Mendelian exceptions 11 3
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes332 views
Mendelian inheritance patterns can be more complex than simple dominant and recessive traits. There are several exceptions including incomplete dominance where a blending phenotype results from heterozygotes, codominance where both alleles are fully expressed simultaneously in heterozygotes producing a third phenotype, multiple alleles where more than two alleles exist for a single trait, and polygenic traits which are influenced by two or more interacting genes resulting in a continuous variation of phenotypes.
1 of 21
Downloaded 25 times



















Recommended
Types of Soil



Types of SoilAddy984715
╠²
There are four main types of soil: sandy soil, silt soil, clay soil, and loamy soil. Sandy soil has large particles that drain well but poor water retention. Clay soil has very small, tightly packed particles that retain water well but drain poorly. Silt soil has intermediate particle size, draining better than clay and retaining water better than sand. Loamy soil is a balanced combination of sand, silt and clay, making it highly fertile and suitable for agriculture.Cytogenetic techniques for gene location and transfer



Cytogenetic techniques for gene location and transferPratik Satasiya
╠²
This document discusses various cytogenetic techniques for gene location and transfer. It describes techniques for locating genes such as using structural and numerical chromosomal aberrations, chromosome banding, and in situ hybridization. Structural aberrations discussed include deficiencies, inversions, and translocations. Numerical aberrations discussed include aneuploids like trisomics, monosomics, and nullisomics. The document also describes techniques for transferring genes between species such as transferring whole genomes, whole chromosomes, chromosome arms, and through various types of interchanges. Specific examples of using these techniques in plants are provided.Location and mapping of chromosomes using conventional and cytological means.



Location and mapping of chromosomes using conventional and cytological means.Noor e Mujjassim
╠²
Different ways of mapping the genes using cytological tools, Difference between conventional and cytological mapping. Case studies.Sex determination sex linkage and multiple allels



Sex determination sex linkage and multiple allelsAlex Harley
╠²
1. The document discusses various mechanisms of sex determination, including chromosomal and environmental mechanisms. It covers examples like XX/XY system in humans and Drosophila.
2. Sex linkage and inheritance of sex-linked traits are described. Examples given include color blindness and hemophilia in humans.
3. The concepts of multiple alleles, pseudoalleles, and isoalleles are introduced. Examples of multiple alleles systems include ABO blood groups in humans and fur color in rabbits.Chiranjeev Patel



Chiranjeev PatelSardar Vallabhbhai Patel University of Agriculture and Technology Meerut 250110
╠²
This document summarizes Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants that established the fundamental laws of inheritance and genetics. It discusses:
- Mendel's experiments in the mid-19th century which established the laws of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. He found traits are controlled by discrete factors (now called genes) that are inherited independently.
- The three Mendelian laws: 1) dominance - dominant alleles mask recessive alleles, 2) segregation - alleles separate into gametes independently, 3) independent assortment - alleles of different traits assort independently during gamete formation.
- Types of gene interactions beyond Mendel's laws, including epistasis where oneInbred development



Inbred developmentMuhammad Jahanzaib
╠²
This presentation discusses inbred development and its evaluation. Inbreeding is the mating of related individuals, which can result in changes to trait means. The objectives are to develop inbred lines with good seed performance, stress resistance, and adaptation. Various terms related to inbreeding are defined, such as inbreeding depression, avoidance, and purging. Inbred strains are nearly identical genotypes useful for reproducible experiments. Evaluation of inbred lines considers genetic variation, adaptation, and yield built into the population under selection.Association mapping



Association mappingSenthil Natesan
╠²
1. Association mapping uses linkage disequilibrium in natural populations to identify markers closely linked to genes influencing traits, allowing for higher resolution than traditional linkage mapping.
2. Key factors for successful association mapping include choosing diverse germplasm with extensive recombination history, collecting high-quality phenotypic data across environments, genotyping candidate genes and markers, and using statistical methods to account for population structure.
3. Combining association mapping with traditional QTL mapping and the various available software tools allows for rapid dissection and evaluation of complex traits.What is chemistry



What is chemistryJamyeJ
╠²
Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. There are five main branches of chemistry: organic, inorganic, physical, analytical, and biochemistry. The scientific method is used to solve problems through observation, hypothesis, experimentation, and theory development. There are two types of research: basic research seeks knowledge, while applied research attempts to solve problems. Matter can be classified as pure substances or mixtures depending on its uniformity of composition.Enzymes



EnzymesJamyeJ
╠²
The document provides information about enzymes and chemical reactions:
1. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur. They speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
2. Examples of enzymes that break down carbohydrates are amylase in saliva and sucrase. Nuclease is an enzyme that cuts DNA strands by binding to DNA at its active site.
3. Enzymes achieve a large increase in reaction rate and a decrease in reaction time by reducing the activation energy needed for reactions to start. They are highly specific and only work with their intended substrate.ņ×Éņłśņä▒Ļ░ĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņ×ÉļōżņØś ļģĖĒĢśņÜ░ļź╝ Ēøöņ│ÉļØ╝Ver3_20101130



ņ×Éņłśņä▒Ļ░ĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņ×ÉļōżņØś ļģĖĒĢśņÜ░ļź╝ Ēøöņ│ÉļØ╝Ver3_20101130sunny seo
╠²
Moneytraining 3ĻĖ░-1ņŻ╝ņ░©CGC OME Presentation



