Measures of Variability
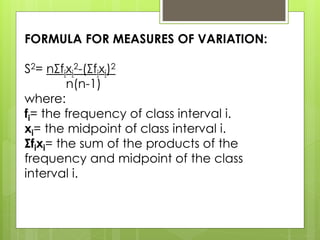
- 1. FORMULA FOR MEASURES OF VARIATION: S2= nÎĢfixi 2-(ÎĢfixi)2 n(n-1) where: fi= the frequency of class interval i. xi= the midpoint of class interval i. ÎĢfixi= the sum of the products of the frequency and midpoint of the class interval i.
- 2. THE QUARTILE DEVIATION: The quartile deviation is used when the median is used as an average; when the data depart noticeably from the normal. It is used for ordinal data. The quartile deviation, Q, is frequently called the semi-interquartile range. It is half of the distance between two quartile points, Q1, and Q3.
- 3. FORMULA FOR QUARTILE DEVIATION: Q= Q3-Q1 2 Q1= L1+ (n/4 âcf)c f Q3= L1+(3n/4 âcf)c f
- 4. EXAMPLE: Given the following data, Class interval f 36- 40 2 31- 35 8 26- 30 12 21- 25 18 16- 20 10
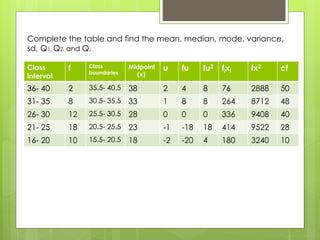
- 5. Complete the table and find the mean, median, mode, variance, sd, Q1, Q2, and Q. Class interval f Class boundaries Midpoint (x) u fu fu2 fixi fx2 cf 36- 40 2 35.5- 40.5 38 2 4 8 76 2888 50 31- 35 8 30.5- 35.5 33 1 8 8 264 8712 48 26- 30 12 25.5- 30.5 28 0 0 0 336 9408 40 21- 25 18 20.5- 25.5 23 -1 -18 18 414 9522 28 16- 20 10 15.5- 20.5 18 -2 -20 4 180 3240 10
- 6. MEAN= ÎĢfi Xi = 1270 = 25.4 n 50 MEDIAN= L1+ (n/2-cf)c = 20.5+ 50/2 -10 (5) = 24.67 f 18 MODE= L1+ (d1)c = 20.5+ _8_ (5)= 23.36 d1+d2 8+6 2-(ÎĢfixi)2 = 50(33770)-(1270) 2 n(n-1) 50(49) VARIANCE= nÎĢfixi = 1688500-1612900 2450 = 75600 = 30.86 2450
- 7. S= íí. íí QUARTILE DEVIATION Q1= L1+ (n/4 âcf)c = 20.5 + (50/4 â 10)5 f 18 = 20.5 + 0.69= 21.19 Q3= L1+(3n/4 âcf)c = 25.5 + (3/4 (50) â 28) 5 f 12 = 25.5 + 3. 96 = 29. 46 Q= Q3-Q1 = 29. 46- 21. 19 = 4. 135 2 2