Message digest & digital signature
Download as PPTX, PDF10 likes4,898 views
This document discusses message digests and digital signatures. It begins by introducing message digests or hashes, which represent a fixed-length string that uniquely identifies a message. It then discusses digital signatures, where a message digest is encrypted with a sender's private key. This allows a recipient to verify the integrity and authenticity of the message by decrypting the signature with the sender's public key and comparing it to a new message digest. The document outlines the steps for digital signatures and notes they can provide integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation, but not privacy. It explains each of these properties in more detail.
1 of 18
Downloaded 115 times















Recommended
SHA- Secure hashing algorithm



SHA- Secure hashing algorithmRuchi Maurya
╠²
Security Hash Algorithm (SHA) was developed in 1993 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and National Security Agency (NSA).
It was designed as the algorithm to be used for secure hashing in the US Digital Signature Standard.
ŌĆó Hashing function is one of the most commonly used encryption methods. A hash is a special mathematical function that performs one-way encryption.
ŌĆó SHA-l is a revised version of SHA designed by NIST and was published as a Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS).
ŌĆó Like MD5, SHA-l processes input data in 512-bit blocks.
ŌĆó SHA-l generates a 160-bit message digest. Whereas MD5 generated message digest of 128 bits.
ŌĆó The procedure is used to send a non secret but signed message from sender to receiver. In such a case following steps are followed:
1. Sender feeds a plaintext message into SHA-l algorithm and obtains a 160-bit SHA-l hash.
2. Sender then signs the hash with his RSA private key and sends both the plaintext message and the signed hash to the receiver.
3. After receiving the message, the receiver computes the SHA-l hash himself and also applies the sender's public key to the signed hash to obtain the original hash H.
Data Encryption and Decryption using Hill Cipher



Data Encryption and Decryption using Hill CipherAashirwad Kashyap
╠²
The document describes a thesis submitted by Amogh Mahapatra and Rajballav Dash for their Bachelor of Technology degree. It examines using the Hill cipher technique and self-repetitive matrices for data encryption and decryption. Specifically, it proposes an innovation to the conventional Hill cipher method using the concept of self-repetitive matrices. This approach is mathematically derived and implemented to simulate a communication channel with compression techniques. The method aims to address issues with inverting the Hill cipher's multiplicative matrix by using periodically repeating matrices.Public Key Cryptography



Public Key CryptographyGopal Sakarkar
╠²
Public key cryptography uses two keys, a public key that can encrypt messages and a private key that decrypts messages. It has six components: plain text, encryption algorithm, public and private keys, ciphertext, and decryption algorithm. Some key characteristics are that it is computationally infeasible to determine the private key from the public key alone, and encryption/decryption is easy when the relevant key is known. The requirements of public key cryptography are that it is easy to generate a public-private key pair, easy to encrypt with the public key, easy for the recipient to decrypt with the private key, and infeasible to determine the private key from the public key or recover the plaintext from the ciphertext and public key aloneCryptography and network security



Cryptography and network securitypatisa
╠²
This document provides an overview of cryptography including:
1. Cryptography is the process of encoding messages to protect information and ensure confidentiality, integrity, authentication and other security goals.
2. There are symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms that use the same or different keys for encryption and decryption. Examples include AES, RSA, and DES.
3. Other techniques discussed include digital signatures, visual cryptography, and ways to implement cryptography like error diffusion and halftone visual cryptography.Vigenere cipher



Vigenere cipherAbd-Ur Rehman Saqib
╠²
The document summarizes the Vigenere cipher, a method of encrypting alphabetic text using polyalphabetic substitution. The cipher uses a table or formula with a repeating keyword to encrypt the plaintext by adding or subtracting letter values. To decrypt, the reverse process is applied using the same keyword to recover the original plaintext from the ciphertext.PUBLIC KEY ENCRYPTION



PUBLIC KEY ENCRYPTIONraf_slide
╠²
Public key cryptography uses key pairs - a public key and a private key - to encrypt and decrypt messages. The public key can be shared widely, while the private key is kept secret. This allows users to securely share encrypted messages without having to first share secret keys. Common applications of public key cryptography include public key encryption and digital signatures.IP Security



IP SecurityDr.Florence Dayana
╠²
Applications of IPsec,Routing Applications,IPsec Services,Security Association (SA),Security Association Database (SAD),Internet Key ExchangeDiffie-hellman algorithm