CGC OME Presentationadonissidh
╠²
CGC Constructions (India) Pvt. Ltd. is a construction and telecommunications services company that is part of a larger group based in the United States. It aims to provide turnkey solutions to telecom service providers. The company has operations in India, the United States, Hong Kong, Dubai, China, and South America. It offers various telecom infrastructure services including project management, civil and electrical works, fiber optic cable installation, call center services, site acquisition, equipment installation and commissioning.Study guide genetics



Study guide geneticsfearonc
╠²
This document provides definitions and explanations of key genetics terms:
- A human baby with two X chromosomes is female, while one with an XY chromosome is male.
- Gregor Mendel is known as the father of genetics. He was an Austrian monk.
- Incomplete dominance in genetics is exemplified by variations in coat color seen in purebred dogs.
- A Punnett square uses capital letters to represent dominant alleles and predicts possible genotypes of offspring.Study guide genetics



Study guide geneticsmomoisawesome
╠²
The document provides definitions and examples for several key genetics terms:
- A human baby's sex is determined by its chromosome makeup - XX for female and XY for male.
- Gregor Mendel is considered the father of genetics. He was an Austrian monk who studied inheritance patterns in pea plants.
- Incomplete dominance is exemplified by variations in coat color seen in purebred dogs and horses.
- A Punnett square uses capital letters to represent dominant alleles and predicts possible genotypes of offspring.
- Polygenic inheritance involves more than two alleles controlling a trait, like eye and skin color in humans.Exception To Mendelism



Exception To MendelismJyotirmoyDas31
╠²
This document discusses exceptions to Mendel's laws of inheritance. It begins by outlining Mendel's original laws and concepts of genes and inheritance. It then notes that not all traits follow Mendel's predictions. There are two types of exceptions: 1) where genotypic ratios follow Mendel but phenotypes do not, and 2) where both genotypes and phenotypes deviate. Specific exceptions covered include incomplete dominance, codominance, polygenic inheritance, multiple alleles, lethal genes, and sex-linked inheritance. Real-world examples are provided for each exception.Genetics Powerpoint.pptx



Genetics Powerpoint.pptxFolusoOyolola
╠²
Genetics is the study of heredity and genes. Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in the 1800s that formed the basis of genetics. Through his work, he discovered the principles of inheritance, including that traits are determined by units now called genes, genes occur in different forms called alleles, dominant alleles mask recessive alleles, and alleles assort independently during gamete formation. Mendel's principles can be used to predict the results of genetic crosses and the inheritance of traits.Genetics and Inheritance



Genetics and InheritanceReginald V. Finley Sr. M.Ed.
╠²
This presentation is all about genetics and inheritance. Grades 6-12. Biology 1. Original Author - Megan Jandy3.4 Notes



3.4 NotesJacob Cedarbaum
╠²
Guided notes covering material from Topic 3.4 of the updated IB Biology syllabus for 2016 exams. Notes sequence and prompts are based on the Oxford IB Biology textbook by Allott and Mindorff.Codominance



CodominanceRAJENDRACHAVHAN2
╠²
Examples of Codominance. The best example, in this case, is the codominance blood type. ABO group is considered to be a codominant blood group where both fatherŌĆÖs and motherŌĆÖs blood group is expressed. It means that the properties of the blood groups exist in the ABO type.
Codominance is a relationship between two versions of a gene. Individuals receive one version of a gene, called an allele, from each parent. If the alleles are different, the dominant allele usually will be expressed, while the effect of the other allele, called recessive, is masked.Heredity: Passing on Traits Offspring ue



Heredity: Passing on Traits Offspring uejianvinmer
╠²
Heredity is the biological process through which genetic traits are passed from parents to their offspring. This process is facilitated by the transmission of DNA, the molecule that carries genetic information. Each organism inherits a unique combination of genes from its parents, which determines a wide range of characteristics, such as physical appearance, behavior, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Genes are segments of DNA located on chromosomes, and they function as instructions for building and maintaining an organism. The study of heredity and genetic variation is known as genetics, a field that has greatly advanced our understanding of how traits are inherited and how genetic disorders arise.
Heredity is the biological process through which genetic traits are passed from parents to their offspring. This process is facilitated by the transmission of DNA, the molecule that carries genetic information. Each organism inherits a unique combination of genes from its parents, which determines a wide range of characteristics, such as physical appearance, behavior, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Genes are segments of DNA located on chromosomes, and they function as instructions for building and maintaining an organism. The study of heredity and genetic variation is known as genetics, a field that has greatly advanced our understanding of how traits are inherited and how genetic disorders arise.
Biology chapter 6 & 7



Biology chapter 6 & 7Lisa Stack
╠²
Meiosis produces gametes with half the normal number of chromosomes. It involves two cell divisions which results in four haploid cells from one diploid cell. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and may exchange genetic material through crossing over. This introduces genetic variation. Mendel's experiments with pea plants established basic principles of heredity including dominant/recessive traits and independent assortment of traits. Genes located on chromosomes code for traits and exist in different alleles that are inherited according to Mendelian genetics.Chapter 5- Heredity



