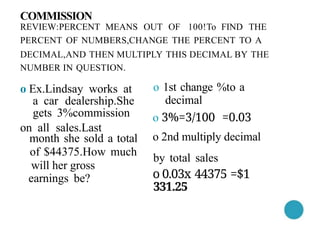
- 28. NUMBER IN QUESTION. o Ex.Lindsay works at a car dealership.She gets 3%commission on all sales.Last month she sold a total of $44375.How much will her gross earnings be? COMMISSION REVIEW:PERCENT MEANS OUT OF 100!To FIND THE PERCENT OF NUMBERS,CHANGE THE PERCENT TO A DECIMAL,AND THEN MULTIPLY THIS DECIMAL BY THE o 1st change %to a decimal o 3%=3/100 =0.03 o 2nd multiply decimal by total sales o 0.03x 44375 =$1 331.25
- 29. o 1stAdd up his sales: o 299450+380200 =$ 679650 o 2nd change %to a decimal o 0.2%=0.2/100 =0.002 o 3rd multiply decimal by his sales. o 0.002x 679650 =$1 359.30 o Ex.Dan works as a real estate agent.He gets 0.2 %commission on the sale price of any house he sells. Last month he sold 2 houses:$299450,and $380200.How much will his gross earnings be?
- 30. o 1st find out his hourly wage amount o $8.80/h x 36 hours = $316.80 o 2nd change %to a decimal,and multiply by his tips o 75%=75/100 =0.75 0.75x155=$116.25 o 3rd add his wage and tips together to get total o $316.80+$116.25 = $433.05 o Ex.Carl works at The Keg restaurant.He makes $8.80/h plus he gets to keep 75%of his tips.If one week he works 36 hours and makes $155 in tips, what will his gross earnings be?
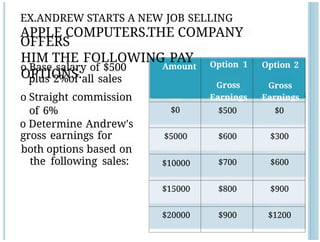
- 31. Amount Option 1 Gross Earnings Option 2 Gross Earnings $0 $500 $0 $5000 $600 $300 $10000 $700 $600 $15000 $800 $900 $20000 $900 $1200 o Base salary of $500 plus 2%of all sales o Straight commission of 6% o Determine Andrew's gross earnings for both options based on the following sales: EX.ANDREW STARTS A NEW JOB SELLING APPLE COMPUTERS.THE COMPANY OFFERS HIM THE FOLLOWING PAY OPTIONS:
- 32. o When is option 1 a o Which would you better choice? choose? o When is option 2 a better choice?
- 35. OVERTIME INCOME CAN BE CALCULATED EASILY. o 1st Determine the number of over time hours worked o 2nd multiply this by the overtime rate (time-and- a-half=x1.5,double time =x2)and current wage. o 3rd add overtime to regular work hours.
- 36. o Regular Pay:40 x 9.25/hr=$370 o Overtime Pay:8x 1.5 x 9.25=$111 o Total Gross:370+111 =$481 o Ex.Rebecca in one week works 40 hours, plus 8 hours over time.She makes $9.25/hr plus time and a half for overtime. How much will she make gross?
- 37. o If you have a service industry job (retail, restaurant,fast food,etc.)you will likely have to work on holidays.See handout for more info.You will likely get paid at least time-and-a-half for all hours worked on a holiday.
- 38. o Regular:8+6+4=18 hours x8.95/hr = $161.10 o Holiday Monday =5 hours x1.5x8.95/hr= $67.13 o Gross Pay:161.10+ 67.13 =$228.23 o Ex.Trent works at Safeway.On Thanksgiving Monday he works 5 hours, Tuesday 8 hours, Thursday 6 hours and Friday 4 hours.If Trent makes $8.95/h regular,how much will his gross pay be for the week?
- 39. o Some service industry jobs will give you"vacation pay¡±instead of paid vacation time;this will likely be a percentage of your yearly gross pay that will work out to be the same as two weeks of pay. This will be either paid out to you in a lump sum annually or on every pay check.If you take time off,you will not be paid while you are away.