Diffie-hellman algorithmComputer_ at_home
╠²
The Diffie-Hellman algorithm was developed by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman in 1976.
This algorithm was devices not to encrypt the data but to generate same private cryptographic key at both ends so that there is no need to transfer this key from one communication end to another.
Diffie ŌĆō Hellman algorithm is an algorithm that allows two parties to get the shared secret key using the communication channel, which is not protected from the interception but is protected from modification.
Pretty good privacy



Pretty good privacyPushkar Dutt
╠²
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is strong encryption software that enables you to protect your email and files by scrambling them so others cannot read them. It also allows you to digitally "sign" your messages in a way that allows others to verify that a message was actually sent by you. PGP is available in freeware and commercial versions all over the world.
PGP was first released in 1991 as a DOS program that earned a reputation for being difficult. In June 1997, PGP Inc. released PGP 5.x for Win95/NT. PGP 5.x included plugins for several popular email programs.DES (Data Encryption Standard) pressentation



DES (Data Encryption Standard) pressentationsarhadisoftengg
╠²
This document discusses data encryption methods. It defines encryption as hiding information so it can only be accessed by those with the key. There are two main types: symmetric encryption uses one key, while asymmetric encryption uses two different but related keys. Encryption works by scrambling data using techniques like transposition, which rearranges the order, and substitution, which replaces parts with other values. The document specifically describes the Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm and the public key cryptosystem, which introduced the innovative approach of using different keys for encryption and decryption.Network security (vulnerabilities, threats, and attacks)



Network security (vulnerabilities, threats, and attacks)Fabiha Shahzad
╠²
Network security involves protecting network usability and integrity through hardware and software technologies. It addresses vulnerabilities that threats may exploit to launch attacks. Common vulnerabilities include issues with technologies, configurations, and security policies. Threats aim to take advantage of vulnerabilities and can be structured, unstructured, internal, or external. Common attacks include reconnaissance to gather information, unauthorized access attempts, denial-of-service to disrupt availability, and use of malicious code like worms, viruses, and Trojan horses.RSA algorithm



RSA algorithmArpana shree
╠²
RSA is a public-key cryptosystem that uses both public and private keys for encryption and decryption. It was the first practical implementation of such a cryptosystem. The algorithm involves four main steps: 1) generation of the public and private keys, 2) encryption of messages using the public key, 3) decryption of encrypted messages using the private key, and 4) potential cracking of the encrypted message. It works by using two large prime numbers to generate the keys and performs exponentiation and modulo operations on messages to encrypt and decrypt them. There were some drawbacks to the original RSA algorithm related to redundant calculations and representing letters numerically that opened it up to easier hacking. Enhancements to RSA improved it by choosingMD5 ALGORITHM.pptx



MD5 ALGORITHM.pptxRajapriya82
╠²
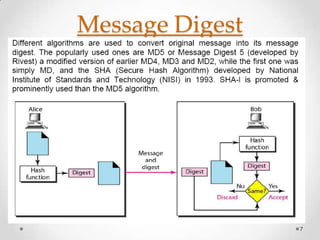
The MD5 algorithm is a cryptographic hash function that generates a 128-bit digest from a message of any length. It works by first padding the message to a length that is a multiple of 512 bits, then appending the message length. It initializes buffers and processes the message in 512-bit blocks using four rounds of 16 operations each, applying different functions to update the buffers. The final buffer values become the MD5 digest. It is commonly used to verify file integrity but is now considered insecure due to possible hash collisions.Diffie hellman key exchange algorithm



Diffie hellman key exchange algorithmSunita Kharayat
╠²
The presentation include:
-Diffie hellman key exchange algorithm
-Primitive roots
-Discrete logarithm and discrete logarithm problem
-Attacks on diffie hellman and their possible solution
-Key distribution center Security Attacks.ppt



Security Attacks.pptZaheer720515
╠²
This document discusses different types of cyber attacks including passive attacks like eavesdropping and masquerading, active attacks like denial of service, and methods attackers use like spoofing, backdoors, brute force attacks, and dictionary attacks. It provides details on how each attack compromises security through unauthorized access, modification of data, denial of service, or repudiation.Unit 1



