Math095- Chapter 3- Linear Equation-Revised (1).pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes4 views
Math095- Chapter 3- Linear Equation-Revised (1).pptx
1 of 22
Download to read offline




















Recommended
Linear equations inequalities and applications



Linear equations inequalities and applicationsvineeta yadav
╠²
This document provides information about chapter 2 of a math textbook. It covers linear equations, formulas, and applications. Section 2-1 discusses solving linear equations, including using properties of equality and identifying conditional, identity, and contradictory equations. Section 2-2 introduces formulas and how to solve them for a specified variable. Section 2-3 explains how to translate words to mathematical expressions and equations, and how to solve applied problems using a six step process. An example at the end solves a word problem about baseball players' home run totals.Contextualized Lesson Plan in Math 7 Linear Equation in One Variable



Contextualized Lesson Plan in Math 7 Linear Equation in One VariableDepartment of Education - Philippines
╠²
This lesson plan is about solving linear equations and inequalities algebraically. Students will learn to find the solution of linear equations in one variable. They will practice translating between verbal and mathematical phrases and evaluating expressions. The lesson will review properties of equality like the reflexive, symmetric, transitive, addition, and multiplication properties. Students will learn steps to solve various types of linear equations using these properties. They will assess their understanding by solving sample equations on their own. For homework, students will solve equations and determine whether they have unique solutions, no solutions, or infinite solutions.Factoring Quadratics



Factoring Quadraticsmholst
╠²
The document discusses solving equations over replacement sets. It provides definitions of key terms like expressions, equations, inequalities, and open sentences. It then gives examples of identifying expressions, equations, inequalities, and whether sentences are true, false, or open. The document also covers properties of equality and strategies for solving equations, like isolating the variable.MATHS - Linear equation in two variable (Class - X) Maharashtra Board



MATHS - Linear equation in two variable (Class - X) Maharashtra BoardPooja M
╠²
MATHS - Linear equation in two variable
(Class - X)
Maharashtra Board
Equations/Expressions
Word Problem
20 Algebra equations (2).pdf



20 Algebra equations (2).pdfAlison Tutors
╠²
This document provides instructions and examples for solving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division equations. It defines key terms like variables, algebraic expressions, and evaluating expressions. Examples are given for writing algebraic expressions to represent word phrases. The document also shows how to simplify expressions and evaluate expressions for a given value of a variable.Grade 9 QI Week 1(Quadratic Equations).pptx



Grade 9 QI Week 1(Quadratic Equations).pptxpreseahencarnacion
╠²
This is a presentation on the Lesson 1 of Math 9 Q1. The power point is all about Quadratic Equations.Algebraic Simplification and evaluation



Algebraic Simplification and evaluationPuna Ripiye
╠²
Lessons on Algebraic simplification and evaluation for students preparing for WASSCE, NECO and JAMB exams. Quadratic Equation



Quadratic Equationitutor
╠²
This document introduces methods for solving quadratic equations beyond factoring, including the square root property, completing the square, and the quadratic formula. It discusses how to determine the number and type of solutions based on the discriminant. The key steps are presented for solving quadratics, graphing quadratic functions as parabolas, and finding the domain and range. Piecewise-defined quadratic functions are also explained.Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables.pptx



Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables.pptxshahanieabbat3
╠²
Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variaMIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: Equations



MIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: EquationsLawrence De Vera
╠²
This document provides information about equations, including definitions, properties, and steps to solve different types of equations. It defines an equation as a statement about the equality of two expressions. Equations can be solved to find all values that satisfy the equation. The key properties of equality, including addition/subtraction and multiplication/division properties, allow equivalent equations to be formed in order to solve equations. The document discusses linear equations, absolute value equations, formulas, and using equations to model real-world situations.Units 1 3 review



