Mobile operating system ppt
- 1. Mobile Operating System (Mobile OS) Presented By:- G. Santosh Kumar 10135A1203 Information Technology
- 2. Contents ’é┤ Introduction ’é┤ Different Mobile OSŌƤs ’é┤ Future Mobile OSŌƤs ’é┤ Conclusion ’é┤ References 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 2
- 3. Introduction ’é┤ An operating system (OS) is an interface between hardware and user. It manages hardware and software resources of the system. ’é┤ An operating system which controls mobile devices is called Mobile OS. They are simple and deal with the wireless versions of broadband and local connectivity. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 3
- 4. Different types of OSŌƤs Mobile OS Symbian OS iPhone OS RIM BlackBerry Windows Mobile Linux Palm OS Android 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 4
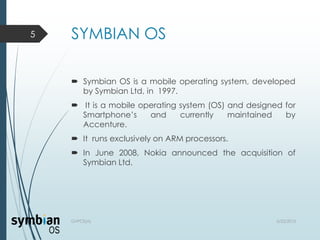
- 5. SYMBIAN OS ’é┤ Symbian OS is a mobile operating system, developed by Symbian Ltd, in 1997. ’é┤ It is a mobile operating system (OS) and designed for SmartphoneŌƤs and currently maintained by Accenture. ’é┤ It runs exclusively on ARM processors. ’é┤ In June 2008, Nokia announced the acquisition of Symbian Ltd. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 5
- 8. ’é┤ It was the most popular smartphone OS across the world till the end of 2010,untill it was overtaken by Android, although in some developing nations, Symbian is still the biggest. ’é┤ The current form of Symbian is an open-source platform developed by Symbian Foundation in 2009. ’é┤ Symbian OS is programmed in C++. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 8
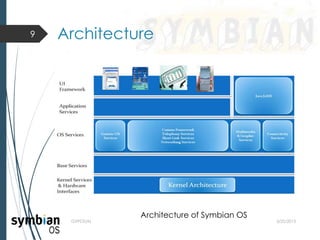
- 10. ’é┤ Frameworks and libraries for constructing a UI. ’é┤ Includes the basic class hierarchies for UI controls. ’é┤ Other frameworks and utilities. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 10 UI Framework Topmost layer of Symbian OS, foundation for variant UI
- 11. ’é┤ Spans the UI Framework and Application Services layer. ’é┤ It defines a platform for dynamically and securely deploying optimized, graphical, networked applications. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 11 JAVA J2ME MIDP Java J2ME MIDP 2.0 and CLDC 1.1
- 12. ’é┤ It provides support independent of the user interface for applications on Symbian OS. ’é┤ Application class (ŌĆ£technology specificŌĆØ) logic. ’é┤ support for specific applications 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 12 Application Services Generic Application class specific - Messaging, browsing Application specific - Word, Sheet
- 13. ’é┤ the ŌĆ×middlewareŌƤ layer of Symbian OS, provides servers, frameworks, and libraries that extend the base-system into a complete operating system. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 13 OS Services Generic OS Services ŌĆ£Middleware" layer of Symbian OS, full range of servers, frameworks, and libraries which extend the base system into a complete OS Multimedia & Graphics Services Connectivity Services
- 14. ’é┤ It includes the File Server and User Library ’é┤ Plug-In Framework which manages all plug-ins ’é┤ Central Repository, DBMS ’é┤ Cryptographic services ’é┤ Services for a functional port 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 14 Base Services Lowest level of user-side services, extends the OS kernel into a useable (but minimal) system
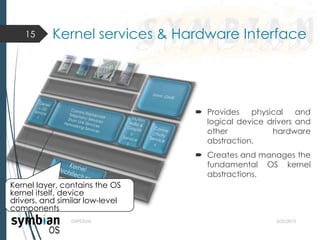
- 15. ’é┤ Provides physical and logical device drivers and other hardware abstraction. ’é┤ Creates and manages the fundamental OS kernel abstractions. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 15 Kernel services & Hardware Interface Kernel layer, contains the OS kernel itself, device drivers, and similar low-level components
- 16. SYMBIAN MOBILE OS VERSION 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 16 ’āś Series 60 3rd edition Feature Pack 2 ’ā╝ Released on 12 July 2006. ’ā╝ Support for Wi-Fi 802.11, HSDPA. ’āś Symbian^1 (Series 60 5th edition):- ’ā╝ Applications should launch up to 75% faster. ’ā╝ Additionally, SQL support is provided by SQLite. ’āś Symbian^3:- ’ā╝ Released in the year 2010. ’ā╝ Symbian^3 is an improvement over previous S60 5th Edition and features single touch menus in the user interface, as well as new Symbian OS kernel with hardware-accelerated graphics.
