Metabolisme obat
- 1. METABOLISME OBAT Kuliah Kimia Medisinal STFB Deden Indra Dinata, M.Si., Apt.
- 2. Metabolisme Obat ŌĆó Metabolisme obat penting karena proses2 transformasi obat mjd metabolitnya sangat mempengaruhi lama kerja (durasi) suatu aksi/efek farmakologis suatu obat. ŌĆó Juga dpt melihat kemungkinan terbentuknya metabolit yg aktif (farmakologis aktif) dan mengetahui tentang bagaimana bentuk metabolit yg akan dieliminasi
- 3. PROSES METABOLISME OBAT I. Tujuan Umum a. Mengubah obat mjd metabolit : - aktif (bioaktivasi) - tidak aktif (bioinaktivasi) - toksik (biotoksifikasi) b. Mudah diekskresikan
- 4. II. Manfaat Metabolisme Obat a. Efikasi dan keamanan b. Pengaturan dosis c. Bahaya zat pengotor d. Evaluasi toksisitas e. Pengembangan proses metabolisme f. Dasar penjelasan proses toksik
- 5. III. Jalur Respon Obat a. Langsung ke ŌĆ£site of actionŌĆØ ’āĀ respon biologis b. Tidak aktif ’āĀ metabolisme ’āĀ aktif ’āĀ ŌĆ£site of actionŌĆØ ’āĀ respon biologis
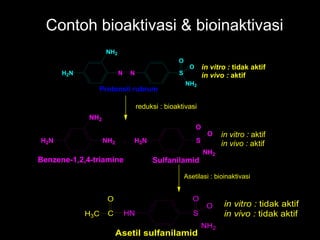
- 6. Contoh bioaktivasi & bioinaktivasi H2N NH2 N N S NH2 O O Protonsil rubrum in vitro : tidak aktif in vivo : aktif reduksi : bioaktivasi H2N NH2 NH2 H2N S NH2 O O SulfanilamidBenzene-1,2,4-triamine in vitro : aktif in vivo : aktif Asetilasi : bioinaktivasi HN S NH2 O O C O H3C Asetil sulfanilamid in vitro : tidak aktif in vivo : tidak aktif
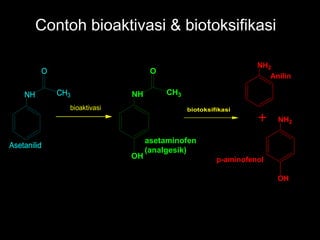
- 7. Contoh bioaktivasi & biotoksifikasi NH O CH3 Asetanilid bioaktivasi NH O CH3 OH asetaminofen (analgesik) biotoksifikasi NH2 NH2 OH Anilin p-aminofenol
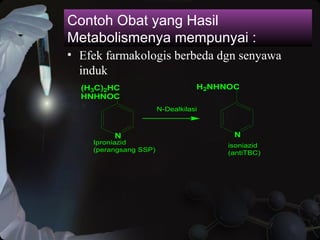
- 8. Contoh Obat yang Hasil Metabolismenya mempunyai : ŌĆó Efek farmakologis berbeda dgn senyawa induk N (H3C)2HC HNHNOC N H2NHNOC N-Dealkilasi Iproniazid (perangsang SSP) isoniazid (antiTBC)
- 9. Contoh hasil metabolisme ŌĆó Bbrp syw tdk mengalami proses metabolisme dan diekskresikan dari tubuh dlm bentuk tdk berubah a. Syw yg tdk larut dlm cairan tubuh, tdk diserap ole saluran cerna dan tahan thd pengaruh kimiawi dan enzimatik saluran cerna. Syw ini lgs dikeluarkan melalui tinja. Contoh : BaSO4 dan oleum ricini b. Syw yg mdh larut dlm cairan tubuh dan tahan thd pengaruh kimiawi dan enzimatik. Syw ini relatif tdk toksik dan cepat dikeluarkan melalui urin. Contoh : Asam mandelat, asam sulfonat alifatik, dan aromatik
- 10. Tempat Metabolisme A. Jaringan B. Organ : hati, usus
- 11. Faktor2 yg mempengaruhi metabolisme Obat a. Genetik/Keturunan b. Perbedaan spesies dan galur c. Perbedaan jenis kelamin d. Perbedaan Umur e. Penghambatan enzim metabolisme f. Induksi enzim metabolisme g. Faktor lain
- 12. Cytochrome P450 Enzim yang ditemukan berada di hati -hormon steroid mengalami biosintesis dari kolesterol -metabolisme xenobiotics-senyawa-senyawa yg tdk umum ditemukan dalam tubuh -obat-obatan -senyawa yang dihasilkan dalam produksi makanan, melalui proses pemasakan (hidrokarbon poliaromatik, juga asap tembakau) atau mikroorganisme Cytochrome P450 meiliki peran yang luas, dalam metabolisme -umumnya utk senyawa-senyawa organik yang kurang larut dalam air
- 13. The OH added by P450 can then be used to attach sulfate (SO4 2- ) or a sugar. The modified drug can be more readily removed by the kidney. Cytochrome P450 aids in the metabolism of xenobiotics by adding OH to increase the water solubility of the compound O2 + substrate + 2 electrons HO-substrate + H2O Because this enzyme catalyzes the addition of one oxygen atom, it is termed a monooxygenase.
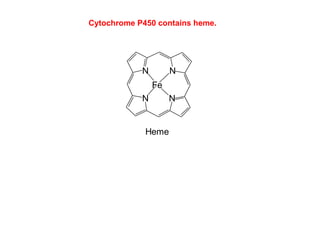
- 14. N NN N Fe Heme The heme group is a cofactor which contains iron. Different forms of heme are found in hemoglobins and proteins known as cytochromes. The iron in a heme can bind oxygen and transfer electrons. Cytochrome P450 contains heme.
- 15. Cytochrome P450ŌĆÖs are integral membrane proteins found in the endoplasmic reticulum- membrane network in cells Cytochrome P450
- 17. Cytochrome P450 At least 57 different isozymes in humans, over 7700 forms in Nature isozyme-catalytically and structurally similar but genetically distinct enzymes-different genes and amino acid sequences Different isozymes have different substrate specificities Individuals have several alleles for P450ŌĆÖs and differ in which isozymes they have A subset of cytochrome P450ŌĆÖs can be induced, so that more is expressed upon exposure to a compound. Because of the number of different isozymes and their different substrates and inhibitors, the metabolism of a drug can be altered if an individual takes a second drug. Since individuals have different combinations of P450ŌĆÖs, they differ in their response to specific drugs
- 18. Tugas Belajar Mandiri ŌĆó Metabolisme Obat ŌĆó Contoh-contoh reaksi pada fase 1 dan 2 ŌĆó Dikumpulkan minggu depan ŌĆó Bisa ditanyakan pada UTS ŌĆó Bobot: 5-10 % dari nilai akhir