Chapter 5- HereditySteven_iannuccilli
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts about heredity and genetics covered in Chapter 5, including:
1) Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring through alleles contained in DNA. Gregor Mendel studied heredity through pea plant experiments.
2) Mendel discovered dominant and recessive traits and that recessive traits can reappear through cross-breeding.
3) Punnett squares are used to determine the probability of traits being passed down based on parental genotypes.
4) Other concepts covered include incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, polygenic inheritance, mutations, sex determination, and genetic engineering techniques.Mendel And The Gene Idea



Mendel And The Gene IdeaCrystal Wood
╠²
Gregor Mendel conducted breeding experiments with pea plants in the 1850s and discovered the laws of inheritance. Through his accurate record keeping and large sample sizes, he found that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units called genes. Mendel also discovered that for each trait, there are two versions of each gene, called alleles, with one allele being dominant and the other recessive. Through his experiments, he developed the laws of segregation and independent assortment, which describe how alleles separate and assort during the formation of gametes. Mendel's discoveries formed the foundation of classical genetics.Mendel 2 revised



Mendel 2 revisedMaria Donohue
╠²
This document discusses Gregor Mendel's principles of inheritance and genetics. It covers Mendel's laws of segregation, dominance, and independent assortment. It also discusses exceptions to Mendelian genetics like incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits, epistasis, and gene linkage. Thomas Hunt Morgan's work with fruit flies provided evidence that genes are located on chromosomes, not assorting independently as Mendel believed, but rather assorting as linked genes on the same chromosome. Gene mapping using recombination rates helped establish the chromosomal theory of inheritance.Classical Genetics



Classical Geneticscgales
╠²
The document summarizes Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants in the 1860s, which laid the foundations for genetics. Mendel studied inheritance patterns of traits in peas and discovered that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes). His work resulted in three main conclusions: 1) traits may be dominant or recessive, 2) alleles segregate and are transmitted independently of one another, and 3) the inheritance of one trait does not influence that of another. Mendel's findings were the start of genetics as a science.Genetic Crosses



Genetic Crossesbarshingert
╠²
This document discusses several genetics concepts including incomplete dominance, codominance, sex-linked traits, polygenic traits, multiple alleles, and blood types. It provides examples and explanations of each concept as well as example genetics problems related to traits in cats and humans.Animal Kingdom



Animal Kingdombarshingert
╠²
The document discusses different genetic concepts including incomplete dominance, codominance, sex-linked traits, polygenic traits, multiple alleles, and blood types. It provides examples and explanations of each concept as well as example genetic crosses and scenarios to illustrate the concepts.Genetic Crosses



Genetic Crossesbarshingert
╠²
The document discusses different genetic concepts including incomplete dominance, codominance, sex-linked traits, polygenic traits, multiple alleles, and blood types. It provides examples and explanations of each concept as well as example genetic crosses and scenarios to illustrate the concepts.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (6)
What is chemistry



What is chemistryJamyeJ
╠²
Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. There are five main branches of chemistry: organic, inorganic, physical, analytical, and biochemistry. The scientific method is used to solve problems through observation, hypothesis, experimentation, and theory development. There are two types of research: basic research seeks knowledge, while applied research attempts to solve problems. Matter can be classified as pure substances or mixtures depending on its uniformity of composition.Enzymes



EnzymesJamyeJ
╠²
The document provides information about enzymes and chemical reactions:
1. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur. They speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
2. Examples of enzymes that break down carbohydrates are amylase in saliva and sucrase. Nuclease is an enzyme that cuts DNA strands by binding to DNA at its active site.
3. Enzymes achieve a large increase in reaction rate and a decrease in reaction time by reducing the activation energy needed for reactions to start. They are highly specific and only work with their intended substrate.ņ×Éņłśņä▒Ļ░ĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņ×ÉļōżņØś ļģĖĒĢśņÜ░ļź╝ Ēøöņ│ÉļØ╝Ver3_20101130



ņ×Éņłśņä▒Ļ░ĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņ×ÉļōżņØś ļģĖĒĢśņÜ░ļź╝ Ēøöņ│ÉļØ╝Ver3_20101130sunny seo
╠²
Moneytraining 3ĻĖ░-1ņŻ╝ņ░©CGC OME Presentation



CGC OME Presentationadonissidh
╠²
CGC Constructions (India) Pvt. Ltd. is a construction and telecommunications services company that is part of a larger group based in the United States. It aims to provide turnkey solutions to telecom service providers. The company has operations in India, the United States, Hong Kong, Dubai, China, and South America. It offers various telecom infrastructure services including project management, civil and electrical works, fiber optic cable installation, call center services, site acquisition, equipment installation and commissioning.Similar to Mendelian exceptions 11 3 (20)
Study guide genetics



Study guide geneticsfearonc
╠²
This document provides definitions and explanations of key genetics terms:
- A human baby with two X chromosomes is female, while one with an XY chromosome is male.
- Gregor Mendel is known as the father of genetics. He was an Austrian monk.
- Incomplete dominance in genetics is exemplified by variations in coat color seen in purebred dogs.
- A Punnett square uses capital letters to represent dominant alleles and predicts possible genotypes of offspring.Study guide genetics