Unit 1Trupti Kodinariya
╠²
The document provides information on classical encryption techniques, specifically covering symmetric cipher models, cryptography, cryptanalysis, and attacks. It discusses substitution and transposition techniques, including the Caesar cipher, monoalphabetic cipher, and Playfair cipher. For each technique, it explains the encryption and decryption process, cryptanalysis methods, and provides examples to illustrate how the techniques work.Hash Function



Hash Functionstalin rijal
╠²
A hash function maps data of arbitrary size to a fixed size value called a hash. Common hash functions include MD5 and SHA, with MD5 producing a 128-bit hash. While hashes were once used to securely store passwords, MD5 is now considered cryptographically broken due to collisions being found in its compression function. One-way signatures allow multiple users to generate linked signatures on the same message in a verifiable chain.Fundamentals of IoT Security



Fundamentals of IoT SecuritySHAAMILIVARSAGV
╠²
The document discusses fundamentals of IoT security. It defines IoT as the interconnection of physical devices to the internet to share and exchange data. IoT security protects connected devices from cyberattacks by securing the network functionality and data privacy. The need for IoT security increased after hacking attacks showed catastrophic consequences. The document outlines eight principles of IoT security including no universal passwords, secured interfaces, proven cryptography, security by default, signed software updates, and a vulnerability reporting scheme.Message digest 5



Message digest 5Tirthika Bandi
╠²
MD5 is a cryptographic hash function that produces a 128-bit hash value for a message of any length. It was originally designed to provide authentication of digital signatures but is no longer considered reliable for cryptography due to techniques that can generate collisions. MD5 operates by padding the input, appending the length, dividing into blocks, initializing variables, processing blocks through 4 rounds of operations with different constants each round, and outputting the hash value. While it was intended to be difficult to find collisions or recover the input, MD5 is no longer considered cryptographically secure due to attacks demonstrating collisions.Hash Function



Hash FunctionSiddharth Srivastava
╠²
This document discusses message authentication techniques including message encryption, message authentication codes (MACs), and hash functions. It describes how each technique can be used to authenticate messages and protect against various security threats. It also covers how symmetric and asymmetric encryption can provide authentication when used with MACs or digital signatures. Specific MAC and hash functions are examined like HMAC, SHA-1, and SHA-2. X.509 is introduced as a standard for digital certificates.RSA Algorithm



RSA AlgorithmSrinadh Muvva
╠²
RSA (RivestŌĆōShamirŌĆōAdleman) is an algorithm used by modern computers to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm.Network security cryptography ppt



Network security cryptography pptThushara92
╠²
This document discusses network security and cryptography. It begins by defining a network and common network threats. It then discusses network security, including transit and traffic security. It covers problems and attacks like secrecy, authentication, and integrity control. The document introduces cryptography and its use in encryption and decryption to securely transmit data. It describes algorithms like RSA, substitution ciphers, and transposition ciphers. It also covers advantages and disadvantages of cryptography along with a proposed concept to strengthen encryption security.Elgamal & schnorr digital signature scheme copy



Elgamal & schnorr digital signature scheme copyNorth Cap University (NCU) Formely ITM University
╠²
Digital signatures provide authentication of digital messages or documents. There are three main algorithms involved: hashing, signature generation, and signature verification. Common digital signature schemes include ElGamal, Schnorr, and the Digital Signature Standard (DSS). The DSS is based on ElGamal and Schnorr schemes. It uses smaller signatures than ElGamal by employing two moduli, one smaller than the other. Digital signatures are widely used to provide authentication in protocols like IPSec, SSL/TLS, and S/MIME.Advanced cryptography and implementation



Advanced cryptography and implementationAkash Jadhav
╠²
The document discusses a technical presentation on advanced cryptography and its implementation. It provides an overview of cryptography, including its history and basic concepts such as encryption, decryption, and cryptanalysis. Examples of cryptography applications discussed include ATM cards, credit cards, e-mail, and lottery tickets.Introduction to Digital signatures



Introduction to Digital signaturesRohit Bhat
╠²
This document provides an introduction to digital signatures, including an overview of encryption, hashing, digital signature creation and verification, and different digital signature schemes like RSA, ElGamal, and Schnorr. It also discusses the legal aspects and advantages/disadvantages of digital signatures.Number theory and cryptography