Units 1 3 reviewmlabuski
╠²
1. The document provides an overview of the curriculum for 6th grade math including topics, pacing, and vocabulary for three units: Expressions and Equations, Solving Equations and Inequalities, and Decimals.
2. Key topics include exponents, order of operations, variables and expressions, translating between words and math, equations and solutions, adding/subtracting/multiplying/dividing decimals.
3. Each unit lists the corresponding textbook chapters and New York State Common Core Learning Standards addressed. Common assessments are also included.Expresiones Algebraicas, Factorizaci├▓n y Radicaci├▓n



Expresiones Algebraicas, Factorizaci├▓n y Radicaci├▓nClaudimarCaizales
╠²
The document outlines an accounting training program taken by Claudimar Ca├▒izalez. It covers the following topics in Unit 1:
1) Addition, subtraction, and evaluation of algebraic expressions
2) Multiplication and division of algebraic expressions
3) Factorization using factoring techniques like common factors, difference of squares, and quadratic formula.
Exercises are provided to demonstrate each technique.Business Math Chapter 3



Business Math Chapter 3Nazrin Nazdri
╠²
The document covers systems of linear equations, including how to solve them using substitution and elimination methods. It provides examples of solving systems of equations with one solution, no solution, and infinitely many solutions. Quadratic equations are also discussed, including how to solve them by factoring, using the quadratic formula, and identifying the nature of solutions based on the discriminant.Dll wk-1-lc-1



Dll wk-1-lc-1JennyRoseSumagui2
╠²
1. The document is a daily lesson log for a Grade 9 mathematics class covering quadratic equations.
2. It outlines the objectives, content, learning resources and procedures used to teach illustrations of quadratic equations, solving by extracting square roots, and solving by factoring.
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving quadratic equations by extracting square roots and factoring. Students will practice solving equations using these methods.Dll wk-1-lc-1



Dll wk-1-lc-1JennyRoseSumagui2
╠²
1. The document is a daily lesson log for a Grade 9 mathematics class covering quadratic equations.
2. It outlines the objectives, content, learning resources and procedures used to teach illustrations of quadratic equations, solving by extracting square roots, and solving by factoring.
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving quadratic equations by extracting square roots and factoring. Students will practice solving equations using these methods.Solving equations one & two step



Solving equations one & two stepchrystal_brinson
╠²
1) The document defines terms, constants, coefficients, and discusses how to solve one-step and two-step equations. It provides examples of solving equations involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
2) Sample one-step equations are provided along with the steps to solve each type. Equations involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are worked through as examples.
3) A two-step practice problem is given along with the answers. Solving two-step equations is introduced.Linear Equation in one variable - Class 8 th Maths



Linear Equation in one variable - Class 8 th MathsAmit Choube
╠²
this ppt give you concepts about the chapter linear equation in one variable class 8th . it wil clear all your doubts.Diapositivas unidad 1



Diapositivas unidad 1IvnDavidVegaJuris
╠²
This document discusses basic algebraic expressions and provides recommendations for working with them. An algebraic expression is a combination of numbers and letters related through basic arithmetic operations. It is important to have a solid understanding of properties, operations, and sign rules when working with algebraic expressions. Expressions can be analyzed based on their terms, degrees, and other characteristics in order to perform operations like factoring. Examples are provided to demonstrate summations, subtractions, multiplications, divisions, and other operations with monomials, binomials, trinomials, and polynomials.Properties of Addition & Multiplication



Properties of Addition & Multiplicationitutor
╠²
The document discusses various properties of real numbers including the commutative, associative, identity, inverse, zero, and distributive properties. It also covers topics such as combining like terms, translating word phrases to algebraic expressions, and simplifying algebraic expressions. Examples are provided to illustrate each concept along with explanations of key terms like coefficients, variables, and like terms.Quarter 2 Week 1 Math 8 Danao.pptx



Quarter 2 Week 1 Math 8 Danao.pptxEvangeline Danao
╠²
This module provides lessons on linear inequalities in two variables, including:
1) Defining linear equations and inequalities, and differentiating between the two. Linear inequalities divide the plane into two half-planes, while equations represent a single line.
2) Explaining how to read and determine solutions to linear inequalities in two variables by substituting values. Graphs of inequalities show the solution set as the shaded region.
3) Demonstrating how to graph linear inequalities by plotting the boundary line and shading the correct half-plane based on testing a point. Steps are provided to graph inequalities in slope-intercept and standard form.
4) Presenting examples of solving word problemsExpresiones algebraicas