Study guide geneticsmomoisawesome
╠²
The document provides definitions and examples for several key genetics terms:
- A human baby's sex is determined by its chromosome makeup - XX for female and XY for male.
- Gregor Mendel is considered the father of genetics. He was an Austrian monk who studied inheritance patterns in pea plants.
- Incomplete dominance is exemplified by variations in coat color seen in purebred dogs and horses.
- A Punnett square uses capital letters to represent dominant alleles and predicts possible genotypes of offspring.
- Polygenic inheritance involves more than two alleles controlling a trait, like eye and skin color in humans.Exception To Mendelism



Exception To MendelismJyotirmoyDas31
╠²
This document discusses exceptions to Mendel's laws of inheritance. It begins by outlining Mendel's original laws and concepts of genes and inheritance. It then notes that not all traits follow Mendel's predictions. There are two types of exceptions: 1) where genotypic ratios follow Mendel but phenotypes do not, and 2) where both genotypes and phenotypes deviate. Specific exceptions covered include incomplete dominance, codominance, polygenic inheritance, multiple alleles, lethal genes, and sex-linked inheritance. Real-world examples are provided for each exception.Genetics Powerpoint.pptx



Genetics Powerpoint.pptxFolusoOyolola
╠²
Genetics is the study of heredity and genes. Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in the 1800s that formed the basis of genetics. Through his work, he discovered the principles of inheritance, including that traits are determined by units now called genes, genes occur in different forms called alleles, dominant alleles mask recessive alleles, and alleles assort independently during gamete formation. Mendel's principles can be used to predict the results of genetic crosses and the inheritance of traits.Genetics and Inheritance



Genetics and InheritanceReginald V. Finley Sr. M.Ed.
╠²
This presentation is all about genetics and inheritance. Grades 6-12. Biology 1. Original Author - Megan Jandy3.4 Notes



3.4 NotesJacob Cedarbaum
╠²
Guided notes covering material from Topic 3.4 of the updated IB Biology syllabus for 2016 exams. Notes sequence and prompts are based on the Oxford IB Biology textbook by Allott and Mindorff.Codominance



CodominanceRAJENDRACHAVHAN2
╠²
Examples of Codominance. The best example, in this case, is the codominance blood type. ABO group is considered to be a codominant blood group where both fatherŌĆÖs and motherŌĆÖs blood group is expressed. It means that the properties of the blood groups exist in the ABO type.
Codominance is a relationship between two versions of a gene. Individuals receive one version of a gene, called an allele, from each parent. If the alleles are different, the dominant allele usually will be expressed, while the effect of the other allele, called recessive, is masked.Heredity: Passing on Traits Offspring ue



Heredity: Passing on Traits Offspring uejianvinmer
╠²
Heredity is the biological process through which genetic traits are passed from parents to their offspring. This process is facilitated by the transmission of DNA, the molecule that carries genetic information. Each organism inherits a unique combination of genes from its parents, which determines a wide range of characteristics, such as physical appearance, behavior, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Genes are segments of DNA located on chromosomes, and they function as instructions for building and maintaining an organism. The study of heredity and genetic variation is known as genetics, a field that has greatly advanced our understanding of how traits are inherited and how genetic disorders arise.
Heredity is the biological process through which genetic traits are passed from parents to their offspring. This process is facilitated by the transmission of DNA, the molecule that carries genetic information. Each organism inherits a unique combination of genes from its parents, which determines a wide range of characteristics, such as physical appearance, behavior, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Genes are segments of DNA located on chromosomes, and they function as instructions for building and maintaining an organism. The study of heredity and genetic variation is known as genetics, a field that has greatly advanced our understanding of how traits are inherited and how genetic disorders arise.
Biology chapter 6 & 7



Biology chapter 6 & 7Lisa Stack
╠²
Meiosis produces gametes with half the normal number of chromosomes. It involves two cell divisions which results in four haploid cells from one diploid cell. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and may exchange genetic material through crossing over. This introduces genetic variation. Mendel's experiments with pea plants established basic principles of heredity including dominant/recessive traits and independent assortment of traits. Genes located on chromosomes code for traits and exist in different alleles that are inherited according to Mendelian genetics.Chapter 5- Heredity



Chapter 5- HereditySteven_iannuccilli
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts about heredity and genetics covered in Chapter 5, including:
1) Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring through alleles contained in DNA. Gregor Mendel studied heredity through pea plant experiments.
2) Mendel discovered dominant and recessive traits and that recessive traits can reappear through cross-breeding.
3) Punnett squares are used to determine the probability of traits being passed down based on parental genotypes.
4) Other concepts covered include incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, polygenic inheritance, mutations, sex determination, and genetic engineering techniques.Mendel And The Gene Idea



Mendel And The Gene IdeaCrystal Wood
╠²
Gregor Mendel conducted breeding experiments with pea plants in the 1850s and discovered the laws of inheritance. Through his accurate record keeping and large sample sizes, he found that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units called genes. Mendel also discovered that for each trait, there are two versions of each gene, called alleles, with one allele being dominant and the other recessive. Through his experiments, he developed the laws of segregation and independent assortment, which describe how alleles separate and assort during the formation of gametes. Mendel's discoveries formed the foundation of classical genetics.Mendel 2 revised



