Metamaterials
- 1. METAMATERIALS ÂĐKostiantyn Denysenko 2012 Monday, December 17, 12
- 2. Scope What are Metamaterials? How they work? Types Limitations FSS My work Monday, December 17, 12
- 3. What are Metamaterials? Metamaterials are artificial materials engineered to provide properties which may not be readily available in nature. These materials usually gain their properties from structure rather than composition, using the inclusion of small inhomogeneities to enact effective macroscopic behavior. Monday, December 17, 12
- 4. History â Theoretical design by Victor Veselago in 1968 â Predicted possibility of opposite properties for artificial materials V.G.Veselago â Dr. John Pendry showed practical method of making metamaterials in 1999 Sir J.Pendry Monday, December 17, 12
- 5. How they work Monday, December 17, 12
- 6. Normally, waves propagate and interact with different media according to Snellâs law Monday, December 17, 12
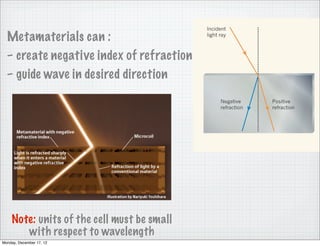
- 7. Metamaterials can : â create negative index of refraction â guide wave in desired direction Note: units of the cell must be small with respect to wavelength Monday, December 17, 12
- 8. Types Electromagnetic Acoustic Seismic Monday, December 17, 12
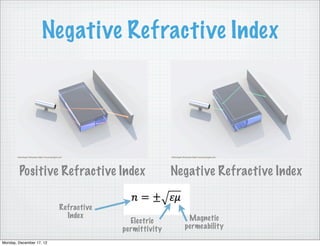
- 10. Negative Refractive Index Positive Refractive Index Negative Refractive Index Refractive Index Magnetic Electric permittivity permeability Monday, December 17, 12
- 11. Antenna Design â Negative index of refraction means more wave bending which means smaller antenna â Manipulate radiation pattern â Can double frequency range â Increase radiated power Monday, December 17, 12
- 12. Invisibility No cloak Cloaked Monday, December 17, 12
- 13. Limitations â Small wavelengths require very small units â Production technologies â Different wavelength requires new structure â Frequency selective surfaces Monday, December 17, 12
- 14. FSS Monday, December 17, 12
- 15. What is FSS? â FSS is any surface construction designed as a filter for plane waves â Angular/Frequency dependance â Band pass/Band stop behavior â FSS degrees of freedom â Element type â Element shape, size, loading â Element spacing and orientation Monday, December 17, 12
- 17. My Work Monday, December 17, 12
- 18. What I started with Monday, December 17, 12
- 19. Objectives â Explore properties of the cube â Explore areas of application â Create algorithm to build structure for specific applications â More? Monday, December 17, 12
- 20. They did it before me â Created the cube â Planarised unit cell â Simulated an array of 24X24X6 cells Monday, December 17, 12
- 21. What they didnât do â Never finished the planarised model â Didnât explore tuning properties â Didnât apply reconfiguring paradigm â More? Monday, December 17, 12
- 22. What we model now Monday, December 17, 12
- 23. And we have some results Monday, December 17, 12
- 25. Thank You! Monday, December 17, 12