Expresiones algebraicasCarlosRamosAzuaje
╠²
Suma, Resta, Valor num├®rico, Multiplicaci├│n, Divisi├│n y Productos Notables de Expresiones algebraicas.
Factorizaci├│n por Productos NotablesLinear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable



Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variablemisey_margarette
╠²
The document discusses linear equations and inequalities in one variable. It defines linear equations and inequalities, and describes methods for solving them including: guess-and-check, cover-up, and working backwards. It also covers properties of equality and inequality, and provides examples of solving linear equations and inequalities using these properties and graphical representations of solution sets on number lines.Algebra Revision.ppt



Algebra Revision.pptAaronChi5
╠²
This document provides an overview of topics covered in intermediate algebra revision including: collecting like terms, multiplying terms, indices, expanding single and double brackets, substitution, solving equations, finding nth terms of sequences, simultaneous equations, inequalities, factorizing common factors and quadratics, solving quadratic equations, rearranging formulas, and graphing curves and lines. The document contains examples and practice problems for each topic.Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)John O'Driscoll
╠²
Here are the steps to solve this equation:
1) The equation is: x + 3 / 6 = 1
2) Multiply both sides by 6: x + 3 = 6
3) Subtract 3 from both sides: x = 3
Therefore, the solution is x = 3.
(d) The equation is: 3(y ŌłÆ 7) = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 + y/2 = 14
(12y ŌłÆ 21)/6 = 14
12y ŌłÆ 21 = 84
12y = 105
y = 9
The solution is y = 9.
(Check: if y =More Related Content
Similar to Math095- Chapter 3- Linear Equation-Revised (1).pptx (20)
Quadratic Equation



Quadratic Equationitutor
╠²
This document introduces methods for solving quadratic equations beyond factoring, including the square root property, completing the square, and the quadratic formula. It discusses how to determine the number and type of solutions based on the discriminant. The key steps are presented for solving quadratics, graphing quadratic functions as parabolas, and finding the domain and range. Piecewise-defined quadratic functions are also explained.Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables.pptx



Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables.pptxshahanieabbat3
╠²
Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variables and differentiate linear inequality and equality in two variable for mathematics 8 in quarter 2. Illustrate Linear Equation in two variaMIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: Equations



MIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: EquationsLawrence De Vera
╠²
This document provides information about equations, including definitions, properties, and steps to solve different types of equations. It defines an equation as a statement about the equality of two expressions. Equations can be solved to find all values that satisfy the equation. The key properties of equality, including addition/subtraction and multiplication/division properties, allow equivalent equations to be formed in order to solve equations. The document discusses linear equations, absolute value equations, formulas, and using equations to model real-world situations.Units 1 3 review



Units 1 3 reviewmlabuski
╠²
1. The document provides an overview of the curriculum for 6th grade math including topics, pacing, and vocabulary for three units: Expressions and Equations, Solving Equations and Inequalities, and Decimals.
2. Key topics include exponents, order of operations, variables and expressions, translating between words and math, equations and solutions, adding/subtracting/multiplying/dividing decimals.
3. Each unit lists the corresponding textbook chapters and New York State Common Core Learning Standards addressed. Common assessments are also included.Expresiones Algebraicas, Factorizaci├▓n y Radicaci├▓n



Expresiones Algebraicas, Factorizaci├▓n y Radicaci├▓nClaudimarCaizales
╠²
The document outlines an accounting training program taken by Claudimar Ca├▒izalez. It covers the following topics in Unit 1:
1) Addition, subtraction, and evaluation of algebraic expressions
2) Multiplication and division of algebraic expressions
3) Factorization using factoring techniques like common factors, difference of squares, and quadratic formula.
Exercises are provided to demonstrate each technique.Business Math Chapter 3



