Me1
- 1. Syllabus Design: Process/product syllabi, synthetic/analytic syllabi, type A/type B syllabi Professor: Dr. Bijani Student: Mansooreh Alavi alavi.m64@gmail.com http://ztefl.mihanblog.com/
- 2. Introduction ÔÇó Difference between Syllabus and Curriculum According to Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics, curriculum is an overall plan for a course or program, as in the freshman composition curriculum. A syllabus is more specific and more concrete than a curriculum and a curriculum may contain a number of syllabi; For example, a curriculum may cover an entire school year, while a language teaching syllabus may make up only one part of the curriculum.
- 3. Definitions of Syllabus Widdowson (1990, p. 127) interprets a syllabus as ÔÇ£the specification of a teaching program or pedagogic agenda which defines a particular subject for a particular group of learners . . . a syllabus specification, then, is concerned with both the selection and the ordering of what is to be taughtÔÇØ. Wilkins (1981) pointed out: "syllabuses are specification of the content of language teaching which have been submitted to some degree of structuring or ordering with the aim of making teaching and learning a more effective process".
- 4. Definitions of Syllabus Nunan (1988) believes that curriculum is wider term as compared with syllabus. Curriculum covers all the activities and arrangements made by the institution throughout the academic year to facilitate the learners and the instructors whereas syllabus is limited to particular subject of a particular class. Yalden (1987, p. 87) also refers to syllabus as a "summary of the content to which learners will be exposed".
- 5. Syllabus types Different approaches to syllabus design are categorized into two main types: ÔùÅ Product-oriented versus process-oriented syllabuses ÔùÅ Analytic versus synthetic syllabuses ÔùÅType A versus Type B syllabuses
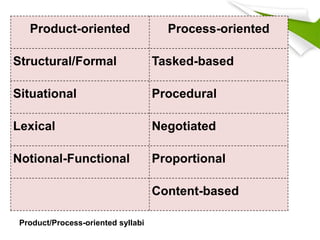
- 6. Product-oriented versus process-oriented syllabuses Product-oriented syllabusi : ÔùÅemphasize the product of language learning ÔùÅdifferent parts of language are taught separately ÔùÅacquisition is a process of gradual accumulation of parts ÔùÅlearner is being exposed to a deliberately limited sample of language (Wilkins, 1976).
- 7. Product-oriented versus process-oriented syllabuses According to Rabbini (2002), Product-oriented syllabuses ), focus on what the learners will know as a result at the end of instruction session. Nunan (1988) explains that product-oriented syllabuses are those in which the focus is on the knowledge and skills which learners should gain as a result of instruction (the product or the end). The grammatical, lexical, situational and notional-functional are the examples of product-oriented syllabus.
- 8. Product-oriented versus process-oriented syllabuses process-oriented syllabi operate in terms of the purposes for which people are learning language and the kinds of language performance that are necessary to meet those purposes (Wilkins, 1976, p. 13). These syllabuses, according to Rabbini (2002) developed as a result of a sense of failure in product-oriented courses to enhance communicative language skills. It is a process rather than a product.
- 9. Product-oriented versus process-oriented syllabuses That is, focus is not on what the student will have accomplished on completion of the program, but on the specification of learning tasks and activities that s/he will undertake during the course. Procedural, process and task syllabuses are examples of analytic, process-oriented syllabuses.
- 10. Product-oriented Process-oriented Structural/Formal Tasked-based Situational Procedural Lexical Negotiated Notional-Functional Proportional Content-based Product/Process-oriented syllabi
- 11. Analytic versus synthetic syllabus Wilkins (1976) separates language syllabi into synthetic and analytical types of syllabi. Synthetic syllabuses: ÔùÅ segment the target language into discrete linguistic items ÔùÅ Different parts of language are taught separately ÔùÅ The learnersÔÇÖ job is to synthesize the language ÔùÅ Structural, lexical, notional and functional, and most situational and topical syllabuses are all synthetic (Long and Crookes, 1992, 1993; Long and Robinson, 1998).
- 12. Analytic versus synthetic syllabus Synthetic syllabuses, also called "focus on forms" in Long and Robinson (1998), however, have been criticized for major problems, which include: (a) Absence of needs analysis; (b) Linguistic grading; (c) Lack of support from language learning theory; (d) Ignorance of learners' role in language development; (e) Tendency to produce boring lessons, despite the best efforts of highly skilled teachers and textbook writers; and (f) Production of many more false beginners than finishers (see Long and Robinson 1998 for more detail).
