Migration in fishes
- 1. FISH MIGRATION Submitted by :- ANURADHA NASKAR (MFSc. 1st Sem.) DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY AND APPLIED AQUACULTURE BARKATULLAH UNIVERSITY, BHOPAL MADHYA PRADESH, 462026
- 2. CONTENTS ? INTRODUCTION ? DEFINITION OF MIGRATION ? MIGRATORY SPECIES ? TYPES OF FISH MIGRATION ? PATTERNS OF FISH MIGRATION ? CAUSES OF FISH MIGRATION ? FACTORS INFLUENCING MIGRATION ? ADVANTAGES OF MIGRATION ? CONCLUSION
- 3. INTRODUCTION Generally fishes restrict their movements within small territorial limits and do not go out of their home range. Some species travel long distances moving from place to place for food or for breeding. Migration may take place in vertical direction or horizontal direction. Some species are able to attain great speed, others swim slowly but travel long distance. Some species migrate within the fresh or marine water, others may move from fresh water to marine water and vice versa.
- 4. DEFINITION OF MIGRATION ? Thompson (1952) ĻC Ą°A true migration as seasonal movement that implies return to the starting point.Ąą ? Baker (1978) ĻC Ą° The act of moving from one spatial unit to another.Ąą ? Dingle (1980) ĻC Ą°Specialized behavior especially evolved for the displacement of the individual in space.Ąą ? In general ĻC Migration of fish defined as a class of movement which involves a long journey to a definite area for some purpose and impels the migrants to return to the region from which they have migrated.
- 5. MIGRATORY SPECIES ? The cod (Gadus morhua) ? Herrings (Clupea harengus) ? Salmon (Salmo sp.) ? Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus) ? TheTunnas (Thunnus thynnus) ? Eel (Anguilla sp.) ? Hilsa (Hilsa ilisha)
- 6. TYPES OF FISH MIGRATION Migration can be any one of the following types :- ? Climatic migration, undertaken to search better climatic and environmental conditions. ? Gametic migration, is undertaken for spawning. ? Alimental migration, is undertaken in search of food and water.
- 7. PATTERNS OF FISH MIGRATION The following terms are generally used to describe the patterns of migration :- ? Diadromous migration : In this type of migration pattern fishes move between sea and freshwater and can be of 3 types :- 1. Anadromous migration 2. Catadromous migration 3. Amphidromous migration
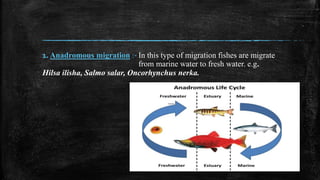
- 8. 1. Anadromous migration :- In this type of migration fishes are migrate from marine water to fresh water. e.g. Hilsa ilisha, Salmo salar, Oncorhynchus nerka.
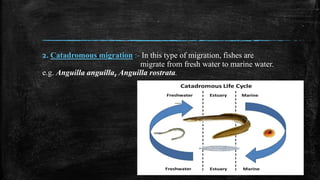
- 9. 2. Catadromous migration :- In this type of migration, fishes are migrate from fresh water to marine water. e.g. Anguilla anguilla, Anguilla rostrata.
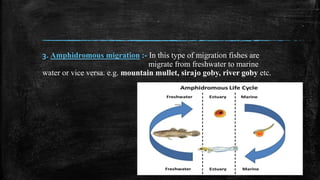
- 10. 3. Amphidromous migration :- In this type of migration fishes are migrate from freshwater to marine water or vice versa. e.g. mountain mullet, sirajo goby, river goby etc.
- 11. ? Potamodromous migration : In these type of migration pattern migratory fishes remain confined to fresh water. e.g. carps and trouts etc.
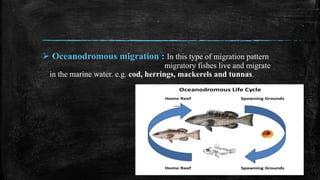
- 12. ? Oceanodromous migration : In this type of migration pattern migratory fishes live and migrate in the marine water. e.g. cod, herrings, mackerels and tunnas.
- 13. CAUSES OF MIGRATION Fish appear to migrate ? to avoid unfavourable conditions, ? to enhance the chances of survival of the offsprings, and ? to exploit the available food in feeding areas. ? Population pressure is also considered a possible cause of migration. The fish migrate in search of new suitable areas where food is abundant and competition is minimum.
- 14. FACTORS INFLUENCING MIGRATION ? Physical Factors ĻC bottom materials, depth of water, temperature, light intensity, turbidity etc. ? Chemical Factors ĻC salinity, pH, smell and taste of water. ? Biological Factors ĻC food, sexual maturity etc.
- 15. ADVANTAGES OF MIGRATION ? Advantages :- 1) Fish get more food, better climatic condition and breeding place. 2) Fish gets better adapting in new places. 3) There will be wide distribution. 4) Less competition.
- 16. CONCLUSION The migration route and pattern is now clearly known to us. Fishes generally employment and income for millions of people in world. Fish remains a subsistence food for many poor coastal communities. ThatĄŊs why we must save this resources by stopping to capture this fish species during migration periods. We must give chance to fish species to grow up willingly. So we can enrich with this natural resources and can able to export fish species by fulfilling our countries demand. That help us in future implementation.
- 17. Thank You