MLGG_for_linkedIn
- 1. Manuel L. Gonzalez-Garay, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, The Center for Research and Development in Health Sciences (CIDICS). Universidad AutÃģnoma de Nuevo LeÃģn. September 18, 2015 (Host: Dr. Steven Norris) Progress toward Genomic and Precision Medicine at UTHealth CIDICS
- 2. Research projects at UTHealth (2009-2015) Project Collaborator(s) YPO Project (81 healthy individuals) Dr. Thomas Caskey Genetics of Schizophrenia and Bipolar Drs. Caskey, Soares, Escamilla Genetics of lymphedema Dr. Eva Sevick Ongoing 2 publications, 2 manuscripts Genetics of Prader-Willi and Autism Drs. Schaaf & Beaudet Dercum's disease Familial multiple lipomatosis Lipedema Madelungâs disease Dr. Karen L. Herbst (Tucson, AZ) Completed 1 manuscript, transferred to UA Rare genetic disorders Inherited hearing disorders Inherited eye disorders Inherited panic disorders Sporadic leucodystrophy Actinic prurigo in Native Americans âĒ Dr. Felipe H. Sandoval-AvilÃĐs âĒ Dr. Miguel ValdÃĐs-Adamchik âĒ Dr. Ricardo Salinas-Ruiz âĒ Dr. Sergio A. Cuevas-Covarrubias âĒ Dr. Augusto Rojas-MartÃnez âĒ Dr. RocÃo Ortiz-LÃģpez WGS Rats with hypertension and kidney failure Dr. Peter Doris Ongoing 2 Publications WGS Induced pluripotential stem cells Dr. Brian Davis Completed 1 publication, 1 manuscript Tuberous sclerosis, Spina bifida Drs. Hope Northrup & Au, Kit-Sing Completed pending manuscripts Differential expression of Candida sp during Infection Dr. Michael Lorenz Completed pending manuscript Completed 3 publications Completed 1 publications Ongoing, transferred to UANL
- 3. Personalized Precision Medicine 99.93 % Similarity between humans 4 million genetic variants per person (against the human template) The use of an individual's genetic profile to guide decisions made in regard to the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disease. Knowledge of a patient's genetic profile can help doctors select the proper medication or therapy and administer it using the proper dose or regimen.
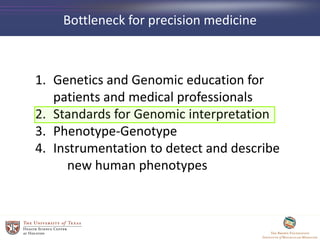
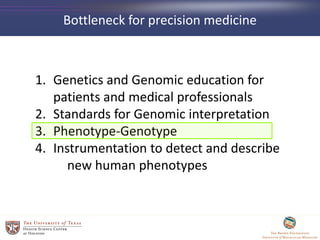
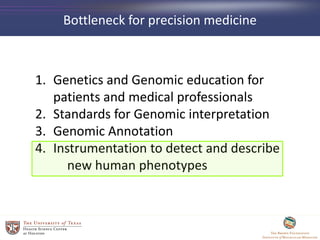
- 4. Bottleneck for precision medicine 1. Genetics and Genomic education for patients and medical professionals 2. Standards for Genomic interpretation 3. Phenotype-Genotype 4. Instrumentation to detect and describe new human phenotypes
- 5. Increasing number of aging adults âĒ We decided to explore the use of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) to provide genetic discoveries to adults âĒ What is the practical value of NGS information for healthy volunteers? âĒ What are the challenges and barriers to the adoption of this powerful technology into medical practice? HCM/DCM/ARVC STROKE ALZHEIMER PARKINSON Other disorders Medicine treats pathologies
- 6. Experimental Design âĒ Genome Education Program (The Cullen Trust for Higher Education) 2009. â Educate Patients and their physicians about genetics âĒ Young Presidentsâ Organization YPO â Requested a education program for their members for their annual competition âĒ Organized with Houston Chapter: 450 members. âĒ Education Conference Day: >150 attendees â Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM), UTHealth at Houston. âĒ IRB approved volunteer protocol âNeed to know resultsâ: 81 volunteers. âĒ Whole Exon sequencing. âĒ Medical report focused on causative alleles for Mendelian disorders. âĒ All participants require a face to face meeting with our genetic counselor [CTC] (medical history and 3 generation pedigree) âĒ A second individual genetic counseling session to discuss the written reports.
