Management-Chapter10-Students
- 1. In the Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent, The Most Merciful
- 2. Welcome to Chapter 10 Class Timings : 02:00 pm to 05:00 pm (Sharp) By: Khurram Khan
- 3. Designing Organizational Structure ’ü¼ Organizing - arranging and structuring work to accomplish an organizationŌĆÖs goals. ’ü¼ Organizational Structure - the formal arrangement of jobs within an organization.
- 4. Designing Organizational Structure ’ü¼ Organizational Design - a process involving decisions about six key elements: 1. Work specialization 2. Departmentalization 3. Chain of command 4. Span of control 5. Centralization and decentralization 6. Formalization
- 5. Exhibit 10-1: Purposes of Organizing
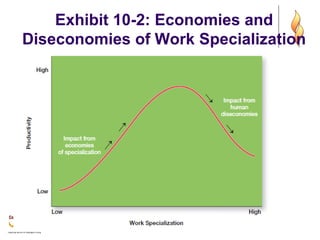
- 6. Organizational Structure Work Specialization ’ü¼ The degree to which tasks in the organization are divided into separate jobs with each step completed by a different person. ’ü¼ Overspecialization can result in human diseconomies such as boredom, fatigue, stress, poor quality, increased absenteeism, and higher turnover.
- 7. Exhibit 10-2: Economies and Diseconomies of Work Specialization
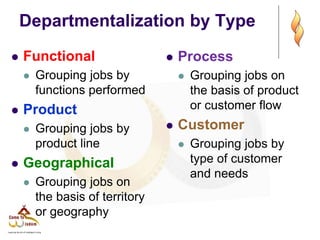
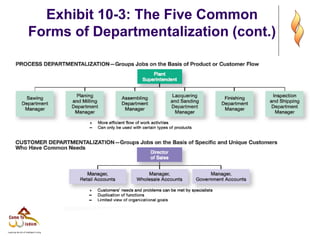
- 8. Departmentalization by Type ’ü¼ Functional ’ü¼ Grouping jobs by functions performed ’ü¼ Product ’ü¼ Grouping jobs by product line ’ü¼ Geographical ’ü¼ Grouping jobs on the basis of territory or geography ’ü¼ Process ’ü¼ Grouping jobs on the basis of product or customer flow ’ü¼ Customer ’ü¼ Grouping jobs by type of customer and needs
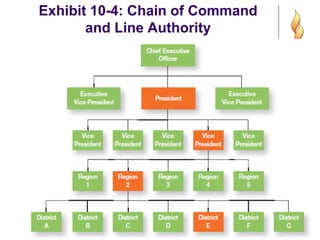
- 9. Organizational Structure (cont.) ’ü¼ Chain of Command - the continuous line of authority that extends from upper levels of an organization to the lowest levels of the organizationŌĆöclarifies who reports to whom.
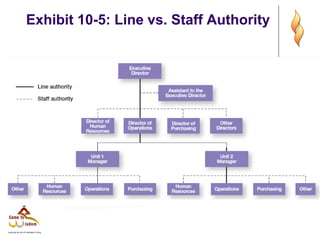
- 10. Organizational Structure (cont.) ’ü¼ Authority - the rights inherent in a managerial position to tell people what to do and to expect them to do it. ’ü¼ Responsibility - the obligation or expectation to perform. ’ü¼ Unity of Command - the concept that a person should have one boss and should report only to that person.
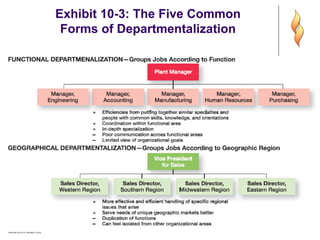
- 11. Exhibit 10-3: The Five Common Forms of Departmentalization
- 12. Exhibit 10-3: The Five Common Forms of Departmentalization (cont.)
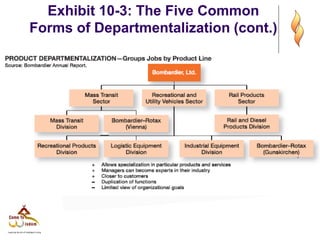
- 13. Exhibit 10-3: The Five Common Forms of Departmentalization (cont.)
- 14. Exhibit 10-4: Chain of Command and Line Authority
- 15. Exhibit 10-5: Line vs. Staff Authority
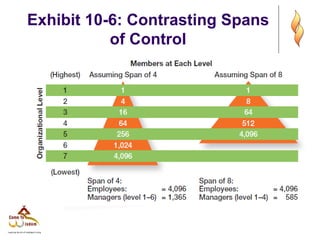
- 16. Span of Control ’ü¼ It is the number of employees who can be effectively and efficiently supervised by a manager.
- 17. Width of span is affected by: ’ü¼ Skills and abilities of the manager ’ü¼ Employee characteristics ’ü¼ Characteristics of the work being done ’ü¼ Similarity of tasks ’ü¼ Complexity of tasks ’ü¼ Physical proximity of subordinates ’ü¼ Standardization of tasks ’ü¼ Sophistication of the organizationŌĆÖs information system ’ü¼ Strength of the organizationŌĆÖs culture ’ü¼ Preferred style of the manager
- 18. Exhibit 10-6: Contrasting Spans of Control
- 19. Centralization ’ü¼ Centralization - the degree to which decision making is concentrated at upper levels in the organization. ’ü¼ This is common in organizations in which top managers make all the decisions and lower-level employees simply carry out those orders.
- 20. Decentralization ’ü¼ Decentralization - when an organization relegates decision making to managers who are closest to the action. ’ü¼ Employee Empowerment ’ü¼ Increasing the decision-making authority (power) of employees
- 21. Exhibit 10-7: Centralization or Decentralization
- 23. Thank you for your Time & Patience Please spread these words & do visit
- 24. My Company Learning the Art of Intelligent Living www.cometowisdom.com