Megaloblastic anaemia
- 1. Drugs in Megaloblastic Anemia Dr . Archana Dhavalshankh Prof & Head Department of Pharmacology
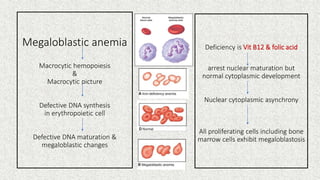
- 2. Megaloblastic anemia Macrocytic hemopoiesis & Macrocytic picture Defective DNA synthesis in erythropoietic cell Defective DNA maturation & megaloblastic changes Deficiency is Vit B12 & folic acid arrest nuclear maturation but normal cytoplasmic development Nuclear cytoplasmic asynchrony All proliferating cells including bone marrow cells exhibit megaloblastosis
- 3. Clinical Symptoms : - Changes in buccal mucosa (glossitis), tongue, diarrhea, cervix, vagina, uterus - Weakness, fatigue - Hyperpigmentation (mature neutrophils show pigmentation of their nuclei with the cell having six or more nuclear lobes.) Blood Picture : -Hypercellular bone marrow (cells show arrested development and die prematurely in bone marrow leading to hypercellular state ) - Hemolysis of immature cells - bilirubin level lactic dehydrogenase level - Low HB - RBCs large & oval (poikilocytosis & anisokilocytosis )
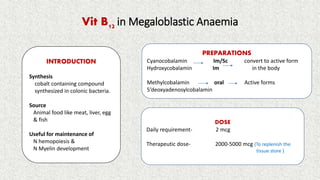
- 4. INTRODUCTION Synthesis cobalt containing compound synthesized in colonic bacteria. Source Animal food like meat, liver, egg & fish Useful for maintenance of N hemopoiesis & N Myelin development PREPARATIONS Cyanocobalamin Im/Sc convert to active form Hydroxycobalamin Im in the body Methylcobalamin oral Active forms 5ˇŻdeoxyadenosylcobalamin DOSE Daily requirement- 2 mcg Therapeutic dose- 2000-5000 mcg (To replenish the tissue store ) Vit B12 in Megaloblastic Anaemia
- 5. THERAPEUTIC USES PERNICIOUS ANAEMIA - Vit B 12 100 mcg daily x 1 week IM 100 mcg once a week x 1 mn 100 mcg monthly x life long MEGALOBLASTIC ANAEMIA - Vit B12 100- 500 mcg daily x 15 days IM 500-1000 mcg daily Oral Folic acid administration along with Vit B12 is important TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS NEUROPATHIES ALCOHOL &NICOTINE AMBLYOPIA PHARMACOKINETICS Absorption - Vit B 12 + Intrinsic factor Transport - Vit B12 + Transcobalamin II Storage - Liver Excretion - Bile Kinetic of elimination - Enterohepatic circulation Vit B12 in Megaloblastic Anaemia
- 6. INTRODUCTION Synthesis Complex of Glutamic acid + Paraminabenzoic acid + Pteridime nucleus Source Fresh green vegetables Liver, yeast, kidney, fruits Useful for maintenance of DNA synthesis PHRMACOKINETICS Polyglutamale cleavage to Monoglutamate TNFA Tetrahydrofolic acid Methylated in blood To tissues as methyl THFA - Stared in liver & Exhaust in 3-4 months - Manifestation appearance takes 3-4 months. Folic Acid in Megaloblastic Anaemia
- 7. DOSE Daily requirement- 50-100 mcg Therapeutic dose- 500-800 mcg THERAPEUTIC USES 1) Megaloblastic Anaemia: Folic acid oral 15 mg daily x 15 days 1 mg daily x life long With vit B12 2) Prophylactic use : In preganancy & Lactation 0.5 mg/day in first trimaster to avoid neural tube defects. 3) Methotrexate toxicity : Folinic acid given Folic Acid in Megaloblastic Anaemia
- 8. Erythropoietin Preparation: Recombinant Epoetin alpha Darbepoetin alpha (Twice t ? ) INTRODUCTION Major growth factor controlling erythropoiesis. It is glycosalated protein Produced by liver in fetus By kidney after birth (Peritubular interstitial cells of kidney) Produce in responses to hypoxia Hypoxia triggers production or blood O2 level affect production Pharmacokinetic Obtained from urine of patient with severe anaemia. Recombinant preparations preferred Given sc/IV route Peak serum levels - 5-10 hrs. T ? 4-13 hrs.
- 9. Erythropoietin THERAPEUTIC USES Correction of Anaemia 1. Chonic Renal failure sc/IV 50-100 U/Kg thrice/WK 2. Cancer related anaemia SC 150 U/Kg thrice/WK 3. Anaemia in AIDS Pt with Zidavudine therapy 100 U/Kg thrice/WK X 8 WKS 4. Surgery Preoperatively reduce need of blood transfusion 5. HIV infection Bone marrow disorders Aplastic anaemia Multiple mycloma Myelodysplasia ADR Hypertension Hb level Thromboembolism hemocrit level Iron deficlency functional disorders Allergic disarders Flu like symptoms.