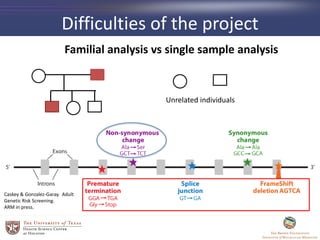
- 7. Difficulties of the project Familial analysis vs single sample analysis Unrelated individuals Caskey & Gonzalez-Garay. Adult Genetic Risk Screening. ARM in press.
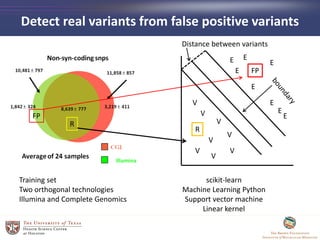
- 8. Detect real variants from false positive variants Training set Two orthogonal technologies Illumina and Complete Genomics FP R scikit-learn Machine Learning Python Support vector machine Linear kernel R FP Distance between variants V V V V V V V E E EE E E E E V
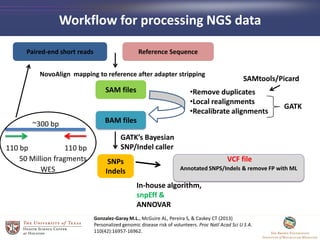
- 9. Workflow for processing NGS data Annotated SNPS/Indels & remove FP with ML SNPs Indels SAM files Reference Sequence NovoAlign mapping to reference after adapter stripping GATKâs Bayesian SNP/Indel caller BAM files âĒRemove duplicates âĒLocal realignments âĒRecalibrate alignments In-house algorithm, snpEff & ANNOVAR GATK Paired-end short reads SAMtools/Picard Gonzalez-Garay M.L., McGuire AL, Pereira S, & Caskey CT (2013) Personalized genomic disease risk of volunteers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110(42):16957-16962. ~300 bp 110 bp 110 bp 50 Million fragments WES VCF file
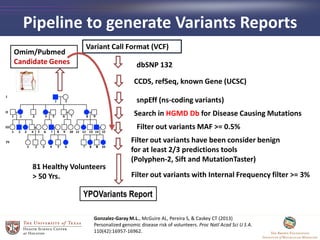
- 10. Pipeline to generate Variants Reports YPOVariants Report dbSNP 132 CCDS, refSeq, known Gene (UCSC) snpEff (ns-coding variants) Filter out variants with Internal Frequency filter >= 3% Search in HGMD Db for Disease Causing Mutations Filter out variants MAF >= 0.5% Filter out variants have been consider benign for at least 2/3 predictions tools (Polyphen-2, Sift and MutationTaster) Omim/Pubmed Candidate Genes Variant Call Format (VCF) Gonzalez-Garay M.L., McGuire AL, Pereira S, & Caskey CT (2013) Personalized genomic disease risk of volunteers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110(42):16957-16962. 81 Healthy Volunteers > 50 Yrs.
