MITOCHONDRIA- THE POWER HOUSE OF THE CELL
- 1. CELL ORGANELLES DR. HIMANI SINGH M.Sc., Ph.D BIOTECHNOLOGY MITOCHONDRIA
- 2. MITOCHONDRIA ’éø The mitochondria is a double membrane- bound organelle found eukaryotic cells, mito= thread chondrion = granule likE ’éø Called Power house of cell and found in cytoplasm of the cell. ’éø Firstly observed by Richard Altman (1894) and term mitochondria was coined by Carl Benda (1898) ’éø The primary function of which is to generate large quantities of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to fuel the cells activities. The function known as aerobic respiration is the reason mitochondria are frequently referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. Aerobic respiration involves: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle ’éø In addition to producing energy, mitochondria store calcium for cell signaling activities, generate heat, and mediate cell growth and death.
- 4. SIZE AND MORPHOLOGY ’éøDIAMETER: Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 ╬╝m in diameter. ’éøSHAPE: normally Sausage shaped, In fibroblasts-elongated and thread like ’éøNUMBER: Depends on type size and functional state of cell. Eg: An average liver cells contain around 1500 mitochondria. ’éøLOCATION: Cells with high energy requirements. Eg: Sperm tail, Muscle, Flagella
- 5. STRUCTURE MITOCHONDRIA DIVIDED INTO FIVE PARTS 1. Outer Membrane 2. Intermembrane Space 3. Inner Membrane 4. Cristae 5. Matrix They are double membrane bound organelle with their own DNA and ribosomes. Outer Membrane- covers the organelle, freely permeable. Inner Membrane- contains extensive folding called cristae. Intermembrane ŌĆō space between outer & inner membrane. Contains cytoplasm. Matrix- within the Inner Membrane. Contains various proteins and enzymes.
- 6. OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION The respiratory chain and oxidative
- 7. INNER MEMBRANE ’éø Simple phospholipid bilayer. Its encloses the mitochondrian. ’éø Contain large number of integral protein structures called porins, which allows molecules to freely diffuse from one side of the membrane to the other. ’éø Porins pass molecules less then 5000 D. ’éø Ions, nutrient molecules, ATP, ADP etc can pass through the outer membrane with ease. ’éø The outer mitochondrial membrane is composed of about 50% INTER MEMBRANE SPACE ’éø It is also known as Perimitochondrial space. ’éø It is a space between inner membrane and outer membrane, is approximately 70 A. ’éø It has high proton concentration. ’éø Because the outer membrane is freely permeable to small molecules, the concentration of small molecules such as ions and sugars in the intermembrane space is same as that of the cytosol. ’éø Proteins present, participate in ATP synthesis
- 8. INNER MEMBRANE ’éø Is freely permeable only to oxygen, COŌéé , HŌééO. ’éø The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins that perform redox reactions in oxidative phosphorylation, ATP synthase, transport proteins, protein import machinery, mitochondria fusion and fission protein. ’éø Several antiport systems exist , allowing exchange of anions between the cytosol and the mitochondrial CRISTAE ’éø Are folds of inner mitochondrial membrane, which expand its surface area , enhancing its ability to produce ATP. ’éø Stalked particles or inner membrane spheres : cristae is covered with this inner membrane spheres called stalked particles or knobs or heads.
- 9. MATRIX ’éøIt is the space enclosed by the inner membrane. ’éøGel like consistency, Dense, homogenous. ’éøContains 2/3 rd of total protein of mitochondria. ’éøMatrix have enzymes, DNA genome, ribosomes, t-RNA, granules, fibrils and tubules. ’éøThe matrix is important in the production of ATP with the aid of the ATP synthase contained in the inner membrane. ’éøMajor enzymes include enzymes involved in Synthesis of nucleic acid and proteins, fatty acid oxidation, TCA cycle
- 10. FUNCTIONS ’éø Aerobic respiration ŌĆō Mitochondria uses complex molecules and oxygen to produce a higher energy molecule known as ATP. ’éø Mitochondria are more abundant in the cell that contain a lot of energy. Eg: muscle. ’éø Extra mitochondrial inheritance: mt-DNA contains plasma genes. ’éø Synthesis of mt-DNA , RNA, protein. ’éø Bring about gene expression through gene duplication transcription and translation. ’éø Synthesis 13 different polypeptides in human. ’éø Production of heat (non shivering thermogenesis). ’éø Role in apoptosis (programmed cell death). ’éø Synthesis of estrogen and testosterone. ’éø Role in neurotransmitter metabolism. ’éø Role on cholesterol metabolism. ’éø Role in heme synthesis.
- 11. SITE OF SEVERAL METABOLIC REACTIONS OUTER MEMBRANE ŌĆóOxidation of epinephrine ŌĆóDegradation of tryptophan ŌĆóElongation of fatty acid ŌĆóKrebŌĆÖs cycle Beta oxidation ŌĆóDetoxification of ammonia in urea cycle ŌĆóStorage of calcium ions MATRIX ŌĆóOxidative phosphorylati on INNER MEMBRANE
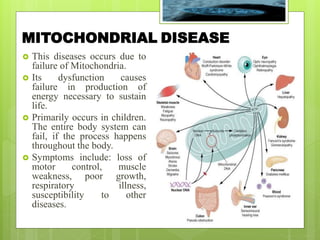
- 12. MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE ’éø This diseases occurs due to failure of Mitochondria. ’éø Its dysfunction causes failure in production of energy necessary to sustain life. ’éø Primarily occurs in children. The entire body system can fail, if the process happens throughout the body. ’éø Symptoms include: loss of motor control, muscle weakness, poor growth, respiratory illness, susceptibility to other diseases.