Marginal cost & cost sheet ppt 1
- 1. GROUP NO: 10SUBMITTED TO : SUBMITTED BY :PROF. SANDEEP S.PARMAR GAURAV (SEC.A-119) VINOD T. PANCHAL (SEC.B-221)FINANCE PROJECT ON COSTING
- 2. MARGINAL COSTINGThe Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, London defines the term marginal cost ŌĆ£the amount at any given volume of output by which aggregates costs are changed if the volume of output is increased or decreased by one unit. ŌĆØ
- 3. Analyzing the above definition , we find that with the increase of one unit of production ŌĆō may be single article or batch articles , the total cost of production is increased and this increase in total cost of production from the existing level to the new level is known as marginal cost.Analyzing the above Definition
- 4. In economics and finance, marginal cost is the change in total cost that arises when the quantity produced changes by one unit. That is, it is the cost of producing one more unit of a good. Mathematically, the marginal cost (MC) function is expressed as the first derivative of the total cost (TC) function with respect to quantity (Q). Note that the marginal cost may change with volume, and so at each level of production, the marginal cost is the cost of the next unit produced.MC = dTC/ dQMarginal Costing
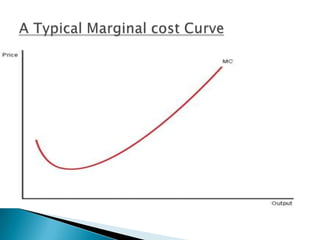
- 5. A Typical Marginal cost Curve
- 6. How much to produce : The level of output which is most profitable for a running concern can be determined . Therefore , the production capacity can be utilised to the maximum possible extent.What to Produce : The manufacturer of which product should be undertaken can be decided upon after comparing the profitability results of different products.How to Produce :A . Method of Manufacturer - which method is adopted for its manufactureB. Hand or Machine LabourAdvantages of Marginal Costing
- 7. When to Produce : In the period of trade recession , whether the product ion in the Plant is to be suspended temporarily or permanently closed down , can be decided upon after carefully examining the marginal cost structure,Whether to Produce : The decision whether a particular product should be manufactured in the factory or brought from outside source can be taken by comparing the price at which it can be had from outside and the marginal cost of producing that article in the factory.At What cost to produce : Efficiency & Economy of Plants, No Profit No Loss Point , Lease or Ownership of Plant , Cost Control , Inventory Valuation etc. Advantages Of Marginal Costing (cont.)
- 8. Classification into fixed and variable elements ŌĆō a difficult task.Faulty DecisionDifficult ApplicationUnder or Over Recovery of overheadsBetter Technique available ŌĆō the systems of budgetary control and standard costing serve the purpose better than marginal costing. Limitation of Marginal Costing
- 9. Break Even Analysis is a widely used technique to study cost volume profit relationship. The narrower interpretation of the term break even analysis refers to a system of determination of that level of activity where total cost equals total selling price.The broader interpretation refers to that system of analysis which determines probable profit at any level of activity . It portrays the relationship between cost of production , volume of Production and sales value.BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS
- 10. BREAK EVEN POINT CURVE
- 11. Advantages Provides detailed & clearly understandable information.Profitability of Products & business can be known.Effect of changes of cost & sale prices can be demonstrated.Cost control can be exercised.Economy & Efficiency can be effected.ADVANTAGES OF BREAKEVEN ANALYSIS
- 12. LimitationsBased on False Assumptions Fixed costs do not always remain constant Variable costs do not always vary proportionately. Sales revenues does not always change Proportionately. Stock changes affect incomes and condition of growth not assumed. Limited InformationNo Necessity : Simple tabulation sufficient , Conclusive guidance not provided , Difficult to Understand, No basis for comparative efficiency.LIMITATIONS OF BREAK EVEN ANALSIS