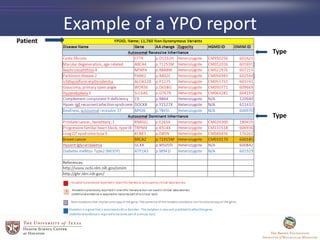
- 11. Example of a YPO report Patient Type Type
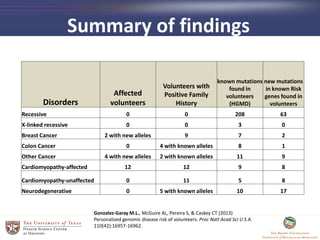
- 12. Disorders Affected volunteers Volunteers with Positive Family History known mutations found in volunteers (HGMD) new mutations in known Risk genes found in volunteers Recessive 0 0 208 63 X-linked recessive 0 0 3 0 Breast Cancer 2 with new alleles 9 7 2 Colon Cancer 0 4 with known alleles 8 1 Other Cancer 4 with new alleles 2 with known alleles 11 9 Cardiomyopathy-affected 12 12 9 8 Cardiomyopathy-unaffected 0 11 5 8 Neurodegenerative 0 5 with known alleles 10 17 Summary of findings Gonzalez-Garay M.L., McGuire AL, Pereira S, & Caskey CT (2013) Personalized genomic disease risk of volunteers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110(42):16957-16962.
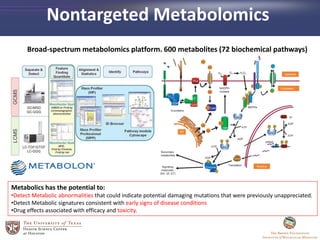
- 13. Nontargeted Metabolomics Broad-spectrum metabolomics platform. 600 metabolites (72 biochemical pathways) Metabolics has the potential to: âĒDetect Metabolic abnormalities that could indicate potential damaging mutations that were previously unappreciated. âĒDetect Metabolic signatures consistent with early signs of disease conditions âĒDrug effects associated with efficacy and toxicity.
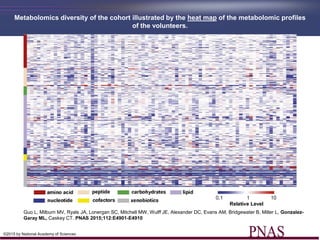
- 14. Metabolomics diversity of the cohort illustrated by the heat map of the metabolomic profiles of the volunteers. Guo L, Milburn MV, Ryals JA, Lonergan SC, Mitchell MW, Wulff JE, Alexander DC, Evans AM, Bridgewater B, Miller L, Gonzalez- Garay ML, Caskey CT. PNAS 2015;112:E4901-E4910 ÂĐ2015 by National Academy of Sciences
- 15. Work flow for searching WES data and metabolomics convergence. ÂĐ2015 by National Academy of Sciences Guo L, Milburn MV, Ryals JA, Lonergan SC, Mitchell MW, Wulff JE, Alexander DC, Evans AM, Bridgewater B, Miller L, Gonzalez- Garay ML, Caskey CT. PNAS 2015;112:E4901-E4910
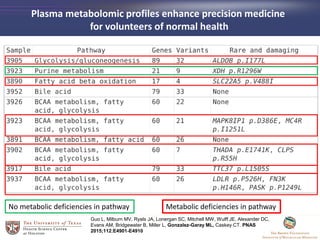
- 16. Plasma metabolomic profiles enhance precision medicine for volunteers of normal health No metabolic deficiencies in pathway Metabolic deficiencies in pathway Guo L, Milburn MV, Ryals JA, Lonergan SC, Mitchell MW, Wulff JE, Alexander DC, Evans AM, Bridgewater B, Miller L, Gonzalez-Garay ML, Caskey CT. PNAS 2015;112:E4901-E4910
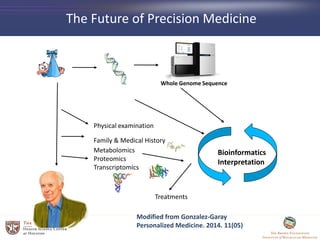