Mendel 2 revisedMaria Donohue
╠²
This document discusses Gregor Mendel's principles of inheritance and genetics. It covers Mendel's laws of segregation, dominance, and independent assortment. It also discusses exceptions to Mendelian genetics like incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits, epistasis, and gene linkage. Thomas Hunt Morgan's work with fruit flies provided evidence that genes are located on chromosomes, not assorting independently as Mendel believed, but rather assorting as linked genes on the same chromosome. Gene mapping using recombination rates helped establish the chromosomal theory of inheritance.Classical Genetics



Classical Geneticscgales
╠²
The document summarizes Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants in the 1860s, which laid the foundations for genetics. Mendel studied inheritance patterns of traits in peas and discovered that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes). His work resulted in three main conclusions: 1) traits may be dominant or recessive, 2) alleles segregate and are transmitted independently of one another, and 3) the inheritance of one trait does not influence that of another. Mendel's findings were the start of genetics as a science.Genetic Crosses



Genetic Crossesbarshingert
╠²
This document discusses several genetics concepts including incomplete dominance, codominance, sex-linked traits, polygenic traits, multiple alleles, and blood types. It provides examples and explanations of each concept as well as example genetics problems related to traits in cats and humans.Animal Kingdom



Animal Kingdombarshingert
╠²
The document discusses different genetic concepts including incomplete dominance, codominance, sex-linked traits, polygenic traits, multiple alleles, and blood types. It provides examples and explanations of each concept as well as example genetic crosses and scenarios to illustrate the concepts.Genetic Crosses



Genetic Crossesbarshingert
╠²
The document discusses different genetic concepts including incomplete dominance, codominance, sex-linked traits, polygenic traits, multiple alleles, and blood types. It provides examples and explanations of each concept as well as example genetic crosses and scenarios to illustrate the concepts.Presentacion clase de ciencias 4_Non-Mendelian_Genetics.ppt



Presentacion clase de ciencias 4_Non-Mendelian_Genetics.pptPAOLAfRANCO89
╠²
Genetica mendeliana y no mendelianaPresentacion clase de ciencias 4_Non-Mendelian_Genetics.ppt



Presentacion clase de ciencias 4_Non-Mendelian_Genetics.pptPAOLAfRANCO89
╠²
Genetica mendeliana y no mendelianaMultiple allelism 



Multiple allelism Neha Mahor
╠²
This document discusses multiple allelism, which refers to more than two alternative allelic forms of a gene occupying the same locus. It provides examples of multiple allelism in eye color in Drosophila, with 14 alleles producing different shades from white to red, and in human blood groups with the A, B, and O alleles. The characteristics of multiple alleles are described, including that only two alleles are present per individual. Multiple allelism in inheritance of blood groups and determining blood group combinations in offspring are also covered.Lesson 3 Modification to MendelŌĆÖs Classic Ratios.pptx



Lesson 3 Modification to MendelŌĆÖs Classic Ratios.pptxDeverlyArceo3
╠²
Modification to MendelŌĆÖs Classic RatiosRecently uploaded (12)
Bouncing Back_ How Strategic Investments Fuel Business Resurgence by Patrick ...



Bouncing Back_ How Strategic Investments Fuel Business Resurgence by Patrick ...Patrick Walsh CEO
╠²
As noted by Patrick Walsh CEO, in the fast-paced business world, itŌĆÖs not uncommon for companies to face sudden setbacks that threaten their survival. Whether caused by economic downturns, poor management decisions, or industry shifts, the path to recovery is often long and challenging. However, for savvy investors, these periods of struggle can present incredible opportunities. The key lies in recognizing which businesses have the potential for a successful resurgence and being ready to support them through recovery.Tran Quoc Bao of City International Hospital Promotes Vietnam as Southeast As...



Tran Quoc Bao of City International Hospital Promotes Vietnam as Southeast As...Ignite Capital
╠²
Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, Chief Planning and Marketing Officer of City International Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City, is spearheading efforts to position Vietnam as a leading medical tourism destination in Southeast Asia. Speaking at the Southeast Asia Hospital Expansion Summit 2019 in Bangkok, Bao highlighted VietnamŌĆÖs rapid growth in healthcare and wellness, emphasizing its increasing appeal to foreign patients seeking affordable, high-quality medical services. With the countryŌĆÖs medical sector expanding by 18-20% annually and attracting over 80,000 international patients, Vietnam is on track to become a key player in the global medical tourism market.
Vietnam's strategic location in Southeast Asia, combined with its political stability, makes it an accessible and safe destination for medical travelers. According to Bao, the country's healthcare providers deliver world-class care at a fraction of the cost compared to neighboring countries, further boosting its potential as a healthcare hub. ŌĆ£There is enormous potential in VietnamŌĆÖs healthcare and medical tourism sectors,ŌĆØ Bao stated at the summit.
Despite the promising outlook, Bao acknowledged the challenges facing the sector, particularly the low level of awareness among foreign patients and the limited number of internationally-accredited hospitals in Vietnam. He proposed several initiatives to address these issues. Key among them is the creation of a nationwide campaign to raise awareness of VietnamŌĆÖs healthcare offerings, using digital platforms and social media to target medical tourists across the region. Additionally, he stressed the importance of Vietnamese hospitals earning international accreditation, such as Joint Commission International (JCI), to build trust and credibility.
Bao also recommended enhancing regional collaboration by sending Vietnamese healthcare representatives to participate in networking events and partnerships with associations in Southeast Asia. This approach would help spread awareness of VietnamŌĆÖs medical tourism potential and foster cross-border patient management systems to optimize healthcare exchanges within the region.
The Southeast Asia Hospital Expansion Summit provided a platform for investors and healthcare leaders to discuss opportunities in the growing medical tourism market, which sees millions of patients traveling across Southeast Asia each year. As a top-ranked international hospital in Vietnam, City International Hospital is at the forefront of this movement, positioning itself as a key institution in the country's healthcare expansion.
With Dr. BaoŌĆÖs leadership, City International Hospital continues to pave the way for Vietnam to become a recognized hub for high-quality, affordable healthcare and medical tourism in Southeast Asia and beyond.MTA - City International Hospital's Tran Quoc Bao Shares Insights on Pioneeri...



