Mitochondria/chemiosmosis presentation
- 1. Mitochondria andMitochondria and ChemiosmosisChemiosmosis Steven GuilfoySteven Guilfoy Fleck CadeauFleck Cadeau Purveena DoobayPurveena Doobay
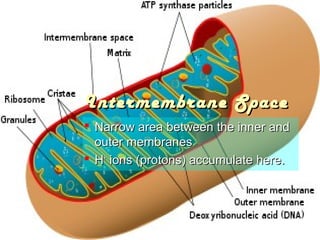
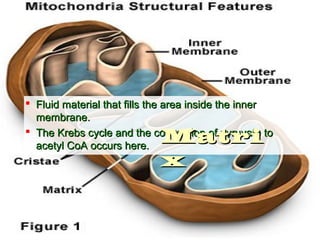
- 2. Parts of the MitochondriaParts of the Mitochondria  Outer MembraneOuter Membrane  Intermembrane SpaceIntermembrane Space  Inner MembraneInner Membrane  MatrixMatrix
- 3.  Like the plasma membrane •Consists of double layer of phospholipids
- 4. Intermembrane SpaceIntermembrane Space  Narrow area between the inner andNarrow area between the inner and outer membranesouter membranes  HH++ ions (protons) accumulate here.ions (protons) accumulate here.
- 5.  Also double phospholipid layerAlso double phospholipid layer  Oxidative phosphorylation occurs hereOxidative phosphorylation occurs here  Has convolutions called cristaeHas convolutions called cristae  The electron transports removes electrons from NADH andThe electron transports removes electrons from NADH and FADHFADH22 HH++ ions from the matrix to the intermembrane spaceions from the matrix to the intermembrane space  Another protein complex, ATP synthase, is responsible forAnother protein complex, ATP synthase, is responsible for the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATPthe phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP
- 6.  Fluid material that fills the area inside the innerFluid material that fills the area inside the inner membrane.membrane.  The Krebs cycle and the conversion of pyruvate toThe Krebs cycle and the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA occurs here.acetyl CoA occurs here. MatriMatri xx
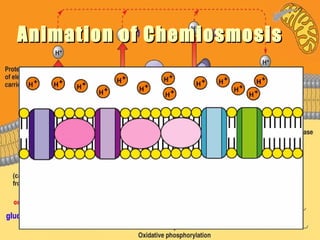
- 7. Chemiosmosis inChemiosmosis in MitochondriaMitochondria  Oxidation PhosphorylationOxidation Phosphorylation  Krebs Cycle produce NADH and FADHKrebs Cycle produce NADH and FADH22  Electrons are removed from NADH andElectrons are removed from NADH and FADHFADH22  H+ ions are transported to intermembraneH+ ions are transported to intermembrane  pH and electrical gradient are createdpH and electrical gradient are created  ATP sythase generates ATPATP sythase generates ATP
- 8. Oxidation PhosporylationOxidation Phosporylation in Mitochondriain Mitochondria Krebs cycle produces NADH and FADHKrebs cycle produces NADH and FADH22 in the matrix, COin the matrix, CO22 isis generated in process of producing ATP.generated in process of producing ATP. Protein complex in inner membrane removes electrons from NADHProtein complex in inner membrane removes electrons from NADH and FADHand FADH22 Protein complexes transport HProtein complexes transport H++ ions form matrix to theions form matrix to the intermembrane space.intermembrane space. A pH and electrical gradient are created across the innerA pH and electrical gradient are created across the inner membrane by Hmembrane by H++ into the intermembrane space.into the intermembrane space.CC Channel Protein assist ATP synthase by allowing protons inChannel Protein assist ATP synthase by allowing protons in intermembrane to flow back into matrix.intermembrane to flow back into matrix.
- 9. Animation of ChemiosmosisAnimation of Chemiosmosis
- 10. Animation of ChemiosmosisAnimation of Chemiosmosis