Mia-Software at Eclipse Modeling Symposium 2010
- 1. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Fr├®d├®ric Madiot, Mia-Software Gr├®goire Dup├®, Mia-Software Using EMF to represent Eclipse 3.x Plug-ins
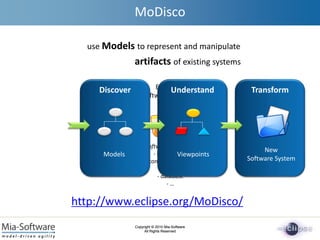
- 2. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Software artifacts : - source code - configuration files - tests - database - ŌĆ” Existing Software System Discover Models use Models to represent and manipulate artifacts of existing systems Understand Viewpoints Transform New Software System MoDisco http://www.eclipse.org/MoDisco/
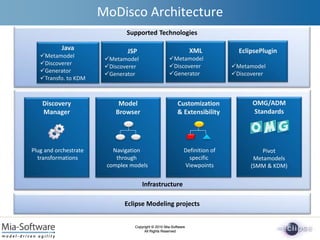
- 3. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Supported Technologies Infrastructure MoDisco Architecture Java ’ā╝Metamodel ’ā╝Discoverer ’ā╝Generator ’ā╝Transfo. to KDM XML ’ā╝Metamodel ’ā╝Discoverer ’ā╝Generator Model Browser Navigation through complex models Customization & Extensibility Definition of specific Viewpoints Discovery Manager Plug and orchestrate transformations Eclipse Modeling projects JSP ’ā╝Metamodel ’ā╝Discoverer ’ā╝Generator OMG/ADM Standards Pivot Metamodels (SMM & KDM) EclipsePlugin ’ā╝Metamodel ’ā╝Discoverer
- 4. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Model-Driven Reverse-Engineering of Eclipse plug-ins
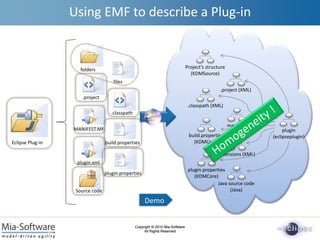
- 5. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Anatomy of an Eclipse 3.x Plug-in MANIFEST.MF plugin.xml Source code build.properties plugin.properties .project .classpath files folders Eclipse Plug-in
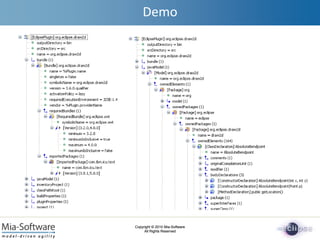
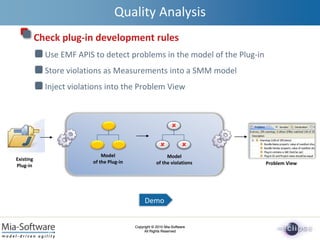
- 6. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Demo Using EMF to describe a Plug-in MANIFEST.MF plugin.xml Source code build.properties plugin.properties .project .classpath files folders Eclipse Plug-in ProjectŌĆÖs structure (KDMSource) .project (XML) .classpath (XML) manifest build.properties (KDMCore) plugin (eclipseplugin) Java source code (Java) plugin.properties (KDMCore) extensions (XML)
- 7. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Demo
- 8. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Demo
- 9. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Demo
- 10. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved What can you do with the EMF model of a plug-in ?