Business Math Chapter 3Nazrin Nazdri
╠²
The document covers systems of linear equations, including how to solve them using substitution and elimination methods. It provides examples of solving systems of equations with one solution, no solution, and infinitely many solutions. Quadratic equations are also discussed, including how to solve them by factoring, using the quadratic formula, and identifying the nature of solutions based on the discriminant.Dll wk-1-lc-1



Dll wk-1-lc-1JennyRoseSumagui2
╠²
1. The document is a daily lesson log for a Grade 9 mathematics class covering quadratic equations.
2. It outlines the objectives, content, learning resources and procedures used to teach illustrations of quadratic equations, solving by extracting square roots, and solving by factoring.
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving quadratic equations by extracting square roots and factoring. Students will practice solving equations using these methods.Dll wk-1-lc-1



Dll wk-1-lc-1JennyRoseSumagui2
╠²
1. The document is a daily lesson log for a Grade 9 mathematics class covering quadratic equations.
2. It outlines the objectives, content, learning resources and procedures used to teach illustrations of quadratic equations, solving by extracting square roots, and solving by factoring.
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving quadratic equations by extracting square roots and factoring. Students will practice solving equations using these methods.Solving equations one & two step



Solving equations one & two stepchrystal_brinson
╠²
1) The document defines terms, constants, coefficients, and discusses how to solve one-step and two-step equations. It provides examples of solving equations involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
2) Sample one-step equations are provided along with the steps to solve each type. Equations involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are worked through as examples.
3) A two-step practice problem is given along with the answers. Solving two-step equations is introduced.Linear Equation in one variable - Class 8 th Maths



Linear Equation in one variable - Class 8 th MathsAmit Choube
╠²
this ppt give you concepts about the chapter linear equation in one variable class 8th . it wil clear all your doubts.Diapositivas unidad 1



Diapositivas unidad 1IvnDavidVegaJuris
╠²
This document discusses basic algebraic expressions and provides recommendations for working with them. An algebraic expression is a combination of numbers and letters related through basic arithmetic operations. It is important to have a solid understanding of properties, operations, and sign rules when working with algebraic expressions. Expressions can be analyzed based on their terms, degrees, and other characteristics in order to perform operations like factoring. Examples are provided to demonstrate summations, subtractions, multiplications, divisions, and other operations with monomials, binomials, trinomials, and polynomials.Properties of Addition & Multiplication



Properties of Addition & Multiplicationitutor
╠²
The document discusses various properties of real numbers including the commutative, associative, identity, inverse, zero, and distributive properties. It also covers topics such as combining like terms, translating word phrases to algebraic expressions, and simplifying algebraic expressions. Examples are provided to illustrate each concept along with explanations of key terms like coefficients, variables, and like terms.Quarter 2 Week 1 Math 8 Danao.pptx



Quarter 2 Week 1 Math 8 Danao.pptxEvangeline Danao
╠²
This module provides lessons on linear inequalities in two variables, including:
1) Defining linear equations and inequalities, and differentiating between the two. Linear inequalities divide the plane into two half-planes, while equations represent a single line.
2) Explaining how to read and determine solutions to linear inequalities in two variables by substituting values. Graphs of inequalities show the solution set as the shaded region.
3) Demonstrating how to graph linear inequalities by plotting the boundary line and shading the correct half-plane based on testing a point. Steps are provided to graph inequalities in slope-intercept and standard form.
4) Presenting examples of solving word problemsExpresiones algebraicas



Expresiones algebraicasCarlosRamosAzuaje
╠²
Suma, Resta, Valor num├®rico, Multiplicaci├│n, Divisi├│n y Productos Notables de Expresiones algebraicas.
Factorizaci├│n por Productos NotablesLinear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable



Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variablemisey_margarette
╠²
The document discusses linear equations and inequalities in one variable. It defines linear equations and inequalities, and describes methods for solving them including: guess-and-check, cover-up, and working backwards. It also covers properties of equality and inequality, and provides examples of solving linear equations and inequalities using these properties and graphical representations of solution sets on number lines.Algebra Revision.ppt