- 13. The points which breaks the total cost and the selling price evenly to show the level of output or sales at which there shall be neither profit nor loss , is regarded as break even point . At this point , the revenue of the business exactly equals its cost.Break even point (of output) = Fixed Cost / Contribution Per Unit Break even point (of Sales) = Fixed Cost * Selling Price Per Unit / Contribution Per Unit or BEP(Of Sales) = Break Even Point (of output) * Selling price per unit BREAK EVEN POINT
- 14. Marginal Cost = Direct Material + Direct Labour +Direct Expenses(variable) + Variable Overheads Marginal Cost = Total Cost ŌĆō Fixed Cost = Total Variable CostContribution = Selling Price - Variable CostContribution = Fixed Cost + ProfitProfit/Volume Ratio (P/V Ratio) = Total Contribution / Total Sales *100P/V Ratio = Change in Contribution / Change in Sales * 100P/V Ratio = Change in Profit / Change in Sales * 100BEP (OF SALES) = Fixed cost / PV Ratio BEP (OF SALES) = Fixed Costs / Total Contribution *Total Sales BEP (OF SALES) = Fixed Costs/1- Variable Cost per unit /Selling Price per unitSOME FORMULAES USED IN MARGINAL COSTING
- 15. At Breakeven point the desired profit is zero, in case the volumes of output or sales is to be computed for a ŌĆśdesired profitŌĆÖ , the amount of desired Profit should be added to Fixed Cost in the formulae given below : Output(Units) for a desired Profit = Fixed Cost + Desired Profit / Contribution Per Unit Sales for a desired Profit = Fixed Cost + Desired Profit / Profit Volume RatioMargin of Safety = Total Sales - Sales at Break Even PointMargin of Safety (as a %) = Margin of Safety /Total Sales *100SOME FORMULAE USED IN MARGINAL COSTING
- 16. Fixed costs are costs which do not vary with output, for example, rent. In the long run all costs can be considered variable.Variable cost also known as, operating costs, prime costs, on costs and direct costs, are costs which vary directly with the level of output, for example, labor, fuel, power and cost of raw material.Social costs of production are costs incurred by society, as a whole, resulting from private production.Average total cost is the total cost divided by the quantity of output.Average fixed cost is the fixed cost divided by the quantity of output.Average variable cost are variable costs divided by the quantity of output.┬ĀOther Costs Definition
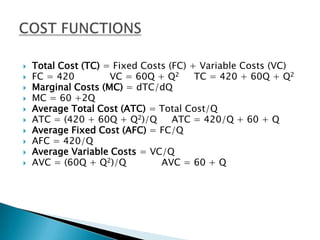
- 17. Total Cost (TC) = Fixed Costs (FC) + Variable Costs (VC)FC = 420 VC = 60Q + Q2 TC = 420 + 60Q + Q2Marginal Costs (MC) = dTC/dQMC = 60 +2QAverage Total Cost (ATC) = Total Cost/QATC = (420 + 60Q + Q2)/Q ATC = 420/Q + 60 + QAverage Fixed Cost (AFC) = FC/QAFC = 420/QAverage Variable Costs = VC/QAVC = (60Q + Q2)/Q AVC = 60 + Q┬ĀCOST FUNCTIONS
- 18. Element of cost& cost sheetFor proper control & managerial decision like sales price, profit margin, management is to provided with necessary data to analyses & classify cost. For this purpose, the total cost is analyses by elements of cost like material cost, labour cost & other expenses. These elements of cost are further analyzed into different element like prime cost, work cost or factory cost, cost of production, total cost. It show the total cost & cost per units produced during the given period.Management to keep a close watch & control over the cost of production.It help in fixing up the selling price more accurately.It helps the businessman to submit quotations with reasonable price against tender for supply of goods. ADVANTAGES OF COST SHEET
- 19. Performa of cost sheet
- 22. This items are not included in cost sheetProvision on taxTransfer to general reserveDividend Rent receivableProfit or loss on sales of investmentShare transfer feeFine & penaltyInterest on debenturePreliminary expenses Underwriting commissionDiscount on issue of shares & debentures