Number theory and cryptographyYasser Ali
╠²
This document provides an overview of number theory and attacks on the RSA cryptosystem. It begins with an introduction to modular arithmetic and congruence relations. It then discusses the Euclidean algorithm, modular inverses, and operations in modular arithmetic. The document explains Diffie-Hellman key exchange, RSA, and the mathematics behind RSA such as Euler's totient function and Fermat's little theorem. It concludes by discussing some attacks on RSA, including factorizing the RSA modulus n to recover the private key.Asymmetric Cryptography



Asymmetric CryptographyUTD Computer Security Group
╠²
An introduction to asymmetric cryptography with an in-depth look at RSA, Diffie-Hellman, the FREAK and LOGJAM attacks on TLS/SSL, and the "Mining your P's and Q's attack".Computer Networks Lab File



Computer Networks Lab FileKandarp Tiwari
╠²
This document contains 11 C programming assignments related to networking concepts like parity checking, bit stuffing, character counting, CRC implementation, LZW compression, TCP server/client programs, and UDP server/client programs. For each assignment, it provides the question, sample code, and output. The programs cover both stream-oriented and datagram-oriented network applications using TCP and UDP on specified port numbers.Lecture1 Introduction 



Lecture1 Introduction rajakhurram
╠²
This document provides an overview of network security. It discusses 16 lectures on the topic over 2 sessions that will include firewall and VPN lab exercises and assignments. Course materials will be available online. Security concepts that will be covered include confidentiality, integrity, authentication, access control, and availability. The document also provides brief histories of ENIGMA and the U-2 spy plane incident and defines security, security violations, and computer and network security. Common security attacks such as interception, modification, and denial of service are also outlined.A Comparative Analysis between SHA and MD5 algorithms 



A Comparative Analysis between SHA and MD5 algorithms Er Piyush Gupta IN ŌŖ×Ōīś’Ż┐
╠²
this paper belongs to deep analysis of secure hash algorithm and message digest version 5 algorithm....More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Pretty good privacy



Pretty good privacyPushkar Dutt
╠²
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is strong encryption software that enables you to protect your email and files by scrambling them so others cannot read them. It also allows you to digitally "sign" your messages in a way that allows others to verify that a message was actually sent by you. PGP is available in freeware and commercial versions all over the world.
PGP was first released in 1991 as a DOS program that earned a reputation for being difficult. In June 1997, PGP Inc. released PGP 5.x for Win95/NT. PGP 5.x included plugins for several popular email programs.DES (Data Encryption Standard) pressentation



DES (Data Encryption Standard) pressentationsarhadisoftengg
╠²
This document discusses data encryption methods. It defines encryption as hiding information so it can only be accessed by those with the key. There are two main types: symmetric encryption uses one key, while asymmetric encryption uses two different but related keys. Encryption works by scrambling data using techniques like transposition, which rearranges the order, and substitution, which replaces parts with other values. The document specifically describes the Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm and the public key cryptosystem, which introduced the innovative approach of using different keys for encryption and decryption.Network security (vulnerabilities, threats, and attacks)



Network security (vulnerabilities, threats, and attacks)Fabiha Shahzad
╠²
Network security involves protecting network usability and integrity through hardware and software technologies. It addresses vulnerabilities that threats may exploit to launch attacks. Common vulnerabilities include issues with technologies, configurations, and security policies. Threats aim to take advantage of vulnerabilities and can be structured, unstructured, internal, or external. Common attacks include reconnaissance to gather information, unauthorized access attempts, denial-of-service to disrupt availability, and use of malicious code like worms, viruses, and Trojan horses.RSA algorithm



RSA algorithmArpana shree
╠²
RSA is a public-key cryptosystem that uses both public and private keys for encryption and decryption. It was the first practical implementation of such a cryptosystem. The algorithm involves four main steps: 1) generation of the public and private keys, 2) encryption of messages using the public key, 3) decryption of encrypted messages using the private key, and 4) potential cracking of the encrypted message. It works by using two large prime numbers to generate the keys and performs exponentiation and modulo operations on messages to encrypt and decrypt them. There were some drawbacks to the original RSA algorithm related to redundant calculations and representing letters numerically that opened it up to easier hacking. Enhancements to RSA improved it by choosingMD5 ALGORITHM.pptx