MTA - City International Hospital's Tran Quoc Bao Shares Insights on Pioneeri...Ignite Capital
╠²
City International Hospital (CIH) has become a leading player in global medical tourism, providing exceptional care to international patients. With over 11 years of experience, CIH specializes in over 20 medical fields, including stroke, cardiology, and surgery, and has earned global recognition. Honored with a Gold Membership from the Medical Tourism Association (MTA), CIH continues to expand its reach, attracting patients from across the globe.
Dr. Tran Quoc, Planning & Marketing Director, discusses the hospital's unique approach to patient care, its comprehensive services, and its vision for the future of medical travel. CIH emphasizes a holistic care model, personalized treatment, and advanced medical technology, fostering a nurturing environment for recovery. The hospital's commitment to excellence is reflected in its features across major global platforms such as Voice of America, U.S. News & World Report, Yahoo, and Hospital Insights. Reimagining Colorado's Future_ The Evolution of Urban Development.pdf



Reimagining Colorado's Future_ The Evolution of Urban Development.pdfRoger Chivukula
╠²
Roger Chivukula is a real estate investor, philanthropist and family man . He is based in Colorado and specializes in property investment and sustainable development. Roger is also passionate about community service and continues to make meaningful contributions through his professional ventures and philanthropic efforts.
Roger Chivukula, was born in New York on July 1, 1974. Roger's early passion for sports, particularly lacrosse, played a significant role in his early years. Lacrosse was a major part of Roger's life in college where, At Le Moyne University, Roger excelled in the classroom and field, earning a degree while becoming a letter-winning Men's Lacrosse team member.
After graduating from La Moyne he soon moved to Colorado to enjoy the great outdoors. He spent a season teaching skiing at Breckenridge and quickly realized Colorado is where he wanted to plant his roots. Roger Chivukula shifted his focus to real estate investing, where he found both challenge and reward. Roger's real estate portfolio includes various properties, from residential developments to commercial ventures.
Roger has focused on acquiring homes with potential for improvement. By investing in properties that need renovations, he has brought them back to life and offered affordable housing options in high-demand areas. His efforts have benefited investors and positively impacted the communities where his properties are located.
Additionally, Roger Chivukula is involved with commercial real estate, particularly office spaces and retail developments. His understanding of market trends and his ability to anticipate shifts in demand have allowed him to make informed decisions that lead to profitable ventures. Whether acquiring undervalued properties or investing in new construction, Roger has shown an impressive ability to see opportunities where others may not.
Real estate development has also been a significant aspect of Roger's career. He has handled projects that contribute to the growth and modernization of Colorado's urban areas. By working closely with contractors, architects, and local officials, Roger has helped shape the scenery of the communities where he operates, ensuring that new developments are profitable, sustainable, and in line with the community's needs.
daily planner for Stay at home moms and housewives.



daily planner for Stay at home moms and housewives.Nabah
╠²
daily planner for Stay at home moms and housewives.Sendero viviente en Autobiograf├Ła de un Iluminado RUSO.pdf



Sendero viviente en Autobiograf├Ła de un Iluminado RUSO.pdfRafael Reverte P├®rez
╠²
SENDERO VIVIENTE
Autobiograf├Ła de un Iluminado
AUTOR: AMERICO
ŌĆó Mi Retiro
ŌĆó La Se├▒al del Hijo del Hombre
ŌĆó Merkaba y La Era de Paz
- Se comenz├│ a transcribir en Abril 2002 (23 abril a 3 mayo alineaci├│n en conjunci├│n Saturno, J├║piter y Mercurio, Venus) -
DERECHOS RESERVADOS
M├®xico 2002
N├║m. de Registro 03-2003-022413471400-01
Revisado por el autor en 2017The Importance of Timely Invoice Processing in NDIS Plan Management.pdf



The Importance of Timely Invoice Processing in NDIS Plan Management.pdfLife Balance NDIS Plan Management
╠²
Timely invoice processing in NDIS plan management ensures smooth service delivery, keeps budgets on track, and reduces stress for participants. It helps avoid disruptions, supports service providers, and ensures compliance with NDIS guidelines, allowing participants to focus on their support needs.Ladies Latin Dance Shoes - Dance America