- 17. Whole Genome Sequence Family & Medical History Physical examination Treatments Bioinformatics Interpretation Metabolomics Proteomics Transcriptomics Modified from Gonzalez-Garay Personalized Medicine. 2014. 11(05) The Future of Precision Medicine
- 18. Bottleneck for precision medicine 1. Genetics and Genomic education for patients and medical professionals 2. Standards for Genomic interpretation 3. Phenotype-Genotype 4. Instrumentation to detect and describe new human phenotypes
- 19. An international effort towards developing standards for best practices in analysis, interpretation and reporting of clinical genome sequencing results in the CLARITY Challenge Genome Biol. 2014 Mar 25;15(3):R53. Best practices for studying the genome 2012 32 international groups 23 finished the contest Centronuclear myopathy Cardiac conduction defects Centronuclear myopathy
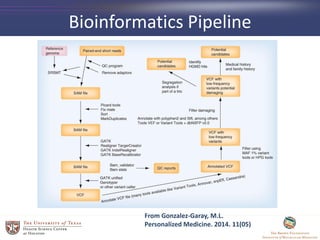
- 20. Bioinformatics Pipeline From Gonzalez-Garay, M.L. Personalized Medicine. 2014. 11(05)
- 21. Bottleneck for precision medicine 1. Genetics and Genomic education for patients and medical professionals 2. Standards for Genomic interpretation 3. Phenotype-Genotype 4. Instrumentation to detect and describe new human phenotypes
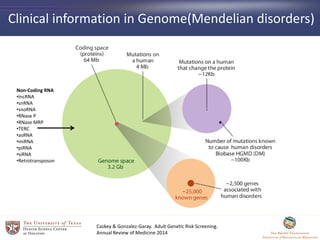
- 22. Clinical information in Genome(Mendelian disorders) Caskey & Gonzalez-Garay. Adult Genetic Risk Screening. Annual Review of Medicine 2014 Non-Coding RNA âĒlncRNA âĒsnRNA âĒsnoRNA âĒRNase P âĒRNase MRP âĒTERC âĒasRNA âĒmiRNA âĒpiRNA âĒsiRNA âĒRetrotransposon
- 23. Rare Genetic Disorders ~7,315 different rare diseases and disorders affecting > 300 million people worldwide *prevalence of less than 200,000 cases in the USA âž300 new Mendelian phenotypes are added to OMIM each year
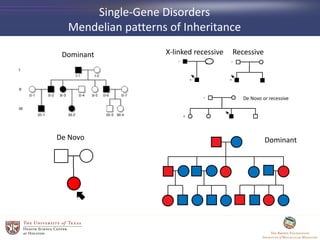
- 24. Single-Gene Disorders Mendelian patterns of Inheritance Dominant De Novo RecessiveX-linked recessive De Novo or recessive Dominant
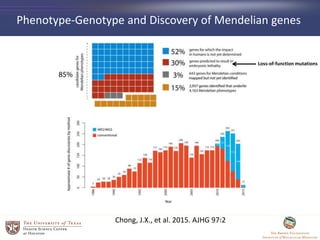
- 25. Phenotype-Genotype and Discovery of Mendelian genes Chong, J.X., et al. 2015. AJHG 97:2 Loss-of-function mutations
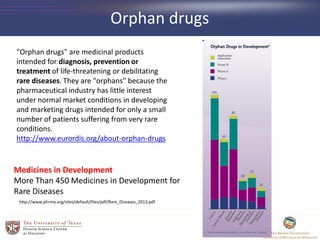
- 26. Orphan drugs "Orphan drugs" are medicinal products intended for diagnosis, prevention or treatment of life-threatening or debilitating rare diseases. They are "orphans" because the pharmaceutical industry has little interest under normal market conditions in developing and marketing drugs intended for only a small number of patients suffering from very rare conditions. http://www.eurordis.org/about-orphan-drugs Medicines in Development More Than 450 Medicines in Development for Rare Diseases http://www.phrma.org/sites/default/files/pdf/Rare_Diseases_2013.pdf