Algebra Revision.pptAaronChi5
╠²
This document provides an overview of topics covered in intermediate algebra revision including: collecting like terms, multiplying terms, indices, expanding single and double brackets, substitution, solving equations, finding nth terms of sequences, simultaneous equations, inequalities, factorizing common factors and quadratics, solving quadratic equations, rearranging formulas, and graphing curves and lines. The document contains examples and practice problems for each topic.Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)John O'Driscoll
╠²
Here are the steps to solve this equation:
1) The equation is: x + 3 / 6 = 1
2) Multiply both sides by 6: x + 3 = 6
3) Subtract 3 from both sides: x = 3
Therefore, the solution is x = 3.
(d) The equation is: 3(y ŌłÆ 7) = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 + y/2 = 14
(12y ŌłÆ 21)/6 = 14
12y ŌłÆ 21 = 84
12y = 105
y = 9
The solution is y = 9.
(Check: if y =Recently uploaded (20)
Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠²
NAPD Annual Symposium
ŌĆ£Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ŌĆØHow to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.How to create security group category in Odoo 17



How to create security group category in Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
This slide will represent the creation of security group category in odoo 17. Security groups are essential for managing user access and permissions across different modules. Creating a security group category helps to organize related user groups and streamline permission settings within a specific module or functionality.Chapter 1. Basic Concepts of Strategic Management.pdf



Chapter 1. Basic Concepts of Strategic Management.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.ITI Turner Question Paper MCQ E-Book Free Download



ITI Turner Question Paper MCQ E-Book Free DownloadSONU HEETSON
╠²
ITI Turner Question Paper MCQ Book PDF Free Download. All Questions collected from NIMI Mock Test, CTS Bharat Skills Question Bank, Previous Exam papers. Helpful for CTS Trade Theory 1st & 2nd Year CBT Exam,╠²Apprentice test, AITT, ISRO, DRDO, NAVY, ARMY, Naval Dockyard, Tradesman, Training Officer, Instructor, RRB ALP CBT 2,╠²Railway Technician, CEPTAM, BRO, PWD, PHED, Air India, BHEL, BARC, IPSC, CISF, CTI, HSFC, GSRTC, GAIL, PSC, Viva, Tests, Quiz╠²& all other technical competitive exams.Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
╠²
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatN.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
╠²
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatManaging expiration dates of products in odoo