MD5 ALGORITHM.pptxRajapriya82
╠²
The MD5 algorithm is a cryptographic hash function that generates a 128-bit digest from a message of any length. It works by first padding the message to a length that is a multiple of 512 bits, then appending the message length. It initializes buffers and processes the message in 512-bit blocks using four rounds of 16 operations each, applying different functions to update the buffers. The final buffer values become the MD5 digest. It is commonly used to verify file integrity but is now considered insecure due to possible hash collisions.Diffie hellman key exchange algorithm



Diffie hellman key exchange algorithmSunita Kharayat
╠²
The presentation include:
-Diffie hellman key exchange algorithm
-Primitive roots
-Discrete logarithm and discrete logarithm problem
-Attacks on diffie hellman and their possible solution
-Key distribution center Security Attacks.ppt



Security Attacks.pptZaheer720515
╠²
This document discusses different types of cyber attacks including passive attacks like eavesdropping and masquerading, active attacks like denial of service, and methods attackers use like spoofing, backdoors, brute force attacks, and dictionary attacks. It provides details on how each attack compromises security through unauthorized access, modification of data, denial of service, or repudiation.Unit 1



Unit 1Trupti Kodinariya
╠²
The document provides information on classical encryption techniques, specifically covering symmetric cipher models, cryptography, cryptanalysis, and attacks. It discusses substitution and transposition techniques, including the Caesar cipher, monoalphabetic cipher, and Playfair cipher. For each technique, it explains the encryption and decryption process, cryptanalysis methods, and provides examples to illustrate how the techniques work.Hash Function



Hash Functionstalin rijal
╠²
A hash function maps data of arbitrary size to a fixed size value called a hash. Common hash functions include MD5 and SHA, with MD5 producing a 128-bit hash. While hashes were once used to securely store passwords, MD5 is now considered cryptographically broken due to collisions being found in its compression function. One-way signatures allow multiple users to generate linked signatures on the same message in a verifiable chain.Fundamentals of IoT Security



Fundamentals of IoT SecuritySHAAMILIVARSAGV
╠²
The document discusses fundamentals of IoT security. It defines IoT as the interconnection of physical devices to the internet to share and exchange data. IoT security protects connected devices from cyberattacks by securing the network functionality and data privacy. The need for IoT security increased after hacking attacks showed catastrophic consequences. The document outlines eight principles of IoT security including no universal passwords, secured interfaces, proven cryptography, security by default, signed software updates, and a vulnerability reporting scheme.Message digest 5



Message digest 5Tirthika Bandi
╠²
MD5 is a cryptographic hash function that produces a 128-bit hash value for a message of any length. It was originally designed to provide authentication of digital signatures but is no longer considered reliable for cryptography due to techniques that can generate collisions. MD5 operates by padding the input, appending the length, dividing into blocks, initializing variables, processing blocks through 4 rounds of operations with different constants each round, and outputting the hash value. While it was intended to be difficult to find collisions or recover the input, MD5 is no longer considered cryptographically secure due to attacks demonstrating collisions.Hash Function



Hash FunctionSiddharth Srivastava
╠²
This document discusses message authentication techniques including message encryption, message authentication codes (MACs), and hash functions. It describes how each technique can be used to authenticate messages and protect against various security threats. It also covers how symmetric and asymmetric encryption can provide authentication when used with MACs or digital signatures. Specific MAC and hash functions are examined like HMAC, SHA-1, and SHA-2. X.509 is introduced as a standard for digital certificates.RSA Algorithm



RSA AlgorithmSrinadh Muvva
╠²
RSA (RivestŌĆōShamirŌĆōAdleman) is an algorithm used by modern computers to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm.Network security cryptography ppt



Network security cryptography pptThushara92
╠²
This document discusses network security and cryptography. It begins by defining a network and common network threats. It then discusses network security, including transit and traffic security. It covers problems and attacks like secrecy, authentication, and integrity control. The document introduces cryptography and its use in encryption and decryption to securely transmit data. It describes algorithms like RSA, substitution ciphers, and transposition ciphers. It also covers advantages and disadvantages of cryptography along with a proposed concept to strengthen encryption security.Elgamal & schnorr digital signature scheme copy



Elgamal & schnorr digital signature scheme copyNorth Cap University (NCU) Formely ITM University
╠²
Digital signatures provide authentication of digital messages or documents. There are three main algorithms involved: hashing, signature generation, and signature verification. Common digital signature schemes include ElGamal, Schnorr, and the Digital Signature Standard (DSS). The DSS is based on ElGamal and Schnorr schemes. It uses smaller signatures than ElGamal by employing two moduli, one smaller than the other. Digital signatures are widely used to provide authentication in protocols like IPSec, SSL/TLS, and S/MIME.Advanced cryptography and implementation



