Marinus GNX SFN poster 16Nov16
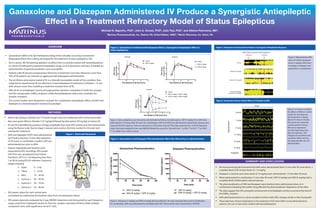
- 1. • Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (10 weeks of age) were pre-implanted with cortical electrodes. • Rats were given lithium chloride (127 mg/kg) followed by pilocarpine (50 mg/kg) to induce SE. • SE was first identified by presence of large amplitude slow wave EEG activity and then behaviorally using the Racine scale. Racine stage 3 seizures were used as the time-marker for SE onset and subsequent treatment. • GNX and diazepam (DZP) were administered via IV bolus injection 15 min after detection of SE onset. In combination studies, DZP was administered just prior to GNX. • Seizure magnitude and duration were measured by EEG recordings. EEG power (mV2/Hz) was calculated by fast Fourier Transform, (FFT) in 1 Hz frequency bins from 1 to 96 Hz using ICELUS software. Frequency ranges analyzed: o Delta 0 – 5 Hz o Theta 5 – 10 Hz o Beta 10 – 30 Hz o Gamma-1 30 – 50 Hz o Gamma-2 50 – 70 Hz o Gamma-3 70 – 96 Hz • EEG power values for each animal were normalized by subtracting the baseline value from all subsequent values. • EEG power data were evaluated by 2-way ANOVA (treatment and time period) at each frequency range using Prism Graphpad (version 6). Post-hoc analysis consisted of Holms-Sidak multiple comparison tests, with significance set at P< 0.05. • Ganaxolone (GNX) is the 3β-methylated analog of the naturally occurring neurosteroid allopregnanolone that is being developed for the treatment of status epilepticus (SE). • SE is a severe, life-threatening epileptic condition that is currently treated with benzodiazepines to control SE followed by standard antiepileptic drugs such as phenytoin and then, if needed, by administration of general anesthetics such as propofol. • Patients with SE become progressively refractory to treatment over time. Moreover, more than 30% of SE patients are resistant to aggressive benzodiazepine administration. • The rat lithium-pilocarpine model of SE is a clinically translatable model of this condition. Rats subjected to experimental SE are refractory to benzodiazepine if treatment is initiated ≥ 15 min after seizure onset; thus modeling a treatment resistant form of SE. • GNX elicits its antiepileptic activity through positive allosteric modulation of both the synaptic and the extrasynaptic GABAA receptors, unlike benzodiazepines which only modulate the synaptic receptors. • The current studies were designed to evaluate the combination antiepileptic effects of GNX with diazepam in a benzodiazepine resistant SE paradigm. Ganaxolone and Diazepam Administered IV Produce a Synergistic Antiepileptic Effect in a Treatment Refractory Model of Status Epilepticus Michael S. Saporito, PhD1, John A. Gruner, PhD2, Julia Tsai, PhD1, and Albena Patroneva, MD1. 1Marinus Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Radnor, PA, United States, 19087; 2 Melior Discovery, Inc. Exton, PA. • We have previously demonstrated that GNX when administered alone 15 min after SE onset elicits a complete block of SE at dose-levels of >12 mg/kg • Diazepam is inactive up to dose-levels of 10 mg/kg when administered >15 min after SE onset • When administered in combination 15 min after SE onset, DZP (5 mg/kg) and GNX (6 mg/kg) elicit a complete block of pilocarpine induced seizures. • The pharmacokinetics of GNX and diazepam were identical when administered alone or in combination indicating that neither drug affected the pharmacokinetic disposition of the other. • The data suggest that this synergistic enhancement of antiepileptic activity occurred at the level of the GABAA receptor. • GNX administered alone in a dose-escalation fashion elicits EEG changes similar to that of propofol. • These data have clinical implications in the treatment of SE when GNX is to be administered to patients who are or have been treated with benzodiazepines. Skull Image From Watson, “The Rat” anchor screw (sinus) Frontal cortex electrodes 3mm ant. to Bregma 2.5mm lateral Hippocampal Electrodes 4mm post. to Bregma 3mm lateral Skull sutures anchor screw (vertex) EEG Ch1 Ch2 Neck Muscles InterauralLine Lambda Bregma Bregma Figure 1. Electrode Placement Figure 2. Status epilepticus was induced by administration of lithium and pilocarpine. DZP (5 mg/kg; IV) or GNX were administered 15 minutes after SE onset. For combinations, DZP and GNX were administered sequentially. Seizures were measured by EEG response. Data are expressed as a EEG power (Log mV2/Hz). Data represent the 10-30 Hz frequency range. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc Dunnett’s test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 from vehicle control. Figure 2. Ganaxolone Combined with Diazepam Elicits a Synergistic Antiepileptic Effect in Status Epilepticus 0 2 4 6 -1 0 1 2 Time Relative to SE Onset (hrs) EEGPower (LogmV2/Hz) DZP (5 mg/kg) Vehicle Treatment 0 2 4 6 -1 0 1 2 Time Relative to SE Onset (hrs) EEGPower (LogmV2/Hz) Vehicle DZP (5 mg/kg) + GNX (3 mg/kg) DZP (5 mg/kg) + GNX (6 mg/kg) Treatment ** * **** **** ** *** 0 2 4 6 -1 0 1 2 Time Relative to SE Onset (hrs) EEGPower (LogmV2/Hz) GNX (3 mg/kg) GNX (6 mg/kg) Vehicle Treatment SE-onset Vehicle Pilocarpine Treatment Diazepam (5 mg/kg) Ganaxolone (6 mg/kg) Diazepam (5mg/kg) + Ganaxolone (6 mg/kg) SSSSSE-onset EEG Traces SE-onset and Treatment Figure 3. Representative EEG traces of vehicle, diazepam alone (5 mg/kg), GNX alone (6 mg/kg) or diazepam and ganaxolone in combination Figure 4. Diazepam (5 mg/kg) and GNX (6 mg/kg) pharmacokinetics (IV) were measured alone and in combination. For combination, GNX was administered immediately after DZP. Plasma levels were measured by LC/MS/MS. Predose 3 mg/kg 9 mg/kg 15 mg/kg 24 mg/kg 30 mg/kg Propofol 6 sec Ganaxolone Figure 5. In order to evaluate the effects of GNX on normal awake rats, the drug was administered at 3 mg/kg (bolus; IV) every 3 minutes. EEG signal was measured continuously for 6 hours. EEG traces represent 6 seconds beginning 2 min after the injection. EEG changes are consistent with anesthetic effects and are first detected after the 3rd administration. Figure 3. Diazepam and Ganaxolone Produce a Synergistic Antiepileptic Response Figure 4. Ganaxolone and Diazepam Pharmacokinetics Were Not Altered by Co-administration Figure 5. Ganaxolone Shows Similar Effects to Propofol on EEG OVERVIEW SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 Diazepam Pharmacokinetics Time (min) Diazepam(ng/mL) DZP (5 mg/kg) GNX (6 mg/kg) + DZP (5 mg/kg) 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 Ganaxolone Pharmacokinetics Time (min) GNXLevels(ng/ml) GNX (6 mg/kg) GNX (6 mg/kg) + DZP (5 mg/kg) METHODS