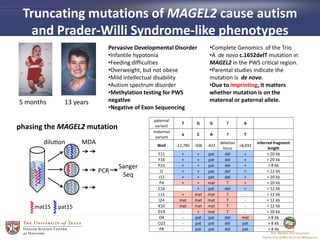
- 27. Truncating mutations of MAGEL2 cause autism and Prader-Willi Syndrome-like phenotypes 5 months 13 years Pervasive Developmental Disorder âĒInfantile hypotonia âĒFeeding difficulties âĒOverweight, but not obese âĒMild intellectual disability âĒAutism spectrum disorder âĒMethylation testing for PWS negative âĒNegative of Exon Sequencing âĒComplete Genomics of the Trio âĒA de novo c.1652delT mutation in MAGEL2 in the PWS critical region. âĒParental studies indicate the mutation is de novo. âĒDue to imprinting, it matters whether mutation is on the maternal or paternal allele. paternal variant T G G ? A maternal variant a C A ? T Well -12,785 -506 -422 deletion locus +8,032 inferred fragment length F11 + + pat del + > 20 kb F16 + + pat del + > 20 kb P23 + + pat del + > 8 kb I2 + + pat del + > 12 kb J12 + + pat del + > 20 kb P4 + + mat T + > 20 kb C16 - + pat del + > 12 kb L11 + mat mat T - > 12 kb I24 mat mat mat T - > 12 kb K10 mat mat mat T - > 12 kb D19 - + mat T - > 20 kb O4 - pat pat del mat > 8 kb O23 - pat pat del pat > 8 kb P8 - pat pat del pat > 8 kb phasing the MAGEL2 mutation
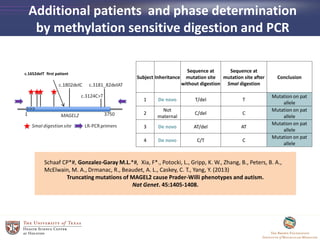
- 28. Additional patients and phase determination by methylation sensitive digestion and PCR Subject Inheritance Sequence at mutation site without digestion Sequence at mutation site after SmaI digestion Conclusion 1 De novo T/del T Mutation on pat allele 2 Not maternal C/del C Mutation on pat allele 3 De novo AT/del AT Mutation on pat allele 4 De novo C/T C Mutation on pat allele c.1652delT first patient Schaaf CP*#, Gonzalez-Garay M.L.*#, Xia, F*., Potocki, L., Gripp, K. W., Zhang, B., Peters, B. A., McElwain, M. A., Drmanac, R., Beaudet, A. L., Caskey, C. T., Yang, Y. (2013) Truncating mutations of MAGEL2 cause Prader-Willi phenotypes and autism. Nat Genet. 45:1405-1408.
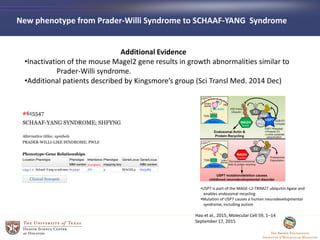
