Marketing channels
- 1. It is a set of practices or activities necessary to transfer the ownership of goods, from the point of production to the point of consumption Role of marketing channel in marketing strategies: âĒLinks producers to buyers âĒInfluences the firmâs pricing strategy âĒCustomizes profits, offer credit etc. âĒAffect product strategy through branding, willingness to stock.
- 2. Evolution ï Agricultural products produced as per physical reach ï Industrial Revolution brought assortment, transportation etc. which brought âtradersâ into the system. ï Concept of branding and economies of scale was significant. Distribution was relevant only for the âplaceâ part of the marketing mix ï Effort put on selling brought a host of independent intermediaries in the form of retailers and wholesalers. ï Two major developments in the US impacted the distribution networks automobile & highway systems ï Early 1950âs are credited with laying the foundation of the marketing concept which means each channel member had to meet the needs of his customers. ï Relationship marketing
- 3. Channel Formats Possible ï Product Driven 1. Company owned Retail outlets:- 2. Consignment selling agents:-The company passes on the physical stocks to the intermediary who pays the company only after products have been sold. 3. Brokers:- The intermediary contacts the user and sells the product on behalf of the company without taking any physical possession of goods. He takes a commission when the sale is consummated. 4. Franchisees:- product and merchandising are decided by the company and the franchisee has to pay from the company to sell
- 4. Channel Formats Possible ï Seller driven 1. Existing retailers: These people are established in the markets and are used by end-users. 2. Supermarkets: They are much bigger retailers who not only sell a large number of branded products but also sell other grocery, stationery and clothing items. 3. Specialty stores:-They are retailers who sell only one type of merchandise only 4. Discount stores: These stores sell the same products and brands as the supermarkets but at much lower prices
- 5. Channel Formats Possible ï Service Driven 1. Transporters: They provide service on contract for companies to reach their ultimate customers. 2. Warehouse owner: They provide space for storage of products closer to consumer markets and reach them with minimum waiting time. 3. Couriers: It is similar to C&FA but handle much smaller packets 4. C&FA: They are on contract and provide both time and place utility- both storage and transport.
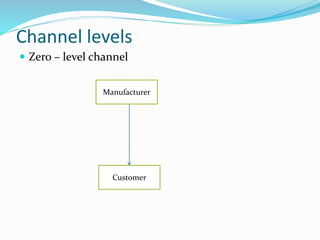
- 6. Channel levels ï Zero â level channel Customer Manufacturer
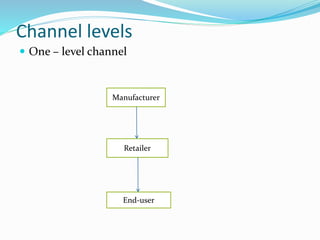
- 7. Channel levels ï One â level channel Manufacturer Retailer End-user
- 8. Channel levels ï Two level Channel Manufacturer C&FA Wholesaler Retailer End-user
- 9. Functions ï Physical Distribution ï Keep contact with the company customers. ï Helps build long term relationships. ï Market feedback to a company ï Company rules, promotions etc. are communicated to the customers. ï Negotiates price with the company and its customers. ï Handles risks for price fluctuations. ï Handles final stage product assembly. ï Provides after sales service