Matter is the matter of all the matter .
- 1. Matter PRESENTED BY MRS. SUNEETHA LUKE M
- 2. What is Matter ? Anything which occupies space, has mass and can be perceived by our physical senses is called matter.
- 3. Characteristics of Matter Volume Mass Weight Perception by physical senses
- 4. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter The main postulates of this theory are: 1.All matter is composed of small particles called molecules or atoms. 2.The particles are in a state of unending motion and a such have kinetic energy. 3.With the supply of heat energy to matter, the kinetic energy of its particles increases. Reverse happens, if the matter is cooled.
- 5. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter 4. The particles attract each other with a force. This force is called cohesive force, if the particles are of the same kind and adhesive force if the particles are of different kinds. 5. The force of attraction between the particles decreases, if the distance between them increases and vice versa.
- 6. Interparticle Space and Interparticle Attraction. Solids 1. The interparticle spaces are very small. 2. the interparticle attraction is very strong and there is no collision of particles.
- 7. Liquids 1. The interparticle space in liquids are larger than in solids 2. The interparticle attraction is much lesser than in solids and their property of collision is much greater than in solids
- 8. Gases 1. The interparticle space is much larger than in liquids. 2. The interparticle attraction is much less than in liquids and the property of collison is much greater than liquids.
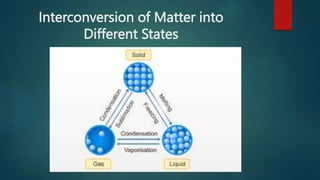
- 9. Interconversion of Matter into Different States
- 10. Law of Conservation of Mass According to this law, “mass can neither be created, nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction. Ex: reaction of CuSo4 and NaCO3
- 11. Physical change A change that alters some specific Property of matter without any change in the composition of its molecules, is called a physical change.
- 12. Chemical Change A change which alters the specific properties of a substance by bringing about a change in its molecular composition, followed by a change of state, is called a chemical change.
- 13. Mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products. Example : Reaction of Barium Chloride (BaCl2) with Sodium Sulphate (NaSO4)
Editor's Notes
- #3: The object you are holding is matter, the chair on which you are sitting is matter, the air you breathe is matter. Even your own body is made up of matter. Anything which occupies space (volume), and has mass and can be perceived by our senses is called matter .
- #4: There are four characteristics of matter, the first one is volume, the matter must occupy space the space occupied by matter is volume. The next one is mass, it represents the quantity of matter, which can be found by a physical balance. The third one is weight , weight represents the the pull of gravity on matter. It can be found by a spring balance.The last one is perception by physical senses, We can notice matter through our physical senses that is sense of touch, hearing, sight, smell, taste.
- #5: A substance from which something is made or can be made is called a material. Wood is a material, water is a material, marble is a material. There are two kinds of materials homogeneous materials and heterogeneous materials Homogeneous materialsarethe materials which have same composition and same properties throughout. For example pure common salt is a homogeneous material. Heterogeneous materials are the materials which have different compositions and different properties in their different parts. For example in a marble rock we can see grey or red grains of other materials.
- #6: Kinetic molecular theory of matter The five main postulates of this theory are All matter is composed of small particles called molecules atoms or ions as the situation demands. Everything is made up of small particles called molecules. The particles are in a state of unending motion or continuous motion and a such have kinetic energy. It means that the particles never stop moving. With the supply of heat energy or thermal energy to matter, the kinetic energy of its particles increases that means they start moving more vigourously. Reverse happens, if the matter is cooled that is heat energy is taken out. This can be explained by water, when we heat water on a high flame for a couple of minutes, water starts to boil, right? If the water is moving that means the particles are moving vigourously. Reverse happens if we put the water in the refrigerator, can we see any movement in the water? No
- #7: Kinetic molecular theory of matter The particles attract each other with a force. This force is called cohesive force , if the particles are of the same kind and adhesive force if the particles are of different kinds. For example, if both are of solid particles then it is cohesive force. If one is a liquid particle and the other a solid particle then the force between them will be adhesive force. The force of attraction between the particles decreases, if the distance between them increases and the force of attraction between the particles increases, if the distance between them decreases. Let us take the example of a magnet, if two magnets are near each other they have strong force and get pulled towards each other, if two magnets are far apart the force between them is really weak. Hence the distance between the magnets is what matters.
- #8: States of matter and their properties There are three states of matter What are the three states of matter ? Yes, you are close. The three states of matter are solid, liquid and gas. They can be distinguished from each other by their properties. The first state of matter is a solid, a solid is a state of matter which has a definite shape and definite volume. Properties of solids They have definite shape and volume. They are generally rigid. If some solid for example rubber changes its shape on the application of external force then it regains its shape on the removal of the force. They can have any number of free surfaces. Their density is generally high. They do not diffuse. The intermolecular spaces are very small and intermolecular forces are very large The dimensions of solids do not increase on large proportion on heating or cooling.
- #9: The definite shape and volume of solids can be explained on the basis of kinetic theory of matter. In solids the kinetic energy of the molecules is least and the force of attraction between the molecules is maximum. The molecules of the solids can just vibrate about their mean positions, but cannot migrate from one position to another. Thus solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. Examples of solids: All metals, wood, etc.
- #11: Explanation of a liquid on the basis of kinetic model On the basis of the kinetic theory of matter we can say that kinetic energy of the molecules of a liquid is very large, and so is the distance between the molecules. Thus, the attractive force of the molecules is small as compared to solids. Therefore, the molecules of a liquid are free to move about within the liquid and hence, the liquid can easily take the shape of the containing vessel. However the volume of the liquid does not change, because the molecules do not leave the liquid. Ex: Water, alcohol, benzene, etc.
- #12: The next topic we are going to discuss is a gas, A gas is a state of matter, which has definite mass, but no definite shape and no definite volume. Properties of Gas A gas contained in a vessel has a definite mass. A gas can occupy the entire space of a given vessel in which it is enclosed. Intermolecular spaces are very, very large as compared to solids and liquids. It is due to this reason that gases are highly compressible. Gases have no free surface and they diffuse in one another to form a homogeneous mixture. There are no intermolecular forces, they expand to a large extent when heated and contract to a large extent when cooled. The density of gases is extremely small as compared to solids and liquids.
- #13: The intermolecular distance between the molecules of a gas are very large with the result that the force of attraction between the molecules is negligible. The molecules have a very large kinetic energy. Thus, the molecules can move in any direction and hence can fill any space. Thus, the gases have no definite shape and no definite volume and are highly compressible. Ex: Oxygen, Nitrogen, hydrogen, etc.
- #19: A change that alters some specific Property of matter without any change in the composition of its molecules, is called a physical change. Examples Melting of ice Formation of iron Magnetisation of iron Etc Total mass does not change in both chemical and physical changes
- #20: A change which alters the specific properties of a substance by bringing about a change in its molecular composition, followed by a change of state, is called a chemical change. Examples Cooking food Formation of curd from milk Rusting of iron etc