maxillary first molar
- 1. ???????? ???????? ???? ????? Maxillary molars Dr:3mmar
- 3. General Features: 1.Twelve in number. 2.Largest and strongest teeth. 3.Have no deciduous predeccesors. 4.Lower 1st molars are formed from 5 lobes. 5.Second and some third molars may have only 4 lobes.
- 4. 6.The 1st molar is the most developed molar. 7.The 3rd molar exhibits the most variable morphology. 8.Molars are multirooted teeth (2-3 roots(. 9.Used in griding food. 10.They support and maintain the vertical dimension of the face.
- 5. 11.They have wide occlusal surface. 12.They are the most posteriorly situated teeth in the mouth (distal to the 2nd premolar(. 13.They are multicuspid teeth. 14.Cervical margin is much less curved than in the anterior teeth.
- 7. ?Enamel organ appearance. ?Beginning of calcification. ?Crown completed. ?Eruption. ?Root completed. Chronology:
- 8. Chronology Appearance of dental organ 4 m.I.U. First evidence of calcification at birth Enamel completed 3-4 years Eruption 6-7 years Root completed 9-10 years
- 9. No. of surfaces: It has five surfaces No. of roots: It has 3 roots BUCCAL PALATAL MESIAL DISTAL OCCLUSAL
- 10. BUCCAL ASPECT The geometric outline: Trapezoidal with small uneven side present cervically DMesial outline: Nearly straight till the contact area at the junction of the occlusal and middle 1/3 Distal outline: Convex till the contact area at the middle of middle 1/3 M
- 11. D M Occlusal outline: Mesio-buccal cusp is broader, shorter and less sharp than disto-buccal cusp (D.B cusp is narrower , longer , sharper) Cervical outline: Irregular and slightly convex toward the root
- 12. D M Anatomical landmarks: * Convex buccal surface. *Buccal groove may terminate at middle third by fault buccal pit or by 2 shallow grooves *Cervical ridge.
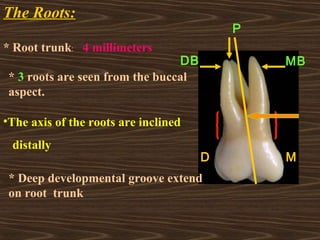
- 13. The Roots: * Root trunk: 4 millimeters * 3 roots are seen from the buccal aspect. P DB MB ?The axis of the roots are inclined distally D M * Deep developmental groove extend on root trunk
- 14. MBR: incline distally DBR: incline mesially Palatal root : incline buccally The longest root is palatal root and the shortest roor is distobuccal root
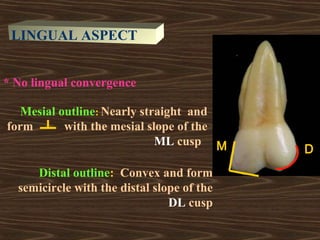
- 15. * No lingual convergence Mesial outline: Nearly straight and form with the mesial slope of the ML cusp Distal outline: Convex and form semicircle with the distal slope of the DL cusp DM LINGUAL ASPECT
- 16. Occlusal outline: ML cusp is the largest and longest cusp , its MD width about three fifth of MD crown diameter. DL cusp is spheroidal Cervical outline: Irregular and slightly convex toward the root DM
- 17. Anatomical landmarks: *Convex lingual surface. *Cusp of carabelli in 60 % of the lingual surface of ML cusp, Its cusp ridges is 2mm cervical to ML cusp *Lingual developmental groove. DM
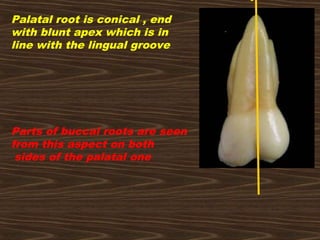
- 18. Palatal root is conical , end with blunt apex which is in line with the lingual groove Parts of buccal roots are seen from this aspect on both sides of the palatal one
- 19. LB The geometric outline: Trapezoidal with small uneven side occlusally Buccal outline: * Convex at cervical 1/3 denoting CR *Concave at the middle 1/3 denoting the termination of buccal developmental groove ?Slightly convex at the occlusal 1/3 representing MB cusp N.B: the great B.L dimension is evident as in all upper molars MESIAL ASPECT
- 20. LB Lingual outline: * Convex with the crest of curvature at the middle 1/3. * The lingual outline dips inward to illustrate the tubercle.
- 21. Occlusal outline: * Represented by ML , MB cusps * Irregular MMR which curve cervically. Cervical outline: Irregular and convex occlusally
- 22. Anatomical landmarks shape: smooth , almost flat elevations: MCA at the junction Of middle and occlusal 1/3 ,buccal to the center. Deppressions: shallow concavity usually present cervical to MCA and extend on the root.
- 23. The roots(MB root , palatal root only seen(. MB root: *broad , flat. *its width at bifurcation area nearly equal 2/3of crown mesurment B.L. *its buccal outline extend upward , outward& .its lingual outline is relatively straight Palatal root: *its longer , narrower than MB root & its banana-shaped. *has blunt apex. DBroot: hidden.
- 25. *Distal Convergence *Convex distal surface except small concave area at c 1/3 *Distal MR curved cervically * Wider mesial surface * Flat mesial surface * Mesial marginal ridge less curved DISTAL ASPECT MESIAL ASPECT Continue
- 26. *Straight cervical line *Root trunk= 5mm *3 roots are seen *Cervical line convex occlusally *Root trunk = 3mm *2 roots are seen DB MBP P DISTAL ASPECT MESIAL ASPECT
- 27. The geometric outline: Rhomboidal MD B L Note: * Disto-buccal convergence. * ML, BD angles are obtuse. *MB, DL angles are acute. Note: the crown is wider lingualy ,mesialy OCCLUSAL ASPECT
- 28. MD B L Anatomical landmarks: Elevations: *Oblique ridge between ML,DB triangular ridge *4 cusps with 4 triangular ridges and tubercle *MMR and DMR
- 29. MD B L Anatomical landmarks: Depression: *2major fossae ( central and distal( *2Minor fossae ( mesial and distal triangular fossae( *Developmental grooves (Buccal DG , Central DG ,Transverse G of oblique ridge, Distal oblique groove , Lingual groove , fifth cusp groove)
- 32. Note: The maxillary 1st molar is the only molar that is wider lingually than buccally.
- 33. The mesiolingual cusp is the largest cusp, followed by the rounded mesiobuccal, the sharp distobuccal, the small distolingual, and the tubercle of Carabelli.
- 34. -The pulp chamber is broader Bucco-lingually than mesio- distally. - The floor is apical to the cervical line. -There is pulp horn beneath each cusp ?Pulp Chamber: ?Pulp cavity
- 35. ?Root Canals: -3 main root canals. -MB root may have 2 root canals ?Pulp cavity Note: Cervical cross section: Rhomboidal Mid root section: MB root canal ( Oval- Kidney) DB root canal (Round-Oval) P root canal ( Round- Oval)
- 36. Enumerate the names of the following elevations and depression? 1-DMR 2-Oblique ridge 3-Distal linear fossa 4-Central fossa 5-Buccal groove 6-Mesial triangular fossa 7-Lingual groove D M L B
- 38. THANK YOU