Ladies Latin Dance Shoes - Dance AmericaDance America
╠²
Looking for high-quality women's Ballroom & Latin dance shoes? Dance America stocks a wide selection of ladies' dance shoes. Order online today! Visit us: https://dance-america.com/collections/ladies-latin-shoesMust have menŌĆÖs accessories and Casual Wear



Must have menŌĆÖs accessories and Casual WearStylish Sequins
╠²
Men's shops in Shahabad began with a simple yet profound vision: to redefine the fashion industry by offering clothing that not only looks good but also feels good. We noticed a gap in the market where style often compromised comfort, and vice versa. Determined to bridge this divide, we set out to create a brand that marries the two seamlessly.15 Summer Gardening Tips to Keep Your Plants Green and Healthy



15 Summer Gardening Tips to Keep Your Plants Green and Healthycivil hospital parasia
╠²
Summer can be a challenging season for gardeners. Rising temperatures, intense sunlight, and dry conditions can stress plants, leading to wilting, poor growth, or even plant loss. However, with proper care, your garden can stay lush, green, and thriving all summer long.
In this guide, weŌĆÖll share 15 essential summer gardening tips to help you maintain moisture, protect plants from heat, and promote healthy growth during the hottest months of the year.VietnamŌĆÖs Growing Medical Tourism: Tran Quoc Bao at the Forefront



VietnamŌĆÖs Growing Medical Tourism: Tran Quoc Bao at the ForefrontIgnite Capital
╠²
Nikkei Asia - Vietnam is quickly becoming an emerging hub for medical tourism, with advanced treatments, cutting-edge technology, and affordable healthcare services attracting international patients. Dr. Tran Quoc Bao, Chief Commercial Officer at Cao Thang Eye Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City, plays a pivotal role in promoting VietnamŌĆÖs healthcare sector to the world. As a healthcare ambassador, he is helping elevate VietnamŌĆÖs medical tourism offerings, positioning the country as a prime destination for foreign patients seeking world-class care at a fraction of the cost.
VietnamŌĆÖs hospitals, equipped with state-of-the-art technology, are drawing both local and international patients, especially for high-tech treatments like organ transplants, cardiovascular interventions, and advanced eye surgeries. Notable hospitals, such as Cao Thang Eye Hospital, are becoming hotspots for medical tourism, thanks to the availability of cutting-edge equipment and advanced techniques, including the ReLex SMILE method for refractive eye surgery. This treatment, along with femtosecond laser techniques, has garnered international attention, attracting patients from Europe, the U.S., and Australia.
The affordability of medical treatments in Vietnam is another key factor fueling the growth of medical tourism. A LASIK treatment in Vietnam costs approximately $600 per eye, compared to $1,000-$3,000 in neighboring countries. Kidney transplants, for instance, are one-third the cost in Vietnam compared to Thailand or China. This affordability, coupled with high-quality care, has made Vietnam a go-to destination for patients seeking cost-effective solutions to complex medical procedures.
Dr. Bao emphasizes the potential of combining healthcare with tourism, noting that foreign patients are increasingly choosing Vietnam not just for medical treatment but also to explore the countryŌĆÖs rich cultural and natural landmarks. This growing trend of medical tourism is reflected in the countryŌĆÖs rising international patient numbers, as more hospitals work to create specialized services tailored to foreign patients.
The Vietnam National Tourism Administration has set its sights on boosting medical tourism further, following in the footsteps of countries like Thailand, South Korea, and Singapore. Hospitals like Cao Thang Eye Hospital are at the forefront, providing high-tech treatments while also promoting VietnamŌĆÖs vibrant tourism industry. With growing interest from international patients and advancements in medical technology, Vietnam is poised to become a significant player in the global medical tourism market.
Under Dr. Tran Quoc BaoŌĆÖs leadership, Cao Thang Eye Hospital continues to build VietnamŌĆÖs reputation as a trusted destination for medical travelers, offering both world-class healthcare and the chance to experience the beauty and culture of Vietnam.The Importance of Timely Invoice Processing in NDIS Plan Management.pdf



