Mirrors ppt
- 1. Mirrors By: Bailey Griggs and Katie Kennedy
- 2. Objectives • Mirrors o Distinguish between Concave and Convex mirrors. o Describe a simple ray diagram. o Distinguish between real and virtual images.
- 3. Mirrors Outline • Types of Mirrors o Convex o Concave o Spherical o Parabolic • Convex Mirrors o How light reflects o Examples
- 4. Mirrors • Concave o How light reflects o Examples • Simple Ray Diagram o Explanation and Examples • Real vs. Virtual Images o Real Images o Virtual Images • Demonstrations • Evaluation Questions
- 5. We are going to explore how concave and convex mirrors work along with describing the simple ray diagrams that go along with each one. We will also discuss the real and/or virtual images that both of these mirrors produce.
- 6. Different Types of Mirrors Convex Concave Spherical Parabolic
- 7. Straight or Plane mirror
- 9. Concave
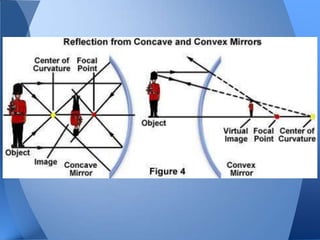
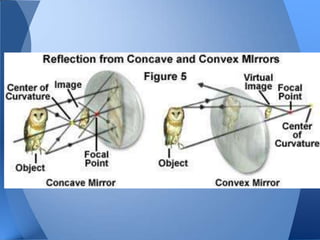
- 10. Concave • Reflection • Curved inward reflective surface • Used to magnify • Produces Real and Virtual Images o depend on object’s distance from the surface of the mirror and the focal length.
- 12. Convex
- 13. Convex • Reflection • Image is small or reduced in size • Image is upright • Image is located behind the convex mirror • Image is always virtual
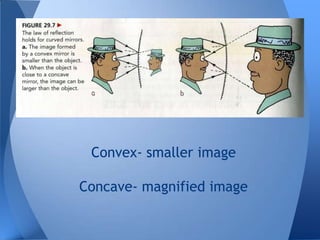
- 15. Convex- smaller image Concave- magnified image
- 17. Simple Ray Diagram • Tool used to determine o location o size o orientation o type of image formed Real or Virtual •
- 18. • Straight/ Plane mirror • Extended Reflected Rays make up image • Behind the mirror
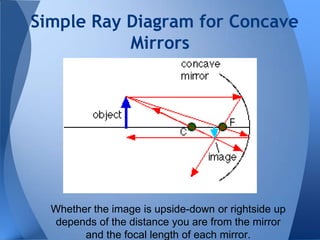
- 19. Simple Ray Diagram for Concave Mirrors Whether the image is upside-down or rightside up depends of the distance you are from the mirror and the focal length of each mirror.
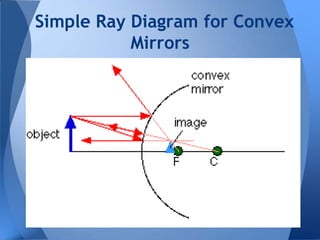
- 20. Simple Ray Diagram for Convex Mirrors
- 23. Real vs. Virtual Images • • Virtual image o Object is less than the focal length of the mirror o Can only be seen by looking at the mirror, not projected Real Image o object is further than focal length of mirror o Can be projected and everyone in the room can look at it
- 26. Evaluation Question #1 Which mirror produces an image behind the mirror, Concave or Convex? Convex
- 27. Evaluation Question #2 True or False: Concave mirrors are used to magnify images. True
- 28. Evaluation Question #3 A _____________ mirror takes a large space and makes it small. Convex
- 29. Evaluation Question #4 An image that is produced that is less than the focal length of the mirror is a ______________ image. Virtual
- 30. Evaluation Question #5 A ______________ image can be projected. Real
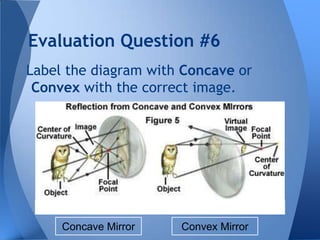
- 31. Evaluation Question #6 Label the diagram with Concave or Convex with the correct image. Concave Mirror Convex Mirror
- 32. Evaluation Question #7 The point at which the extensions of the reflected rays intersect is the _________ of the image being produced. a. Bottom b. Top c. Center
- 33. Evaluation Question #8 Concave mirrors produce: a. Real Images b. Virtual Images c. Both
- 34. Bibliography Flinn, G. (n.d.). HowStuffWorks "Types of Mirrors". HowStuffWorks "Science". Retrieved October 21, 2013, from http://science.howstuffworks.com/innovation/everyday-innovations/mirror3.htm Flinn, G. (n.d.). HowStuffWorks "Types of Mirrors". HowStuffWorks "Science". Retrieved October 21, 2013, from http://science.howstuffworks.com/innovation/everyday-innovations/mirror3.htm Henderson, T. (n.d.). Reflection and Image Formation for Convex Mirrors. The Physics Classroom. Retrieved October 21, 2013, from http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/u13l4a.cfm Hewitt, P. G. (2002). Conceptual physics: the high school physics program. Needham, Mass.: Prentice Hall. Moore, C. (n.d.). Concave and Convex Mirrors. More House. Retrieved October 18, 2013, from https://www.morehouse.edu/facstaff/cmoor