- 13. Analytic versus synthetic syllabus The second fundamental type of syllabus distinguished by Wilkins is the analytic. The analytical syllabus is a semantic, meaning-based syllabus, which aims at developing the learners communicative competence. In analytic syllabuses, the Analytic approaches are organized in terms of the purposes for which people  are learning language and the kinds of language performance that are necessary to meet those purposes (Wilkins, 1976:13). Analytic syllabuses focus on the learner and his needs and on the kinds of linguistic performance necessary to achieve those goals (Wilkins, 1976:13-14).
- 14. Analytic versus synthetic syllabus Here a chunk of language is presented to the learner in the context of a meaning oriented lesson. AnalyticÔǃ refers not to what the syllabus designer does, but to the operations required of the learner to recognize and analyze the linguistic components of the language chunks presented. Long and Crookes (1993: 11) update Wilkins definition, points out that ÔÇ£analytic syllabuses are those that present the target language whole chunks at a time, in molar rather than molecular units, without linguistic interference or control.
- 15. Analytic versus synthetic syllabus Procedural, process, and task syllabuses are examples of the analytic syllabus type. Some types of analytic syllabuses, also called "focus on meaning" in Long and Robinson (1998), have been criticized for, for example, Lack of needs analysis, Lack of accuracy attained, unlearn ability of some grammatical features from positive evidence only, And deprivation of the opportunity to speed up the rate of learning.
- 16. Analytic syllabuses Synthetic syllabuses Tasked-based Structural Procedural Situational Notional-functional [According to Wilkins (1976)] Notional-functional [(According to Long & Crooks (1992)) Content-based Negotiated Analytic/Synthetic-oriented syllabi
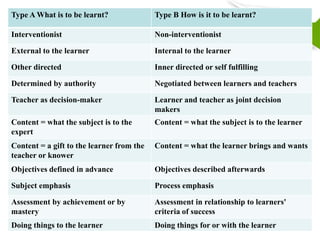
- 17. Type A versus Type B syllabuses A broader conceptualization of syllabus types can be found in White (1988), who presents the differences between syllabus types from the point of view of course design, methodology, language learning, and evaluation. According to White, Type A syllabi are concerned with what should be learned. Without considering who the learners may be or how languages are acquired, they determine a series of objectives and they ÔÇÿpre-packageÔÇÖ the language by dividing it into small, discrete units.
- 18. Type A versus Type B syllabuses They are externally imposed on the learner who has no say in them; the authoritative role is given to the teacher; they attach importance to the subject-matter of instruction; and they are product-oriented, so they evaluate the outcomes in terms of mastery of the language. All synthetic syllabi, regardless of whether they have grammar structures, notions and functions, or lexical items as their units, are considered Type A syllabi.
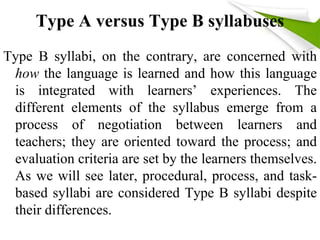
- 19. Type A versus Type B syllabuses Type B syllabi, on the contrary, are concerned with how the language is learned and how this language is integrated with learnersÔÇÖ experiences. The different elements of the syllabus emerge from a process of negotiation between learners and teachers; they are oriented toward the process; and evaluation criteria are set by the learners themselves. As we will see later, procedural, process, and task-based syllabi are considered Type B syllabi despite their differences.
- 20. Type A What is to be learnt? Type B How is it to be learnt? Interventionist Non-interventionist External to the learner Internal to the learner Other directed Inner directed or self fulfilling Determined by authority Negotiated between learners and teachers Learner and teacher as joint decision makers Teacher as decision-maker Content = what the subject is to the Content = what the subject is to the learner expert Content = a gift to the learner from the Content = what the learner brings and wants teacher or knower Objectives defined in advance Objectives described afterwards Subject emphasis Process emphasis Assessment by achievement or by mastery Doing things to the learner Doing things for or with the learner Assessment in relationship to learners' criteria of success
- 21. Conclusion A good and valid syllabus covers more or less all aspects of both these types, therefore, proper and appropriate implementation of syllabus in language teaching is expected. Without proper implementation of syllabus, on the one hand, desired objectives will be hard to obtain and on the other hand students will suffer from a lack of appropriate syllabus which could fulfill their immediate pedagogical requirements.
- 22. Thank You !!














![Analytic syllabuses Synthetic syllabuses
Tasked-based Structural
Procedural Situational
Notional-functional
[According to Wilkins
(1976)]
Notional-functional
[(According to Long &
Crooks (1992))
Content-based
Negotiated
Analytic/Synthetic-oriented syllabi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/me1-141206023523-conversion-gate02/85/Me1-16-320.jpg)