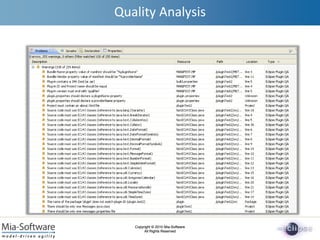
- 11. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Quality Analysis Check plug-in development rules Use EMF APIS to detect problems in the model of the Plug-in Store violations as Measurements into a SMM model Inject violations into the Problem View Existing Plug-in ’ā╗ ’ā╗ ’ā╗ Model of the Plug-in Model of the violations Problem View Demo
- 12. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Quality Analysis Examples of rules Yearly simultaneous release Version number ends with ┬½ qualifier ┬╗ Source code must use ICU4J classes The project must contain an ┬½ about.html ┬╗ file Packages name should start with the plug-in ID Plug-in must not contain JARs files Plug-in should contain only one ┬½ message.properties ┬╗ and ┬½ Message.java ┬╗ files Mia-Software internal rules ŌĆ£PLUGIN_IDŌĆØ variable of ŌĆ£Activator.javaŌĆØ should be initialized with the plug-in Id Plug-in Id and Project name should be equal ┬½Bundle-Vendor┬╗ property value of ┬½ MANIFEST.MF ┬╗ should be ┬½ %providerName ┬╗ ┬½ plugin.properties ┬╗ should declare a ┬½ providerName ┬╗ property ┬½Bundle-Name┬╗ property value of ┬½ MANIFEST.MF ┬╗ should be ┬½ %pluginName ┬╗ ┬½ plugin.properties ┬╗ should declare a ┬½ pluginName ┬╗ property
- 13. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Quality Analysis
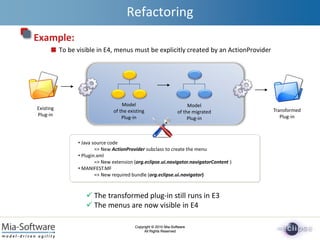
- 14. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved E4 Plug-in 3.x Plug-in Compatibility Layer Refactoring Runs Eclipse 3.x plug-ins into E4 Strategy #1: Generate an E4 Plug-in from a 3.x Plug-in Problem: The new plug-in canŌĆÖt run in 3.x => 2 plug-ins to maintain Strategy #2: Use the backward compatibility layer Problem: The compatibility layer doesnŌĆÖt support all the existing plug-ins A solution : Refactor the E3 plug-in for the backward compatibility layer 3.x
- 15. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Refactoring Example: To be visible in E4, menus must be explicitly created by an ActionProvider ŌĆó Java source code => New ActionProvider subclass to create the menu ŌĆó Plugin.xml => New extension (org.eclipse.ui.navigator.navigatorContent ) ŌĆó MANIFEST.MF => New required bundle (org.eclipse.ui.navigator) Transformed Plug-in Existing Plug-in Model of the existing Plug-in Model of the migrated Plug-in ’ā╝ The transformed plug-in still runs in E3 ’ā╝ The menus are now visible in E4
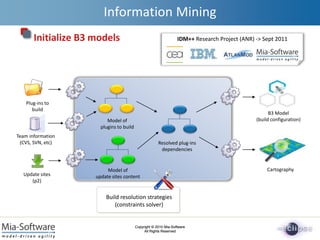
- 16. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Information Mining Initialize B3 models B3 Model (build configuration) Plug-ins to build Model of plugins to build Team information (CVS, SVN, etc) Update sites (p2) Model of update sites content Resolved plug-ins dependencies Build resolution strategies (constraints solver) Cartography IDM++ Research Project (ANR) -> Sept 2011
- 17. Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Copyright ┬® 2010 Mia-Software All Rights Reserved Thank you ! Eclipse projects http://www.eclipse.org/MoDisco/ http://www.eclipse.org/modeling/emft/facet/ Company http://www.mia-software.com/ http://www.sodifrance.fr/ Blog http://fmadiot.blogspot.com/
Editor's Notes
- #3: The approach we propose with MoDisco consists in creating fine-grained models from the different kinds of artifacts which compose an existing system. From these models we can extract specific viewpoints to understand the existing system. And these models can also be used to regenerate a new version of the system.
- #4: MoDisco is composed of several kinds of components. A first layer provides components which are completely independent from any legacy technology : a Discovery Manager, a Model Browser to navigate through complex models, several extensibility mechanisms to define viewpoints on models, and the implementation of OMG specification which can serve as pivot metamodels. On top these generic components Modisco provides components which are dedicated to specific legacy technologies.
- #17: The last example is about building plug-ins. We have recently started to work on this problem with CEA (the french nuclear agency), IBM and Atlanmod. The problem when you build a set of plug-ins is that, depending on the content of the update sites declared in your configuration, you donŌĆÖt know exactly which version of depending plug-ins will really be integrated. The default strategy takes the latest version available for each plugin. We are experimenting a solution, based on a constraint solver, to calculate build configurations depending on other strategies. Each build configuration can be converted into a B3 model or exported to a graphical cartography tool.