Advanced cryptography and implementationAkash Jadhav
╠²
The document discusses a technical presentation on advanced cryptography and its implementation. It provides an overview of cryptography, including its history and basic concepts such as encryption, decryption, and cryptanalysis. Examples of cryptography applications discussed include ATM cards, credit cards, e-mail, and lottery tickets.Introduction to Digital signatures



Introduction to Digital signaturesRohit Bhat
╠²
This document provides an introduction to digital signatures, including an overview of encryption, hashing, digital signature creation and verification, and different digital signature schemes like RSA, ElGamal, and Schnorr. It also discusses the legal aspects and advantages/disadvantages of digital signatures.Number theory and cryptography



Number theory and cryptographyYasser Ali
╠²
This document provides an overview of number theory and attacks on the RSA cryptosystem. It begins with an introduction to modular arithmetic and congruence relations. It then discusses the Euclidean algorithm, modular inverses, and operations in modular arithmetic. The document explains Diffie-Hellman key exchange, RSA, and the mathematics behind RSA such as Euler's totient function and Fermat's little theorem. It concludes by discussing some attacks on RSA, including factorizing the RSA modulus n to recover the private key.Asymmetric Cryptography



Asymmetric CryptographyUTD Computer Security Group
╠²
An introduction to asymmetric cryptography with an in-depth look at RSA, Diffie-Hellman, the FREAK and LOGJAM attacks on TLS/SSL, and the "Mining your P's and Q's attack".Computer Networks Lab File



Computer Networks Lab FileKandarp Tiwari
╠²
This document contains 11 C programming assignments related to networking concepts like parity checking, bit stuffing, character counting, CRC implementation, LZW compression, TCP server/client programs, and UDP server/client programs. For each assignment, it provides the question, sample code, and output. The programs cover both stream-oriented and datagram-oriented network applications using TCP and UDP on specified port numbers.Elgamal & schnorr digital signature scheme copy



Elgamal & schnorr digital signature scheme copyNorth Cap University (NCU) Formely ITM University
╠²
Viewers also liked (20)
Lecture1 Introduction 



Lecture1 Introduction rajakhurram
╠²
This document provides an overview of network security. It discusses 16 lectures on the topic over 2 sessions that will include firewall and VPN lab exercises and assignments. Course materials will be available online. Security concepts that will be covered include confidentiality, integrity, authentication, access control, and availability. The document also provides brief histories of ENIGMA and the U-2 spy plane incident and defines security, security violations, and computer and network security. Common security attacks such as interception, modification, and denial of service are also outlined.A Comparative Analysis between SHA and MD5 algorithms 



A Comparative Analysis between SHA and MD5 algorithms Er Piyush Gupta IN ŌŖ×Ōīś’Ż┐
╠²
this paper belongs to deep analysis of secure hash algorithm and message digest version 5 algorithm....Cryptography by Epul



Cryptography by EpulAgate Studio
╠²
This document discusses cryptography and different encryption methods. It begins with definitions of cryptography terms like crypto, graph, and cryptology. It then explains how encryption works using Alice and Bob as an example, where a message is encrypted with a key into ciphertext. The document goes on to provide examples of different ciphers, including the Vigenere cipher. It notes that the one-time pad cipher is theoretically unbreakable but impractical. It concludes by stating that future discussions will cover modern ciphers and how keys are used.Cryptography 



Cryptography pravin pandey
╠²
Cryptography involves encrypting messages to make them secure and immune to attacks. There are traditional ciphers like substitution and transposition ciphers that encrypt text by shifting letters or rearranging them. Modern algorithms like DES use symmetric keys and RSA uses public/private key pairs to encrypt and decrypt messages. Public key cryptography uses different public and private keys, allowing secure communication without pre-sharing keys. Digital signatures authenticate messages using the sender's private key and can be verified by anyone using their public key.Hash function 



Hash function Salman Memon
╠²
A hash function usually means a function that compresses, meaning the output is shorter than the input
A hash function takes a group of characters (called a key) and maps it to a value of a certain length (called a hash value or hash).
The hash value is representative of the original string of characters, but is normally smaller than the original.
This term is also known as a hashing algorithm or message digest function.
Hash functions also called message digests or one-way encryption or hashing algorithm.
http://phpexecutor.comMessage Authentication using Message Digests and the MD5 Algorithm