- 29. Additional Evidence âĒInactivation of the mouse Magel2 gene results in growth abnormalities similar to Prader-Willi syndrome. âĒAdditional patients described by Kingsmoreâs group (Sci Transl Med. 2014 Dec) New phenotype from Prader-Willi Syndrome to SCHAAF-YANG Syndrome âĒUSP7 is part of the MAGE-L2-TRIM27 ubiquitin ligase and enables endosomal recycling âĒMutation of USP7 causes a human neurodevelopmental syndrome, including autism Hao et al., 2015, Molecular Cell 59, 1â14 September 17, 2015
- 30. Bottleneck for precision medicine 1. Genetics and Genomic education for patients and medical professionals 2. Standards for Genomic interpretation 3. Genomic Annotation 4. Instrumentation to detect and describe new human phenotypes
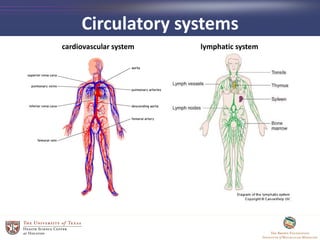
- 31. Circulatory systems cardiovascular system lymphatic system
- 32. Lymphedema
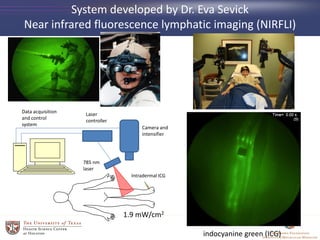
- 33. Camera and intensifier Laser controller 785 nm laser Data acquisition and control system Intradermal ICG 1.9 mW/cm2 System developed by Dr. Eva Sevick Near infrared fluorescence lymphatic imaging (NIRFLI) indocyanine green (ICG)
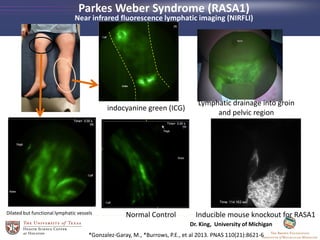
- 34. *Gonzalez-Garay, M., *Burrows, P.E., *Rasmussen, J.C., Aldrich, M.E., Guilloid, R., Maus, E.A., Fife, C.E., Kwon., S., Lapinski, P.E., King. P.D., and E.M. Sevick- Muraca, âLymphatic abnormalities are associated with RASA1 mutations in mouse and man,â PNAS, 2013 21;110(21):8621-6 Parkes Weber Syndrome Capillary malformations and arteriovenous fistulas Paradominant inheritance model
- 35. Dilated but functional lymphatic vessels Normal Control Lymphatic drainage into groin and pelvic region *Gonzalez-Garay, M., *Burrows, P.E., et al 2013. PNAS 110(21):8621-6 Inducible mouse knockout for RASA1 indocyanine green (ICG) Parkes Weber Syndrome (RASA1) Near infrared fluorescence lymphatic imaging (NIRFLI) Dr. King, University of Michigan
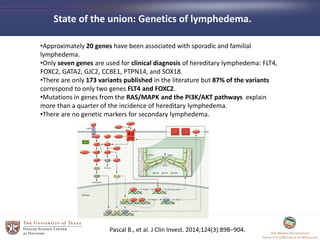
- 36. âĒApproximately 20 genes have been associated with sporadic and familial lymphedema. âĒOnly seven genes are used for clinical diagnosis of hereditary lymphedema: FLT4, FOXC2, GATA2, GJC2, CCBE1, PTPN14, and SOX18. âĒThere are only 173 variants published in the literature but 87% of the variants correspond to only two genes FLT4 and FOXC2. âĒMutations in genes from the RAS/MAPK and the PI3K/AKT pathways explain more than a quarter of the incidence of hereditary lymphedema. âĒThere are no genetic markers for secondary lymphedema. State of the union: Genetics of lymphedema. Pascal B., et al. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(3):898â904.
