Maria(histones)
- 2. ’üĮ histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes.They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation. Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA, (~6 ft) but wound on the histones it has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin,
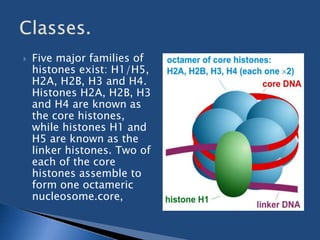
- 3. ’üĮ Five major families of histones exist: H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are known as the core histones, while histones H1 and H5 are known as the linker histones. Two of each of the core histones assemble to form one octameric nucleosome.core,
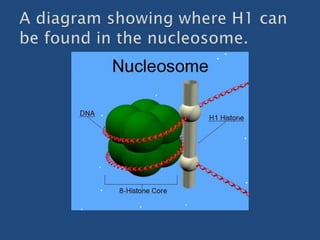
- 4. ’üĮ Histone H1 is one of the five main histone protein families which are components of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Though highly conserved, H1 proteins feature a central globular domain and long C- and short N-terminal tails. H1 is involved with the packing of the "beads on a string" sub-structures into a high order structure. it is not the globular domain but rather the highly positively charged C-tail that imparts to linker histones their unique ability to bind to linker DNA through nonspecific electrostatic interactions.
- 5. 3D -Structure H1 with Nucleosome
- 7. ’üĮ Unlike the other histones, H1 does not make up the nucleosome "bead". Instead, it sits on top of the structure, keeping in place the DNA that has wrapped around the nucleosome. H1 is present in half the amount of the other four histones, which contribute two molecules to each nucleosome bead. In addition to binding to the nucleosome, the H1 protein binds to the "linker DNA" (approximately 20-80 nucleotides in length) region between nucleosomes, helping stabilize the zig-zagged 30 nm chromatin fiber.