Message Authentication using Message Digests and the MD5 AlgorithmAjay Karri
╠²
Message authentication is important to prevent undetected manipulation of messages, which can have disastrous effects. Examples where message authentication is crucial include internet commerce and network management. Cryptographic hash functions are often used to authenticate messages by providing a digital fingerprint of the message contents.Digital Signature



Digital SignatureJonathon Dosh
╠²
The document discusses different types of digital signatures, including direct digital signatures and arbitrated digital signatures. A direct digital signature only involves a sender and receiver, while an arbitrated digital signature includes a third party arbiter to verify the signature before the recipient receives the message. The advantages of digital signatures are authentication and verification between sender and recipient, while disadvantages include relying on the sender owning their public key and potential delays in signature generation and verification.A Comparative Study between RSA and MD5 algorithms 



A Comparative Study between RSA and MD5 algorithms Er Piyush Gupta IN ŌŖ×Ōīś’Ż┐
╠²
This document provides a comparative analysis of the RSA and MD5 algorithms. It discusses the basics of cryptography and describes how MD5 works to generate a 128-bit hash value from a variable-length message using four rounds of processing. The document also compares different versions of MD5 (MD2, MD4, MD5) and describes how RSA uses a public/private key pair to enable secure communication.Modified MD5 Algorithm for Password Encryption



Modified MD5 Algorithm for Password EncryptionInternational Journal of Computer and Communication System Engineering
╠²
This document discusses weaknesses in the MD5 hashing algorithm for password encryption and proposes modifications to strengthen it. It begins by introducing MD5 and how it is commonly used to hash passwords for storage. However, MD5 is vulnerable to dictionary and rainbow table attacks. The document then suggests three modifications to MD5 to improve security: 1) Adding a salt value to each hashed password, 2) Iteratively hashing the password multiple times, and 3) Adding a random prefix or suffix to each hashed value before storage. These modifications aim to strengthen MD5 against cracking attempts.Hashing Algorithm: MD5



Hashing Algorithm: MD5ijsrd.com
╠²
This document discusses the MD5 hashing algorithm. It begins by defining message digests and their purpose in detecting changes to data. It then provides details on the MD5 algorithm, including that it produces a 128-bit hash value and describes the main steps of the algorithm. It also discusses how MD5 can be used to authenticate file transmissions by comparing hash values of the sent and received files.Network security



Network securityquest university nawabshah
╠²
Network security involves protecting computer networks from threats. It targets a variety of threats to stop them from entering or spreading on a network. The objectives of network security are access, confidentiality, authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation. As networks became more common in the 1980s and 1990s, security concerns increased and organizations like CERT were created to address issues. Network security uses multiple layers including firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, antivirus software, and encryption to secure networks from threats.The MD5 hashing algorithm



The MD5 hashing algorithmBob Landstrom
╠²
An introduction to the MD5 Hashing Algorithm and its importance in the data center as an essential component of cryptography. http://boblandstrom.comLinux booting process



Linux booting processPrashant Hegde
╠²
The Linux booting process begins with the BIOS performing basic checks before activating the MBR, which then loads the boot loader GRUB. GRUB executes the Linux kernel, which loads the root file system, init, device drivers, and runlevels to start Linux in single-user, multi-user, or graphical mode.Disk



DiskKrishna Yadav Kyadav308
╠²
Hard disks are organized into tracks and sectors through low-level formatting. Partitions divide the hard disk into separate areas that function as individual drives. High-level formatting defines the file allocation table (FAT) for each partition to locate files. Common storage devices include IDE/EIDE and SCSI hard drives, floppy disks, and CD-ROMs. RAID configurations provide fault tolerance through disk redundancy and parity.Md5



Md5annamalai
╠²
This document summarizes the MD5 algorithm and proposes methods to strengthen it against cracking. It analyzes the MD5 algorithm and common cracking approaches. It then proposes several measures to improve MD5 security, including increasing password complexity, using secondary encoding, and increasing the length of the MD5 hash value through concatenation to reduce collision probability. It includes a demonstration program that implements one proposed method of increasing hash length through multiple encodings and concatenation.Ch31