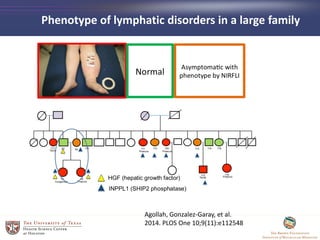
- 37. Phenotype of lymphatic disorders in a large family Agollah, Gonzalez-Garay, et al. 2014. PLOS One 10;9(11):e112548
- 38. Src Homology 2-domain containing 5â-inositol phosphatase-2 (SHIP2) PI3K/AKT pathway
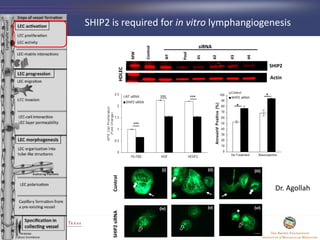
- 39. SHIP2 is required for in vitro lymphangiogenesis Control NT Pool #1 #2 #3 #4 MW SHIP2 Actin HDLEC siRNA ControlSHIP2siRNA (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) Dr. Agollah
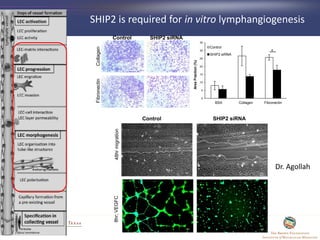
- 40. SHIP2 is required for in vitro lymphangiogenesis CollagenFibronectin SHIP2 siRNAControl 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 BSA Collagen Fibronectin AreaFraction(%) Control SHIP2 siRNA * SHIP2 siRNAControl48hrmigration8hr;VEGFC Dr. Agollah
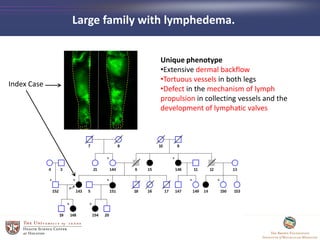
- 41. Large family with lymphedema. Index Case Unique phenotype âĒExtensive dermal backflow âĒTortuous vessels in both legs âĒDefect in the mechanism of lymph propulsion in collecting vessels and the development of lymphatic valves
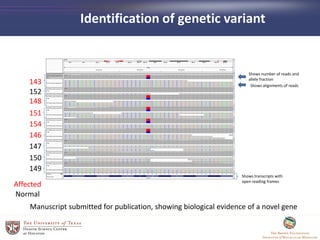
- 42. Identification of genetic variant 143 152 148 151 154 146 147 150 149 Shows number of reads and allele fraction Shows alignments of reads Shows transcripts with open reading frames Affected Normal Manuscript submitted for publication, showing biological evidence of a novel gene
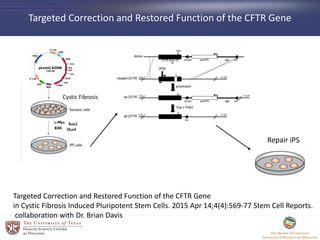
- 43. Targeted Correction and Restored Function of the CFTR Gene Targeted Correction and Restored Function of the CFTR Gene in Cystic Fibrosis Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. 2015 Apr 14;4(4):569-77 Stem Cell Reports. collaboration with Dr. Brian Davis Cystic Fibrosis Repair iPS
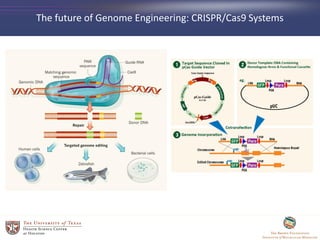
- 44. The future of Genome Engineering: CRISPR/Cas9 Systems
- 45. Acknowledgments: âĒThe Cullen Trust for Higher Education âĒThe Greater Houston Community Foundation CMI Dr. Caskey Dr. Soares Dr. Escamilla Dr. Schaaf Dr. Beaudet Dr. Herbst Dr. Rojas-MartÃnez Dr. Ortiz-LÃģpez Dr. Doris Dr. Davis Dr. Northrup Dr. Kit-Sing Au Dr. Lorenz





![Experimental Design
âĒ Genome Education Program (The Cullen Trust for Higher Education) 2009.
â Educate Patients and their physicians about genetics
âĒ Young Presidentsâ Organization YPO
â Requested a education program for their members for their annual competition
âĒ Organized with Houston Chapter: 450 members.
âĒ Education Conference Day: >150 attendees â Institute of Molecular
Medicine (IMM), UTHealth at Houston.
âĒ IRB approved volunteer protocol âNeed to know resultsâ: 81 volunteers.
âĒ Whole Exon sequencing.
âĒ Medical report focused on causative alleles for Mendelian disorders.
âĒ All participants require a face to face meeting with our genetic counselor
[CTC] (medical history and 3 generation pedigree)
âĒ A second individual genetic counseling session to discuss the written
reports.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3b397722-b56c-44d7-823d-292b23556aa4-151006021901-lva1-app6891/85/MLGG_for_linkedIn-6-320.jpg)