Masters Proposal Powerpoint Presentation
- 1. METAL BIOACCUMULATION AND BIOMARKER RESPONSES OF THE TIGERFISH, HYDROCYNUS VITTATUS , FROM THREE SOUTH AFRICAN POPULATIONS. Miss E. Fisher, Prof. V Wepener & Prof. N. Smit
- 2. PROBLEM STATEMENT: Top predators Distribution: Okavango, Zambezi, Phongolo and the Limpopo systems (Skelton 2001). Bioaccumulate and Biomagnify (Mhlanga 2000). Few bioaccumulation studies on tigerfish. Few studies indicating whether or not tigerfish experience stress as a result of bioaccumulation.
- 3. AIM: To show that tigerfish bioaccumulate and biomagnify toxicants as a result of predatory habits. To show that tigerfish are experiencing stress as a result of metal exposure and accumulation.
- 4. HYPOTHESIS The degree of metal bioaccumulation in tigerfish is an indication of environmental exposure to metals. Concomitant biomarker responses will provide an indication of stress as a result of bioaccumulation.
- 5. STUDY OBJECTIVES To determine The environmental partitioning of heavy metals in the Olifants and Levuvhu Rivers, and the Jozini Dam, The spatial and temporal extent of heavy metals in the muscle tissue of tigerfish from these ecosystems. Biomarker responses on a spatial and temporal level and to relate the biomarker responses to the metal bioaccumulation in the muscle tissue of tigerfish.
- 6. LITERATURE REVIEW Pollution of increasing concern (Jamil 2000; Walker et al . 2006) Metals can adhere to solid matrix e.g sediment (Walker et al . 2006). Bioaccumulation: Movement of toxicants (Hoffman et al . 1995) Food chain or environment Bioconcentration: non-dietary (Hoffman et al . 1995) Biomagnification: increase through trophic level (Hoffman et al . 1995) Exposure: only a portion taken up (Connell et al . 1999) Naturally occurring metals low Changes cause bioaccumulation/bioconcentration (Nussey et al . 1999).
- 7. CONT. OF LITERATURE REVIEW Why tigerfish? High trophic level (Skelton 2001) Robbers, minnows, sardines (Skelton 2001) Bioaccumulate and biomagnify (Mhlanga 2000) Liver used for biomarkers Metabolism Site of accumulation Biotransformation (Braunbeck et al . 1998)
- 8. CONT. OF LITERATURE REVIEW Biomarkers: AChE (Ellman et al . 1961; Connell et al . 1999) LP (MDA) (Ohkawa et al . 1979; Uner et al . 2005) & SOD (Farombi et al . 2007) CA (Cohen et al . 1970) EROD (Viarengo et al . 1997; Flammation et al . 1998; Flammarion &Garic 1997; Burke & Mayer 1974; Besselink et al . 1997; Connell et al . 1999) PC (Parvez & Raisuddin 2005; Levine et al . 1990; Fernandes et al . 2008; Floor & Wetzel 1998) Metallothioneins (Viarengo et al . 1997; Viarengo et al . 1999; Atli & Canli 2008; Fernandes et al . 2008; Hubbard 2005; Connell et al . 1999) CEA (de Coen & Janssen 1997; de Coen & Janssen 2003)