Ch31bitistu
╠²
The document discusses network security and provides an overview of five security services: message confidentiality, message integrity, message authentication, message nonrepudiation, and entity authentication. It describes how each of these services can be achieved using techniques like symmetric and asymmetric encryption, hashing, digital signatures, challenge-response authentication, and key management protocols.Information Security Cryptography ( L02- Types Cryptography)



Information Security Cryptography ( L02- Types Cryptography)Anas Rock
╠²
talk about types of cryptography based of types of key , text cryptography and Strength encryption system.Intro to modern cryptography



Intro to modern cryptographyzahid-mian
╠²
The document discusses the history and concepts of encryption, including ancient encryption methods like hieroglyphs and the Caesar cipher. It then covers modern digital encryption, describing how public/private key encryption works using plaintexts, ciphertexts, encryption/decryption keys, and algorithms. The document also discusses hash values, digital signatures, types of attacks against encryption, different cipher implementations like DES and AES, and reasons why attacks can still succeed despite encryption.Byte Rotation Algorithm



Byte Rotation AlgorithmEngr0918
╠²
This document proposes a new encryption algorithm called Byte Rotation Encryption Algorithm (BREA). BREA is a symmetric key, block cipher that encrypts fixed-length blocks of 16 bytes using byte rotation and a randomly generated 16 byte key matrix. It employs a multithreading model to encrypt blocks in parallel, improving encryption speed. The algorithm assigns numbers 1-26 to letters, adds the plaintext and key matrices, then rotates rows and columns before replacing values with letters to generate the ciphertext. BREA is designed to be faster and require fewer resources than previous algorithms while still providing secure encryption.Raid_intro.ppt



Raid_intro.pptwebhostingguy
╠²
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) uses multiple disk drives to increase performance and availability. It provides parallelism for higher performance and redundancy for data availability. Different RAID levels offer different tradeoffs between performance, availability, and cost. RAID levels include RAID 0 for striping without redundancy, RAID 1 for mirroring, RAID 3 and 5 for striping with parity redundancy.Modified MD5 Algorithm for Password Encryption



Modified MD5 Algorithm for Password EncryptionInternational Journal of Computer and Communication System Engineering
╠²
Message digest & digital signature
- 1. Message Digest & Digital Signature. Presented By ’üČ Lamack Jose (Roll No 16) ’üČ Dinesh Kodam (Roll No 34) ’üČ Manoj Patil (Roll No 36)
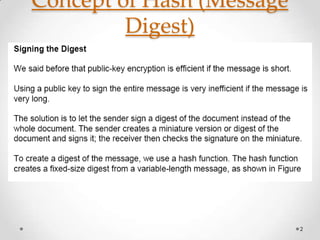
- 2. Concept of Hash (Message Digest) 2
- 3. Concept of Hash (Message Digest) 3
- 4. Idea of a Message Digest 4
- 5. Idea of a Message Digest 5
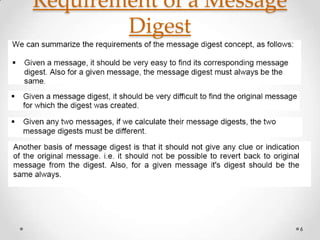
- 6. Requirement of a Message Digest 6
- 11. Steps for the process 11
- 15. Properties of Digital Signatures ŌĆó Digital signature does not provide privacy. If there is a need for privacy, another layer of encryption/decryption must be applied. ŌĆó 1. 2. 3. Digital signatures can provide Integrity, Authentication, and Nonrepudiation. 15
- 16. Properties of Digital Signatures 16
- 17. Properties of Digital Signatures 1. 2. Integrity The integrity of a message is preserved because if Eve intercepted the message and partially or totally changed it, the decrypted message would be unreadable. Authentication We can use the following reasoning to show how a message can be authenticated. If Eve sends a message while pretending that it is coming from Alice, she must use her own private key for encryption. The message is then decrypted with the public key of Alice and will therefore be nonreadable. Encryption with Eve's private key and decryption with Alice's public key result in garbage. 17
- 18. Properties of Digital Signatures 3. Nonrepudiation Digital signature also provides for nonrepudiation. Bob saves the message received from Alice. If Alice later denies sending the message, Bob can show that encrypting and decrypting the saved message with Alice's private and public key can create a duplicate of the saved message. Since only Alice knows her private key, she cannot deny sending the message. 18