The Importance of Timely Invoice Processing in NDIS Plan Management.pdfLife Balance NDIS Plan Management
╠²
Mendelian exceptions 11 3
- 1. Mendelian Exceptions Chapter 11 Section 3
- 2. MendelŌĆÖs Principles Revisited Inheritance of biological _____________ is determined by individual units known as ______. During sexual reproduction, genes are passed from parents to _________. Two or more forms of the gene for a single _____ exist, some forms of the gene may be _________ and others may be recessive. characteristics offspring genes trait dominant
- 3. MendelŌĆÖs Principles Revisited Organisms typically have ____copies of each gene, (one from each _______) An organismŌĆÖs _____ of genes (2 alleles) are segregated from each other when ________ are formed. Alleles for different ______ usually segregate _____________ of one another. (through meiosis) (Law of Independent Assortment) independently parent two gametes genes pair
- 4. Independent Assortment in Peas __ Round yellow __ Round green __ Wrinkled yellow __ Wrinkled green 9 3 3 1
- 5. Incomplete Dominance In incomplete dominance, neither allele is __________ so there is a blending of ______ when two different alleles for the same trait occur together. Colors blend together (______________ individuals = 3 rd phenotype) dominant traits heterozygous red white pink
- 6. Incomplete Dominance In Four OŌĆÖ Clocks, if you cross a red _____ (which is always pure) with a white _____ (that is also always pure) , you get a pink _____ (which is always hybrid / heterozygous RR WW RW RW RW RW RW
- 7. Incomplete Dominance In another flower, if red ____ and blue ____ flowers are crossed, they produce a 3 rd purple ____ flower What would be the genotype ratio and phenotype ratio if you crossed two purple flowers? RR BB RB
- 8. Incomplete Dominance Cross of two purple flowers ____ X ____ What are gamete possibilities? genotype ratio 1RR : 2RB : 1BB phenotype ratio 1red : 2 purple : 1 blue Can you have a heterozygous red or hybrid blue flower? ___ B R R B BB RB RR RB red purple purple blue RB RB no
- 9. Codominance Both _______ contribute to the phenotype of the organism by showing up simultaneously (at the same time) in heterozygous individuals. In cattle and horses, if you cross a pure ____ ( RR) with a pure ______ (WW), you get (RW) which produces the color _____ . alleles red white roan
- 10. Codominance These cattle or horses actually have both red and white hairs intermixed, or are spotted. Roan is a third ___________ . If you cross a roan with a whiteŌĆ” W W R W WW RW RW WW phenotype roan roan white white
- 11. Codominance Andalusian chickens also show this pattern of inheritance. If you cross a black (BB) chicken With a white (WW) chicken You get black+white speckled (BW) chicken
- 12. Multiple Alleles In this pattern of inheritance, the genes have more than _____ alleles controlling them and are therefore said to have multiple alleles. No individual has more than _____ alleles, but there are more than _____ possible alleles in a population, so a ______ will be expressed in more than two forms. two two two trait
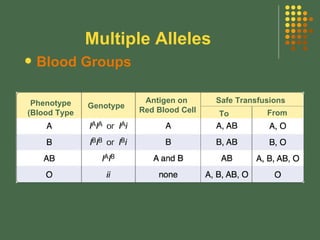
- 13. Multiple Alleles Blood type in humans is an example of this inheritance pattern. The ______ different blood groups: A, B, O, and AB Are produced by ______ different alleles: A, B, and O four three Phenotype Genotype A AA or AO B BB or BO AB AB only O OO only
- 14. Multiple Alleles Examples of Blood type crosses
- 15. Multiple Alleles Phenotype (Blood Type Genotype Blood Groups Antigen on Red Blood Cell Safe Transfusions To From
- 16. Multiple Alleles The example of _______ hair color, which has at least four different alleles, (on text pg 273) is seen in these different Rex rabbits. rabbit
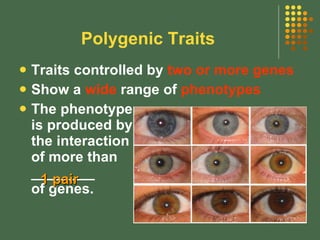
- 17. Polygenic Traits Traits controlled by two or more genes Show a wide range of phenotypes The phenotype is produced by the interaction of more than ________ of genes. 1 pair
- 18. Polygenic Traits These are called ___________ traits, which means ŌĆ£having _______ genesŌĆØ. In humans, _____ color, _____ color, polygenic many skin eye
- 19. Polygenic Traits These are called ___________ traits, which means ŌĆ£having _______ genesŌĆØ. In humans, _____ color, _____ color, and _____ color polygenic many skin eye hair
- 20. Polygenic Traits These are called ___________ traits, which means ŌĆ£having _______ genesŌĆØ. In humans, _____ color, _____ color, and _____ color are just a few of the many traits __________ by many genes. polygenic many skin controlled eye hair
- 21. Polygenic Traits Sometimes the combination of the different genes results in continuous __________ of these traits. The combined size of all the ______ parts from head to foot, determines the _______ of the person. variation body height James Bond Height Chart
Editor's Notes
- #8: http://www.gwu.edu/~darwin/BiSc150/One/rose.GIF
- #9: http://www.gwu.edu/~darwin/BiSc150/One/rose.GIF
- #11: http://www.ccs.k12.in.us/chsteachers/Amayhew/Biology%20Notes/beyond%20dominance%20notes_files/image004.jpg
- #18: http://anthro.palomar.edu/adapt/images/skin_color_range.jpg http://www.sciam.com/media/inline/0002E7CA-F27B-13A1-AFAA83414B7FFE9F_1.gif
- #19: http://anthro.palomar.edu/adapt/images/skin_color_range.jpg http://www.sciam.com/media/inline/0002E7CA-F27B-13A1-AFAA83414B7FFE9F_1.gif
- #20: http://anthro.palomar.edu/adapt/images/skin_color_range.jpg http://www.sciam.com/media/inline/0002E7CA-F27B-13A1-AFAA83414B7FFE9F_1.gif
- #21: http://anthro.palomar.edu/adapt/images/skin_color_range.jpg http://www.sciam.com/media/inline/0002E7CA-F27B-13A1-AFAA83414B7FFE9F_1.gif
- #22: http://anthro.palomar.edu/adapt/images/skin_color_range.jpg http://www.sciam.com/media/inline/0002E7CA-F27B-13A1-AFAA83414B7FFE9F_1.gif