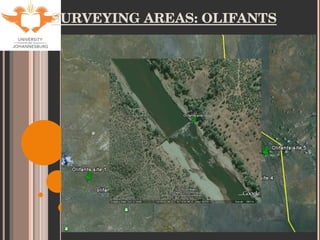
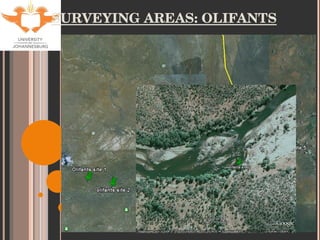
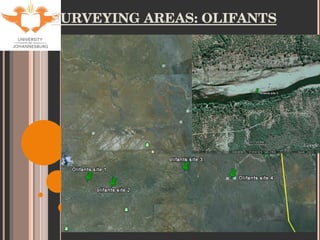
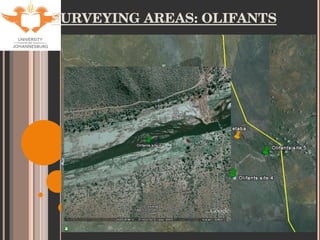
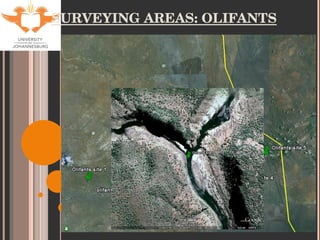
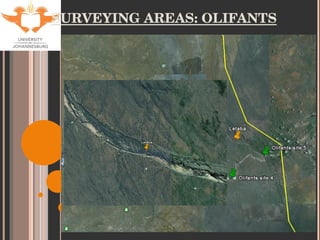
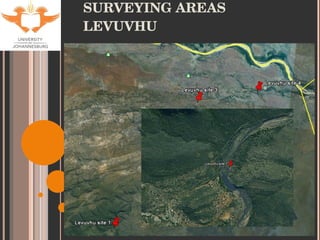
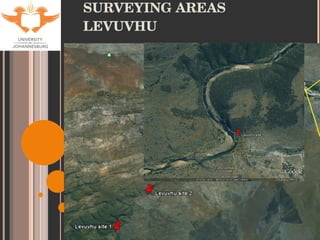
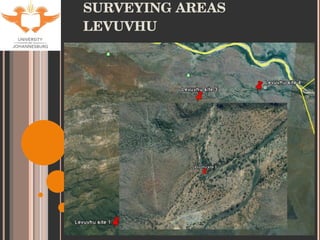
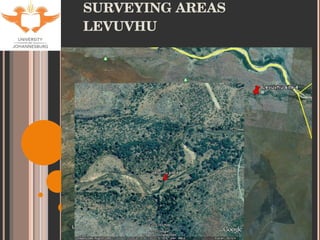
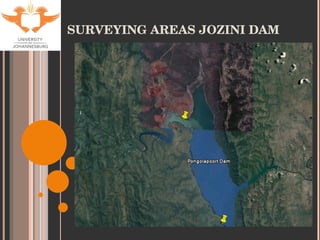
- 9. SITE SELECTION Accessibility Historical data for tigerfish Sites used by KNP Aquatic Sciences Varying degrees of impacts (with respect to metal contamination only). Levuvhu: relatively un-impacted Olifants: heavily impacted Jozini Dam: slightly impacted
- 20. SURVEYING AREAS JOZINI DAM
- 21. SAMPLING Bi-annually Samples per site Water (triplicate, polypropylene jars) Sediment (triplicate, polypropylene jars) Tigerfish muscle (Bioaccumulation: polypropylene falcon tubes, Biomarkers: cryotubes & Hendrickson stabilisation buffer) Tigerfish liver (biomarkers: cryotubes & Hendrickson stabilisation buffer)
- 22. CONT. OF SAMPLING Physico-chemical characteristics of water & sediment Water quality parameters pH Temperature DO (Percentage saturation and content) EC TDS
- 23. CONT. OF SAMPLING Sediment Characteristics Organic carbon content Particle size distribution Metal Concentrations using BCR sequential extraction (Ho and Evans 1997) Water Characteristics NO 3 - ,NO 2 - , NH 4 + , PO 4 2- ,SO 4 2- , Cl - , Turbidity. Dissolved metals Suspended metals
- 24. CONT OF SAMPLING Biomarkers: AChE (Ellman et al . 1961) LP (MDA) (Ohkawa et al . 1979; Uner et al . 2005) CA (Cohen et al . 1970) SOD (Farombi et al . 2007) EROD (Viarengo et al . 1997; Flammation et al . 1998; Flammarion &Garic 1997; Burke & Mayer 1974; Besselink et al . 1997) PC (Parvez & Raisuddin 2005; Levine et al . 1990; Fernandes et al . 2008; Floor & Wetzel 1998) Metallothioneins (Viarengo et al . 1997; Viarengo et al . 1999; Atli & Canli 2008; Fernandes et al . 2008; Hubbard 2005) CEA (de Coen & Janssen 1997; de Coen & Janssen 2003)
- 25. STATISTICS One-way analysis of variance and co-variance will be used to compare the concentrations of metals and biomarker responses across sites and sampling periods. Data that deviate from normal distribution will be appropriately transformed prior to testing by parametric tests. The relationship between metal bioaccumulation and biomarker responses will be tested using regression and correlation analysis.
- 26. RESULTS EXPECTED Speciation and distribution of heavy metals Bioaccumulation Response of tigerfish Source of metal exposure
- 27. ╠²