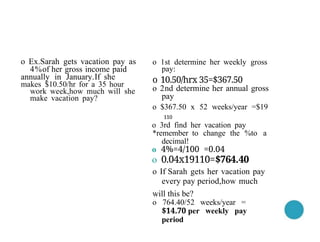
- 40. o 1st determine her weekly gross pay: o 10.50/hrx 35=$367.50 o 2nd determine her annual gross pay o $367.50 x 52 weeks/year =$19 110 o 3rd find her vacation pay *remember to change the %to a decimal! o 4%=4/100 =0.04 o 0.04x19110=$764.40 o If Sarah gets her vacation pay every pay period,how much will this be? o 764.40/52 weeks/year = $14.70 per weekly pay period o Ex.Sarah gets vacation pay as 4%of her gross income paid annually in January.If she makes $10.50/hr for a 35 hour work week,how much will she make vacation pay?
- 42. DAY 5:DEDUCTIONS-UNION DUES,HEALTH PLANS, CHARlTABLE DEDUCTIONS §¦§´§³.
- 43. o Gross Income/Pay-income earned before deductions o Net Income/Pay-Income received after deductions(your ¡°take home¡±pay) o Before taxes are calculated on gross pay,there are certain¡°before-tax¡±or¡°tax exempt¡± deductions. o These include: o Union dues,RRSP (registered retirement savings plan),charitable donations and pension
- 44. 1st determine here gross annual income:$650/ week x 52 weeks =$33800 2nd determine her annual union dues $14.10/week x 52 weeks =$733.20 3rd determine the %of her annual gross income that she pays for union dues: *remember,percent is part of a whole* $733.20/$33800 = 0.0216.. 0.0216¡x100 =2.2 %of her gross income is spent on union dues. o Ex.Lilly works as a receptionist.She makes $650 a week.Her union dues are $14.10 per pay check.What percent of Lilly's gross pay does she pay in union dues? o o o o o o
- 45. o In addition to these deductions,many people pay amounts from their gross pay for a wide range of benefits and programs such as dental plans and savings plans. o Many employers also offer lifestyle benefits. Such as discounts on merchandise,services,or bonus items like movie tickets etc.
- 46. o Marmot Basin example
- 47. o Ex.You have a 16-week contract at Marmot Basin in Jasper,where you will be working between 15 hours a week.Your employer offers you a choice of o $10.75/hr or o $8.80/hr plus a weekday season pass that has a value of $680.
- 48. o How much will you make for the first choice? o $10.75/hrx 240 hrs = $2580 o How many hours total will you work during the 16-week contract? o 16 week x15 hours /week =240 hours
- 49. o $8.80/hr x 240 hrs = $2112 PLUS a $680 season pass. o How much will you make for the second choice? o Which would you choose?Why?
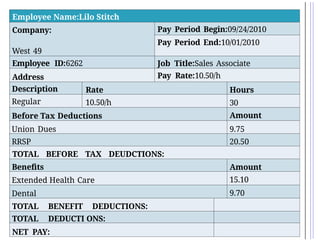
- 50. Employee Name:Lilo Stitch Company: West 49 Pay Period Begin:09/24/2010 Pay Period End:10/01/2010 Employee ID:6262 Job Title:Sales Associate Address Pay Rate:10.50/h Description Rate Hours Regular 10.50/h 30 Before Tax Deductions Amount Union Dues 9.75 RRSP 20.50 TOTAL BEFORE TAX DEUDCTIONS: Benefits Amount Extended Health Care 15.10 Dental 9.70 TOTAL BENEFIT DEDUCTIONS: TOTAL DEDUCTI ONS: NET PAY:
- 51. D§Ñ§å 7: §³§²§², EI AND INCO§®§¦ §´§¡§·
- 52. §à * Remember: Taxable Income = Your incom e, §¡§¦§´§¦§£ D§¦DU§³§´IONS is taxed by both the federal and provincial governments. §à *§®§°§´§¦: Ta§çable income is §³§£§°§¿§© §´§®§³§°§®§¦ minus any tax exempt deductions such as pension, RRSP, union dues etc.