- 17. Contd.. ’āś Symbian Anna and Symbian Belle:- ’ā╝ Released in the year 2011. ’ā╝ Free-form, differently-sized, live widgets ’ā╝ More home screens ’ā╝ Improved status bar ’ā╝ Modernised navigation ’ā╝ New apps ’ā╝ Informative lock screen ’ā╝ NFC devices 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 17
- 18. Features ’āś Processes and Threads: ’ā╝ Symbian OS is a multitasking and multithreaded operating system. ’ā╝ Many processes can run concurrently, can communicate with each other, and can utilize multiple threads that run internal to each process. ’āś Common File System support: ’ā╝ Symbian OS organizes access to system storage using a file system model, just like larger Operating systems. ’ā╝ It has a default file system compatible with windows (by default it uses FAT-32 file system). ’ā╝ It supports several different file systems , like FAT 16 & FAT 32, NTFS etc. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 18
- 19. Contd.. ’āś Networking: Symbian OS supports TCP/IP networking as well as several other communication interfaces such as serial, infrared and Bluetooth. ’āś Memory Management: Although Symbian OS does not use or have the facilities for mapped virtual memory , it organizes memory access in pages and allows for the replacement of the pages, that is , bringing pages in, but not swapping them out. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 19
- 20. Technologies in Symbian ’é┤ Symbian SDK ’é┤ Carbide.c++ 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 20
- 22. ’é┤ iOS (previously iPhone OS) is a mobile operating system developed and distributed by Apple Inc. ’é┤ Originally released in 2007 for the iPhone and iPod Touch, it has been extended to support other Apple devices such as the iPad and Apple TV. ’é┤ In June 2010, Apple rebranded iPhone OS as "iOS". 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 22 iOS
- 23. contd.. ’é┤ The trademark "IOS" had been used by Cisco for over a decade for its operating system, IOS, used on its routers. ’é┤ In 2011, iOS accounted for 60% of the market share for smartphones and tablet computers. By the end of 2012, iOS accounted for 21% of the smartphone OS market and 43.6% of the tablet OS market. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 23
- 29. Previous versions ’é¦ iOS4: iOS4 was the first version of the OS to be a free upgrade on the iPod touch. ’é¦ iOS4.0.1: There were several antenna issues in the previous version, iOS4.0.1 included a fix to the reception signal strength indicator. ’é¦ iOS4.1: iOS4.1 for the iPhone and iPod touch was released with an update fixed some bugs reported by users, improved battery life and added several new features such as Game Center. ’é¦ iOS4.2: iOS4.2 was never released but instead iOS4.2.1 was released which added iPad compatibility. Further on iOS4.2.5 was released as a demo version for the CDMA version of the iPhone 4. ’é¦ iOS4.3: The public release of iOS4.3 included many new features such as a Nitro JavaScript engine in Safari. iTunes Home Sharing also received a major revision in iOS4.3; it allows users to connect to their home Wi-Fi networks . 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 29
- 30. Technologies in iOS ’é┤ iOS framework ’é┤ Simulator framework ’é┤ iOS developer tools ’é┤ Xcode 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 30
- 31. App store for IPhone Os 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 31
- 32. Future Mobile OSŌƤs ’é┤ Firefox OS ’é┤ Ubuntu Touch ’é┤ Tizen OS 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 32
- 33. Firefox OS ’é┤ Firefox OS is a Linux-based open source operating system for smartphones and tablet computers being developed by Mozilla. ’é┤ Programmed in HTML5, C++, JavaScript and CSS. ’é┤ The first smartphone running Firefox OS should be released in the first half of 2013 (expecting July, 2013). ’é┤ Firefox have also announced that LG Electronics, ZTE, Huawei and TCL Corporation have committed to making Firefox OS devices. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 33
- 34. Ubuntu Touch ’é┤ Ubuntu Touch OS developed by Canonical Ltd. ’é┤ Ubuntu Touch aims to provide a similar user experience as the Unity desktop. ’é┤ Canonical aims to release handsets running the operating system by October 2013. ’é┤ Ubuntu Touch devices can be equipped with a full Ubuntu session and may change into a full desktop operating system when plugged into a docking station. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 34
- 35. Tizen OS ’é┤ Tizen is an operating system for devices including smartphones, tablets, in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) devices, and smart TVs. ’é┤ It is an open source system that aims to offer a consistent user experience across devices. ’é┤ The Tizen project resides within the Linux Foundation and is governed by a Technical Steering Group (TSG) composed of Intel and Samsung. ’é┤ Tizen provides an environment for application developers based on the JavaScript libraries JQuery and JQuery Mobile. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 35
- 36. Conclusion ’é┤ For developers the operating system is an ultimate platform to develop apps innovatively and publish in market very easily. Not only in mobile phones, the OS is diverging in various fields like Tabs, Smart TVs and Cameras etc. ’é┤ A mobile OS should be a result of factors like user experience, battery life, cloud readiness, security and openness. A successful mobile OS is a result of a design between software and hardware together. 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 36
- 37. References ’é┤ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symbian ’é┤ http://www.developer.nokia.com/Community/Wiki/C ategory:Symbian ’é┤ http://eketab.files.wordpress.com/2007/09/thesymbia nosarchitecturesourcebook.pdf ’é┤ http://www.developer.nokia.com/Resources/Library/ ’é┤ http://developer.apple.com/library/ios/#releasenotes /General/WhatsNewIniOS/Introduction/Introduction.ht ml ’é┤ http://developer.apple.com/library/ios/#documentati on/miscellaneous/conceptual/iphoneostechoverview /Introduction/Introduction.html ’é┤ http://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentatio n/miscellaneous/conceptual/iphoneostechoverview/i PhoneOSTechOverview.pdf 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 37
- 38. Cond.. ’é┤ http://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/partners/# ’é┤ http://www.ubuntu.com/devices/phone ’é┤ https://www.tizen.org/about 5/22/2013GVPCE(A) 38