Mantra of marketing,mix,customer values
- 1. Mantra of Marketing Marketing’s job is to create, communicate and deliver value to a target market at a profit. Market Management needs to “Create Value,” “Communicate Value,” and “Deliver Value.” There are three businesses here: Product Management; Brand Management; and Customer Management. (Kotler at London Business Forum)
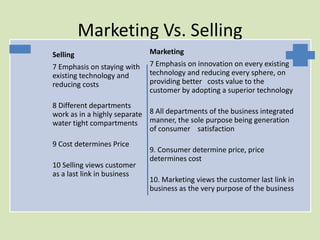
- 2. Marketing Vs. Selling SELLING MARKETING 1 Emphasis is on the product 1 Emphasis on consumer needs wants 2 Company Manufactures the 2 Company first determines customers product first needs and wants and then decides out 3 Management is sales how to deliver a product to satisfy these volume oriented wants 4 Planning is short-run- 3 Management is profit oriented oriented in terms of today’s 4 Planning is long-run-oriented in today’s products and markets products and terms of new 5 Stresses needs of seller products, tomorrow’s markets 6 Views business as a good and future growth producing process 5 Stresses needs and wants of buyers 6 Views business as consumer producing process satisfying process
- 3. Marketing Vs. Selling Selling Marketing 7 Emphasis on staying with 7 Emphasis on innovation on every existing existing technology and technology and reducing every sphere, on reducing costs providing better costs value to the customer by adopting a superior technology 8 Different departments work as in a highly separate 8 All departments of the business integrated water tight compartments manner, the sole purpose being generation of consumer satisfaction 9 Cost determines Price 9. Consumer determine price, price determines cost 10 Selling views customer as a last link in business 10. Marketing views the customer last link in business as the very purpose of the business
- 4. Marketing Mix Marketing Mix is the combination of four elements, called the 4P’s (Product, Price, Promotion and Place), that every company has the option of adding, subtracting, or modifying in order to create a desired marketing strategy. (Philip Kotler)
- 5. Marketing Mix - A mixture of several ideas and plans followed by a marketing representative to promote a particular product or brand is called marketing mix. Several concepts and ideas combined together to formulate final strategies helpful in making a brand popular amongst the masses form marketing mix. Elements of Marketing Mix The elements of marketing mix are often called the four P’s of marketing. • Product- Goods manufactured by organizations for the end-users are called products. (Tangible Product and Intangible Product -Services) • Price - The money which a buyer pays for a product is called as price of the product. • Place - Place refers to the location where the products are available and can be sold or purchased. • Promotion - Advertising, Print media, Television, radio , Billboards, hoardings, banners, Taglines , Word of mouth. Lately three more P’s have been added to the marketing mix. They are as follows: • People - The individuals involved in the sale and purchase of products or services come under people. • Process - Process includes the various mechanisms and procedures which help the product to finally reach its target market • Physical Evidence - With the help of physical evidence, a marketer tries to communicate the USP’s and benefits of a product to the end users
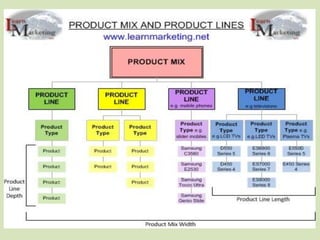
- 7. Product Mix • Set of all product offered for sale by a company. • It consist of various product line. • Any company’s product mix has four dimension : 1. Width, 2. Length, 3. Depth, 4. Consistency.
- 8. Product Mix • Width : Number of different product lines carries by the company. • Length : Total number of items in the product mix of the company. • Depth : Assortment of size, color and models offered in each item of a product line. • Consistency : It refers to the relationship of various product line either in their end use, production requirement, distribution channel or other way.
- 11. 5 Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty Marketing Management, 13th ed
- 12. Chapter Questions • What are customer value, satisfaction, and loyalty, and how can companies deliver them? • What is the lifetime value of customers? • How can companies cultivate strong customer relationships? • How can companies both attract and retain customers? • What is database marketing? Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 13. What is Customer Perceived Value? Customer perceived value is the difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all the benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
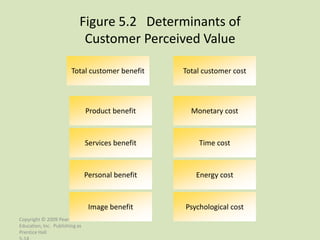
- 14. Figure 5.2 Determinants of Customer Perceived Value Total customer benefit Total customer cost Product benefit Monetary cost Services benefit Time cost Personal benefit Energy cost Image benefit Psychological cost Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 15. Steps in a Customer Value Analysis • Identify major attributes and benefits that customers value • Assess the qualitative importance of different attributes and benefits • Assess the company’s and competitor’s performances on the different customer values against rated importance • Examine ratings of specific segments • Monitor customer values over time Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 16. What is Loyalty? Loyalty is a deeply held commitment to re-buy or re-patronize a preferred product or service in the future despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching behavior. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 17. Top Brands in Customer Loyalty • Avis • Land’s End • Google • Coors • L.L. Bean • Hyatt • Samsung (mobile • Marriott phones) • Verizon • Yahoo! • KeySpan Energy • Canon (office copiers) • Miller Genuine Draft • Amazon Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 18. Measuring Satisfaction • Periodic surveys • Customer loss rate • Mystery shoppers • Monitor competitive performance Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 19. What is Quality? Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 20. Maximizing Customer Lifetime Value • Customer profitability • Customer equity • Lifetime value Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 21. What is Customer Relationship Management? CRM is the process of carefully managing detailed information about individual customers and all customer touch points to maximize customer loyalty. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 22. Framework for CRM • Identify prospects and customers • Differentiate customers by needs and value to company • Interact to improve knowledge • Customize for each customer Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 23. Customer Retention • Acquisition of customers can cost 5 times more than retaining current customers. • The average customer loses 10% of its customers each year. • A 5% reduction to the customer defection rate can increase profits by 25% to 85%. • The customer profit rate increases over the life of a retained customer. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 24. Customer Life time Value customer lifetime value (CLV), lifetime customer value (LCV), or user lifetime value (LTV) is a prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer.
- 25. Customer Lifetime Value Advantages of CLV: • management of customer relationship as an asset • monitoring the impact of management strategies and marketing investments on the value of customer assets • determination of the optimal level of investments in marketing and sales activities • encourages marketers to focus on the long-term value of customers instead of investing resources in acquiring "cheap" customers with low total revenue value • implementation of sensitivity analysis in order to determinate getting impact by spending extra money on each customer. • optimal allocation of limited resources for on going marketing activities in order to achieve a maximum return • a good basis for selecting customers and for decision making regarding customer specific communication strategies • measurement of customer loyalty (proportion of purchase, probability of purchase and repurchase, purchase frequency and sequence etc.