- 53. o Canada Pension Plan(CPP)-Provides income for workers after they retire.Every employee between 18-65 must pay into it. o To estimate CPPdeductions,use 4.95%of your earnings up to a max.deduction of $2,163.15
- 54. o Employment Insurance (EI)-A fund that employees pay into to insure themselves against being unemployed.To estimate,use 1.73%of your earnings (up to earnings of $43200).Your employer usually pays 1.4 times your contribution into the fund. o THE MAXIMUM contribution amount for the employee is $747.36
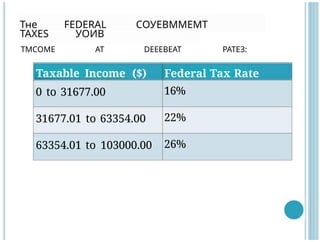
- 55. Taxable Income ($) Federal Tax Rate 0 to 31677.00 16% 31677.01 to 63354.00 22% 63354.01 to 103000.00 26% §´§ß§Ö F§¦D§¦R§¡L §³§°§µ§¦§£§®§®§¦§®§´ §´§¡§·§¦S §µ§°§ª§£ §´§®§³§°§®§¦ §¡§´ D§¦§¦§¦§£§¦§¡§´ §²§¡§´§¦§©:
- 56. o Provincial tax rates vary from province to province.¡Alberta is currently 10%
- 57. o Go through the following example with the students on an over-head: o Ex.Simon earns a biweekly salary of $1152. o a. What is Simon's gross yearly salary? o Biweekly =26 times paid per year o $1152x 26 =$29952
- 58. §à b. How much will Simon pay in CPP and EI each year? §ï §³§²§² ¡ª4.95% o{ gross earnings *change to a decimal!* 4.95% ¡ª 0.0495 §à $29 952 §ç 0.0495 = 81 482.62 §à EI = 1.73% ofgross earnings *change to a decimal!* 1.73% - 0.0173 §à $ 29 952 §ç 0.0173 = $518.17
- 59. o d. How much Federal tax does Simon pay? o$29952¡úSimon is in the first range (16%) *change to a decimal!*=0.16 o $29952x0.16=$4792.32
- 60. o e. How much provincial tax does Simon pay? o Alberta Income Tax rate is 10%*change to a decimal!*=0.10 o $29952x0.10 =$2995.20
- 61. o f. Determine Simon's total year deductions o $1482.62+$518.17+$4792.32+$2995.20= $9 788.31
- 62. o g. How much does Simon earn a year net? o $29952-$9788.31=$20163.69
- 63. o h. What is Simon's biweekly take home pay? o*biweekly=26 times paid per year!* o $20163.69/26=$775.53
- 65. o Graphs are a visual way to represent data. o A circle graph is divided into pieces to represent part of 100%.An entire circle graph should add up to 100%,
- 66. o For example: o 50%of people prefer coke o 25%prefer Pepsi o 15%prefer sprite o And 10%prefer Root Beer. o Draw a graph to represent this ¡ú o*Notice that e of the circle is represented by coke(50%!)
- 68. IF YOU POLLED 325 PEOPLE,HOW MANY WOULD YOU EXPECT TO PREFER COKE? o 50%=0.50 325x0.50=162.5 people o SO about 162 people (we cannot have half a person!)
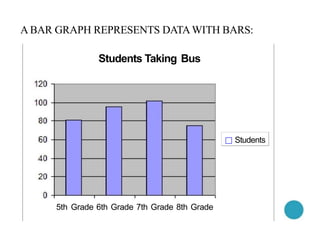
- 69. A BAR GRAPH REPRESENTS DATAWITH BARS: Students Taking Bus 5th Grade 6th Grade 7th Grade 8th Grade ¡õ Students
- 70. o About how many students take the bus in 5th grade?Go to the top of the 5th grade bar,and look to the left ¡úabout 80 students. o To construct a bar graph,create an appropriate scale on the left-hand side (the up and down or Y- axis)and a scale on the bottom (the left to right or X-axis).