Migration
- 1. DEVELOPMENT & USE OF HUMAN RESOURCES
- 2. ’éĪ The movement of people from one place to another. ’éĪ The permanent relocation of people from one place to another. ’éĪ The temporary movement of people from one place to another. ’éĪ NB ŌĆōTemporary migration is not to be confused with COMMUTING!
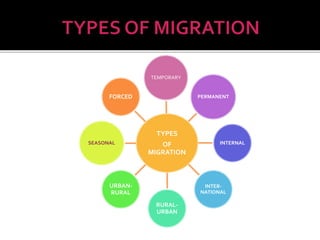
- 3. TEMPORARY TYPES OF MIGRATION PERMANENT INTERNAL INTER-NATIONAL RURAL-URBAN FORCED SEASONAL URBAN-RURAL
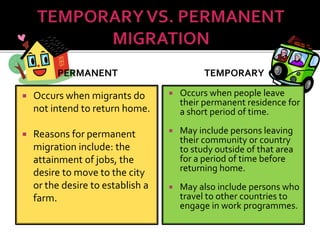
- 4. PERMANENT ’éĪ Occurs when migrants do not intend to return home. ’éĪ Reasons for permanent migration include: the attainment of jobs, the desire to move to the city or the desire to establish a farm. TEMPORARY ’éĪ Occurs when people leave their permanent residence for a short period of time. ’éĪ May include persons leaving their community or country to study outside of that area for a period of time before returning home. ’éĪ May also include persons who travel to other countries to engage in work programmes.
- 5. ’éĪ INTERNAL ’éĪ This refers to the movement of people from one area to another within a country. ’éĪ It may be either temporary or permanent ’éĪ Usually characterized by movement from rural areas to urban areas. ’éĪ Most likely consequence is urbanization
- 6. RURAL-TO-URBAN ’éĪ Movement from rural areas to urban areas ’éĪ Usually movement from farming communities to towns or cities ’éĪ Normally as a result of the low wages received in rural areas ’éĪ Has led to decline in demand for agricultural workers URBAN-TO- RURAL ’éĪ Occurs when people relocate to obtain jobs ’éĪ People are attracted to rural areas as they want to leave polluted cities ’éĪ People also leave urban areas as they want to get away from the outbreaks of violence or from being targeted by criminals
- 7. ’éĪ Rural-TO- RURAL ’éĪ Occurs when people move from one rural area to another rural area in search of work . ’éĪ If the land they are tending becomes unproductive. ’éĪ If agricultural land is taken over for another land use such as mining or development
- 8. ’éĪ External migration occurs when people move from one country to settle in another. ’éĪ It may be either permanent or temporary. ’éĪ Intra-regional migration- refers to movement within the Caribbean. ’éĪ Usually occurs for employment opportunities and pursuit of higher education. ’éĪ Most likely consequence is ŌĆ£brain drainŌĆØ
- 9. SEASONAL ’éĪ This is very common with agricultural cycles ’éĪ In Jamaica, people usually migrate to North America to reap crops such as apples, oranges, tomatoes. This is referred to as the farm work programme. ’éĪ Also, some people migrate seasonally to work in the hospitality industry. FORCED ’éĪ Also called deracination ’éĪ It is characterized by coerced movement of a person or persons from their home. ’éĪ Sometimes it is accompanied by religious and political persecution ’éĪ Example: Transatlantic Slave Trade
- 10. IMMIGRATION EMIGRATION ’éĪ Also called in-migration ’éĪ Describes movement into a country, island or region. ’éĪ It is often controlled strictly by government. ’éĪ It is usually permanent movement were the immigrant leaves the country of origin in order to find a new job. ’éĪ Also called out-migration ’éĪ Describes movement out of a country, island or region. ’éĪ It is not usually restricted by governments. ’éĪ It usually results in permanent settlement and application for citizenship in the new country.
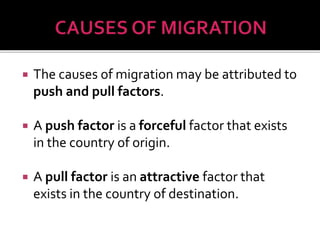
- 11. ’éĪ The causes of migration may be attributed to push and pull factors. ’éĪ A push factor is a forceful factor that exists in the country of origin. ’éĪ A pull factor is an attractive factor that exists in the country of destination.
- 12. ’éĪ Lack of jobs ’éĪ Political instability ’éĪ Poor medical facilities ’éĪ Lack of religious freedom ’éĪ Poor educational opportunities ’éĪ Financial stress ’éĪ Prevalence of natural disasters ’éĪ Lack of public amenities and utilities ’éĪ Infertile land ’éĪ Job opportunities ’éĪ Better living conditions ’éĪ Political & religious freedom ’éĪ Better healthcare ’éĪ Higher quality education ’éĪ Social & financial security ’éĪ Family reunion ’éĪ Modern infrastructure ’éĪ More reliable source of food
- 13. ’ü▒ Migration carries with it numerous consequences for both the host/receiving country and the country of origin as well as on an individual level. ’ü▒ Consequences may be either positive or negative ’ü▒ Effects of migration may also be categorized as social, political or economic
- 14. POSITIVE ’éĪ ŌĆ£Brain GainŌĆØ ’éĪ Cultural diversity ’éĪ Increase in labour force ’éĪ Growth in total population ’éĪ Expansion of industries NEGATIVE ’éĪ Greater pressure on resources of the country ’éĪ Greater pressure on social services of the country ’éĪ Growth in total population ’éĪ Financial resources exported outside of country
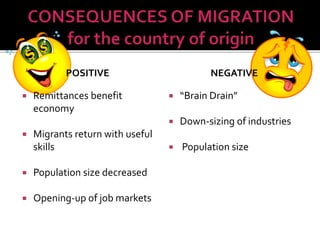
- 15. POSITIVE ’éĪ Remittances benefit economy ’éĪ Migrants return with useful skills ’éĪ Population size decreased ’éĪ Opening-up of job markets NEGATIVE ’éĪ ŌĆ£Brain DrainŌĆØ ’éĪ Down-sizing of industries ’éĪ Population size
- 16. POSITIVE ’éĪ Increase in income ’éĪ New cultural experience ’éĪ Learning new skills ’éĪ Better educational and health facilities ’éĪ Greater access to recreational facilities NEGATIVE ’éĪ Family instability ’éĪ Burden of dependency ’éĪ Culture shock
- 17. ’éĪ This is usually as a result of rural to urban migration ’éĪ Human movement to more central locations lead to expansion into the surrounding countryside ’éĪ Such movement has a number of consequences
- 18. ’éĪ Inadequate housing ’éĪ Development of slums ’éĪ Underemployment ’éĪ increase in unemployment levels ’éĪ Increase in social unrest and crime ’éĪ Poor sanitation ’éĪ Pests and diseases ’éĪ Pollution