Managing expiration dates of products in odooCeline George
╠²
Odoo allows users to set expiration dates at both the product and batch levels, providing flexibility and accuracy. By using Odoo's expiration date management, companies can minimize waste, optimize stock rotation, and maintain high standards of product quality. The system allows users to set expiration dates at both the product and batch levels, providing flexibility and accuracy.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
╠²
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Rest API Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Rest API Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Rest API Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatResearch & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Math095- Chapter 3- Linear Equation-Revised (1).pptx
- 1. Chapter 3 Linear Equations Section 3-1 Addition Property of Equality 1. Solve linear equations, using the addition property of equality 2. Translate mathematics expressions into English and English expressions into mathematics.
- 2. Solve linear equations, using the addition property of equality solving the equation is The process of find the solution(s) of an equation variable = constant 1) m - 7 = - 8 3) x + 7 - 3 = 6 -11 An equation states that two mathematical expressions are equal. 2) t + 6 = 5
- 3. 4) ŌĆō 7 ŌĆō 8 = ŌĆō 8x ŌĆō 15 + 9x Solving equations. Simplify your answer 5) 6 (a + 3) ŌĆō 5a = 8 6) 13y ŌĆō 4 (3y + 5) = 12
- 4. 7) ŌĆō10( 2x + 4) + 7( 3x ŌĆō 2) ŌĆō 7= 5 ŌĆō 9
- 5. Translating English sentences into mathematics sentences. 1. Search for operation key words. 2. Translate (is / were) into equal sign (=) 3. Use a variable for some number 2. Thirty ŌĆō five is some number subtracted from eight. 1. Some number minus two is equal to nine. 4. Six more than m is twelve . 3. The difference between a number and negative four is Thirteen.
- 6. Translating English sentences into mathematics sentences. 1. Five more than some number is negative 12. A. 5 ŌĆō x = -12 B. x ŌĆō 5 = - 12 C. x + 5 = - 12 D. -12 + x = 5 2. Eight less than some number is negative twenty-five. A. 8 ŌĆō x = -25 B. x ŌĆō 8 = - 25 C. x ŌĆō 25 = - 8 D. x +8 = - 25 3. Twenty-nine is some number decreased by eleven. A. 28 = 11 ŌĆō x B. x ŌĆō 11 = 28 C. 28 = x ŌĆō 11 D. 28 = x + 11 4. - 9 subtracted from some number is 25 . A. x + 9 = 25 ; 16 B. x ŌĆō 9 = 25 ; 34 C. ŌĆō 9 + x = 25 ; 34 D. x + 9 = 25 ; 2 4
- 8. Section 3-2 Multiplication Property of Equality Solve equations by using the multiplication property of equality.
- 9. 1. 9 y = -27 Solve equations 2. Øæź ŌłÆ7 = 9 3. 3Øæź 17 = ŌłÆ15 4. ŌłÆ 5Øæź 8 = ŌłÆ20 Translate from English to a mathematical sentence and solve. Use x as the variable. -6 times a number is 18
- 10. 1) 24x + 7 ŌĆō 26x = 8 ŌĆō 9 2) ŌĆō5 (3a ŌĆō 1) ŌĆō 12 a = 2 3) 25c + 8 ŌĆō 28c = 4 ŌĆō 5
- 11. 1. Translating English sentences into mathematics sentences and solve. use x as the variable. The product of four and some number is negative twenty- six. A. x ŌĆō 4 = ŌĆō 26 B. 4 x = ŌĆō 26 C. x + 4 = ŌĆō 26 D. ŌĆō 26 x = 4 The solution is x = 2. Solve ŌłÆ 5 Øæź 8 = 20
- 12. Section 3-3 Solve equation using Addition & Multiplication Property of Equality B. Solve linear equations, using both the addition and multiplication property of equality. B. Determine whether an equation is an Identity or contradiction.
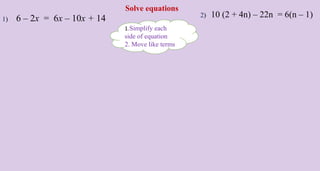
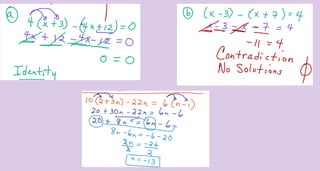
- 13. 1) 6 ŌĆō 2x = 6x ŌĆō 10x + 14 2) 10 (2 + 4n) ŌĆō 22n = 6(n ŌĆō 1) Solve equations 1.Simplify each side of equation 2. Move like terms
- 14. 3) 5(4a ŌĆō 1) ŌĆō 4 = 15a + 6 Solve equations
- 15. Determine whether the equation is an identity or a contradiction. An Identity is An equation that is true for all values of the variable for which the equation is defined. Identity Solution is ŌĆ£ all real numbersŌĆØ 3(w +2) - 4 = w + 2w + 2 Same result on both sides of equation The variable can be Any real number
- 16. Determine whether the equation is an identity or a contradiction. A contradiction is An equation that has no solution. NO SOLUTION 6 (w +1) -2 = 6w + 8 The result on both sides are Not equal No Solution
- 17. Determine whether the equation is an identity or a contradiction and indicate solutions 1) 6x ŌĆō 3 (x + 3) = 6 x ŌĆō 6 ŌĆō 3( x ŌĆō 4) 2) 4a + 9 = 4(a +1) +5
- 18. Determine whether the equation is an identity or a contradiction and indicate solutions 3) 8w ŌĆō 4 (w + 4) = 4(2w ŌĆō 4) ŌĆō 4(w ŌĆō 5) 4) 4 (c + 2) = 8c + 4 ŌĆō 4c + 4








