mod 1 (1)ppt.pptx
- 1. 22ESC 142 Introduction to Electrical Engineering
- 2. MODULE-1
- 3. Sources of Energy and classification of the sources of energy
- 5. Conventional Energy sources Non-Conventional Energy sources 1.These sources of energy are also known as a Non-Renewable source of energy. 1. These sources of energy are also known as a Renewable source of energy. 2. They find both commercial and industrial purposes. 2. They are mainly used for household purposes. 3. These can be considered to be one of the reasons for the cause of pollution. 3. These are not responsible for the cause of pollution. 4. Examples: Coal, fossil fuels are two 4.Examples: Wind, solar energy and Biomass Advantage :The efficiency and the production expenses of the conventional energy sources are low Advantage :Non-conventional sources of energy are environmentally friendly, inexhaustible and easy to operate. Dis-advantage:Conventional energy sources are not environmentally friendly and it can deplete soon. Importance: Non-conventional sources of energy are considered to be important as they are renewable, pollution-free, availability of them is in abundance, and they are environmentally friendly.
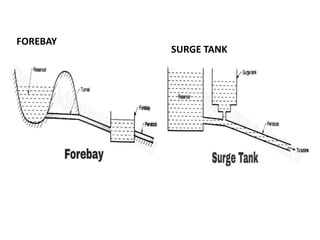
- 6. Hydropower to Electric Power
- 7. Hydro Electric Power Plant
- 9. Inside a Hydro power plant
- 10. Concept of Green Energy • Green energy comes from natural sources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, plants, algae and geothermal heat. These energy resources are renewable, that is, they're naturally replenished. • Green energy can replace fossil fuels in all major areas of use including electricity, water and space heating and fuel for motor vehicles. • Some common types of green energy sources: Solar Power - Photovoltaic or concentrated solar power systems. Wind Power, Hydropower, Geothermal Energy Biomass, Biofuels, etc..
- 12. What is Solar Power Systems? Solar Power systems are nothing but a system comprising of solar panels and the other mechanism according to the various uses of the system for different purposes. It mainly uses solar energy as the main power source for its operation.
- 13. Block Diagram of a Solar Power Plant The largest non-conventional source of energy is solar energy.
- 14. Components of Solar Power Systems The basic components of a solar power system includes: 1. PV Module 2. Inverter 3. Main Fuse Box 4. Utility Meter 5. Grid
- 15. • PV Modules A PV module is nothing but a panel consisting of large number of solar cells that stores the solar energy and convert it into electricity for further usage. • Inverter An inverter is a small set-up that has simple working principle of converting Direct current(D.C.) to Alternating current(A.C.). • Main Fuse Box: It is a distribution box that supplies the power to different appliances according to the requirement of individual appliances.
- 16. • Utility Meter: A utility meter is defined according to its usage. The utility is in the form of electricity, Gas, Water, Heat etc.. • Grid: The Grid is a connection of Photovoltaic or PV modules used to generate more and more electricity using solar energy. It consists of a large number of inverters according to the number of panels connected in the grid.
- 17. • Wind is a form of solar energy. • Winds are caused by the uneven heating of the atmosphere by the sun, the irregularities of the earth's surface, and rotation of the earth. Wind flow patterns are modified by the earth's terrain, bodies of water, and vegetation . • Wind is formed when hot surface heat the air making it to rise. The cooler air moves into empty space creating wind. Wind Power Plant
- 18. Wind Power Plant
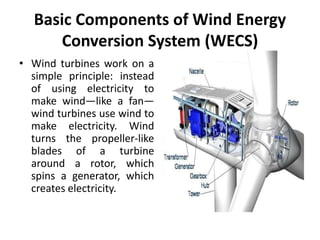
- 19. Basic Components of Wind Energy Conversion System (WECS) • Wind turbines work on a simple principle: instead of using electricity to make wind—like a fan— wind turbines use wind to make electricity. Wind turns the propeller-like blades of a turbine around a rotor, which spins a generator, which creates electricity.
- 20. • How a wind turbine works: • Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in the wind into mechanical power. A generator converts the mechanical power into electricity • Basic parts: • Blades (B) and • Rotor (A) which rotate when the wind blows • Shaft (C) • Gearbox (D) to adjust for the speed of the wind • Generator (G), which generates the electricity . • The dynamo works by rotating a permanent magnet inside a coil of copper wire. The magnet causes the electrons inside the wire move in a particular direction. At the end of the coil are wires which carry electrons to provide electrical energy
- 21. Basic Components of Wind Energy Conversion System (WECS) • Here, • 1) Wind Turbine: Converts wind energy into rotational (mechanical) energy • 2) Gear system and coupling: It steps up the speed and transmits it to the generator rotor • 3) Generator: Converts rotational energy into electrical energy. • 4) Controller: Senses wind direction, wind speed, generator output and temperature and initiates appropriate control signals to take control action. • 5)Tower:Four types of supporting tower can be considered for use: a) The pole tower b) The reinforced concrete tower c) The truss tower and
- 23. Nuclear Power Plant • The working principle of nuclear power plant depends upon mainly four components. • 1. Nuclear Reactor • 2. Heat Exchanger • 3. Steam Turbine • 4. Alternator
- 24. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF NUCLEAR REACTOR: